The mineralogy of Xenon
| About Xenon |
|---|
| Xenon is a noble gas and as such does not form any natural minerals. |
| General Properties | |
|---|---|
| Symbol: | Xe |
| Atomic Number: | 54 |
| Standard atomic weight (Ar): | 131.293(6) |
| Electron configuration: | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 |
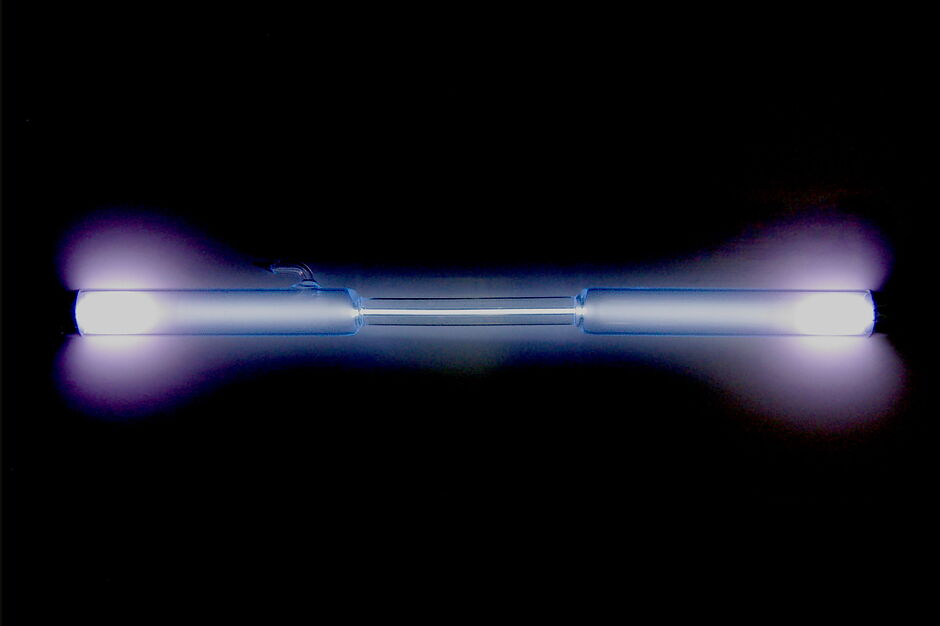
| Photos | ||
|---|---|---|
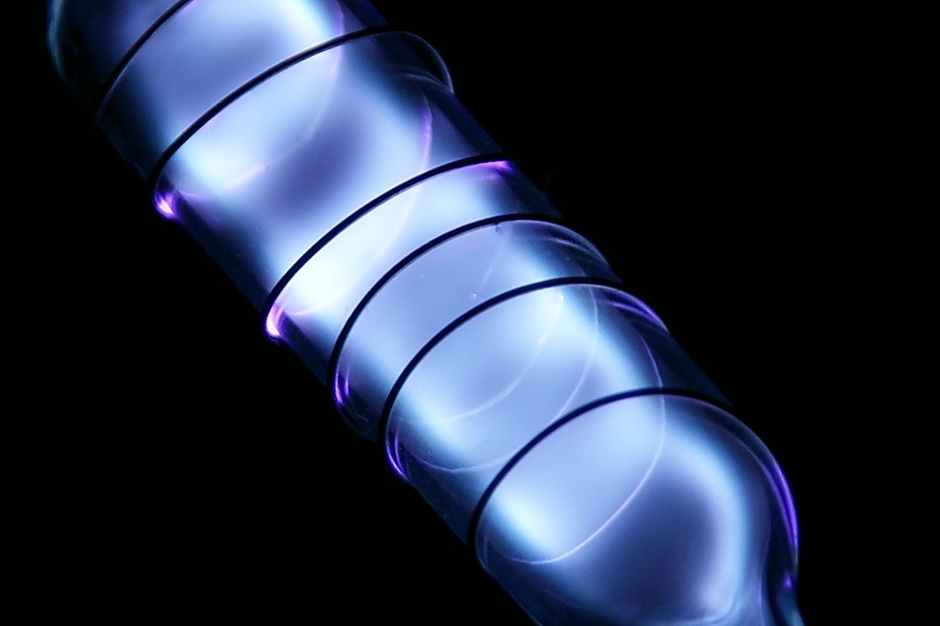
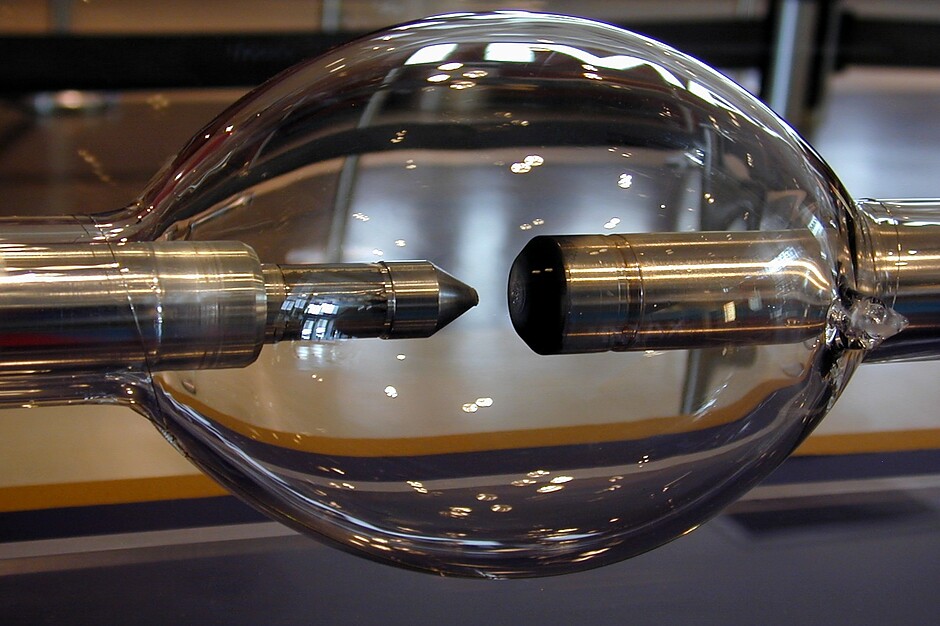
| < | Xenon filled discharge tube | > |
| Atomic Properties | |
|---|---|
| Atomic Radius: | 108 pm |
| Ionic Radius: | 48 pm (+8) |
| Van der Waals Radius: | 216 pm |
| 1st Ionization energy: | 1170 kJ/mol |
| Oxidation States: | 2,4,6,8 |
| Physical Properties | |
|---|---|
| Standard State: | gas |
| Bonding Type: | atomic |
| Melting Point: | 161 K |
| Boiling Point: | 165 K |
| Density: | 0.01 g/cm3 |
| Metal/Non-Metal: | noble gas |
| Main isotopes of Xenon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isotope | % in Nature | Half Life | Decay type | Decay product |
| 124Xe | 0.095% | >4.8×1016y | β+β+ ? | 124Te |
| 125Xe | synthetic | 16.9h | ε | 125I |
| 126Xe | 0.089% | - | β+β+ ? | 126Te |
| 127Xe | synthetic | 36.345d | ε | 127I |
| 128Xe | 1.91% | - | Spontaneous fission ? | |
| 129Xe | 25.4% | - | Spontaneous fission ? | |
| 130Xe | 4.07% | - | Spontaneous fission ? | |
| 131Xe | 21.2% | - | Spontaneous fission ? | |
| 132Xe | 26.9% | - | Spontaneous fission ? | |
| 133Xe | synthetic | 5.247d | β− | 133Cs |
| 134Xe | 10.4% | >1.1×1016y | β-β- ? | 134Ba |
| 135Xe | synthetic | 9.14h | β− | 135Cs |
| 136Xe | 8.86% | 2.165×1021y | β-β- | 136Ba |
| Main ions of Xenon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Ion | Example minerals | ||
| xenon(IV) | Xe4+ | |||
| xenon(VI) | Xe6+ | |||
| xenon(VIII) | Xe8+ | |||
| Other Information | |
|---|---|
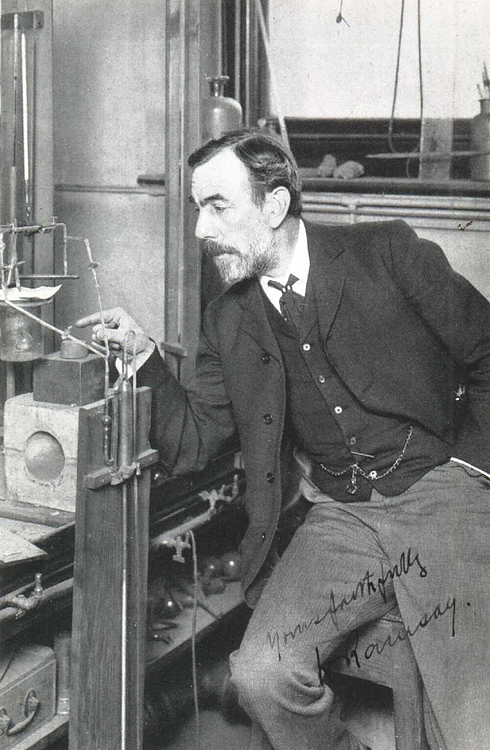
| Year Discovered: | 1898 |
| Discovered By: | William Ramsay and Morris Travers |
| Year Isolated: | 1898 |
| Isolated By: | William Ramsay and Morris Travers |
| Named For: | From the Greek: xenos - "foreign, a stranger" |
| CPK color coding: | #429EB0 |
| External Links: | WikipediaWebElementsLos Alamos National LaboratoryTheodore Gray's PeriodicTable.com |