Issue published November 24, 2025
- Volume 10, Issue 22
- Previous Issue
Naydenov et al. report that the septin cytoskeleton localizes to apical junctions of intestinal epithelial cells and maintains barrier integrity, thus protecting the intestinal epithelium from inflammation. The cover image shows the surface of the ileum where SEPT9 is expressed.
On the cover: The septin cytoskeleton is a regulator of intestinal epithelial barrier integrity and mucosal inflammation
In-Press Preview - More
Abstract
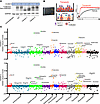
Autoimmune diabetes encompasses rapidly progressive type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) and indolent latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), representing distinct inflammatory set points along a shared autoimmune spectrum. Yet the immunological mechanisms that determine these divergent inflammatory states remain unresolved. We performed single-cell RNA sequencing with paired T and B cell receptor profiling on over 400,000 peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with LADA, newly diagnosed T1D, and healthy controls. PBMC composition was comparable across cohorts, indicating that qualitative rather than quantitative immune differences underlie disease heterogeneity. In T1D, pan-lineage activation of NF-κB, EGFR, MAPK, and hypoxia pathways, coupled with a TNF-centered communication hub, enhanced MHC signaling, and disrupted adhesion, promoted systemic inflammation. LADA, by contrast, exhibited global suppression of NF-κB/EGFR activity, retention of moderate JAK/STAT tone, reinforced natural killer cell inhibitory checkpoints via HLA-C–KIR2DL3/3DL1 interaction, and stabilized CD8⁺ T cell synapses through HLA-C–CD8 binding, collectively restraining effector activation. Single-cell V(D)J analysis revealed multiclonal, patient-unique adaptive repertoires, emphasizing the primacy of signaling context over receptor convergence. These findings define autoimmune diabetes as an inflammatory–inhibitory set-point continuum, positioning the NF-κB/EGFR–JAK/STAT gradient and HLA-C–KIR axis as potential therapeutic targets to preserve residual β-cell function.
Authors
Ivan I. Golodnikov, Elizaveta S. Podshivalova, Vadim I. Chechekhin, Anatoliy V. Zubritskiy, Alina A. Matrosova, Nikita A. Sergeev, Margarita D. Samsonova, Yaroslav V. Dvoryanchikov, Tatiana V. Nikonova, Ekaterina V. Bondarenko, Marina Yu. Loguinova, Yulia A. Medvedeva, Dmitry N. Laptev, Rita I. Khusainova, Ildar R. Minniakhmetov, Marina V. Shestakova, Natalia G. Mokrysheva, Ivan I. Dedov
Abstract
Neurocognitive impairment is a prevalent co-morbidity in virologically suppressed people living with HIV (PLWH), yet the underlying mechanisms remain elusive and treatments lacking. We explored use of participant-derived directly induced neurons (iNs) to model neuronal biology and injury in PLWH. iNs retain age- and disease-related donor features, providing unique opportunities to reveal important aspects of neurological disorders. We obtained primary dermal fibroblasts from six virologically suppressed PLWH (range: 27-64 years, median: 53; 83% Male) and seven matched people without HIV (PWOH) (range: 27-66, median: 55; 71% Male). iNs were generated using transcription factors NGN2 and ASCL1, and validated by immunocytochemistry, single-cell-RNAseq, and electrophysiological recordings. Transcriptomic aging analyses confirmed retention of donor age-related signatures. Bulk-RNAseq identified 29 significantly differentially expressed genes between PLWH and PWOH iNs. Of these, 16 were downregulated and 13 upregulated in PLWH iNs. Protein-protein interaction network mapping indicates iNs from PLWH exhibit differences in extracellular matrix organization and synaptic transmission. IFI27 was upregulated in PLWH iNs, complementing independent post-mortem studies demonstrating elevated IFI27 expression in PLWH-derived brain tissue. FOXL2NB-FOXL2-LINC01391 expression was reduced in PLWH iNs and negatively correlated with neurocognitive impairment. Thus, we identified an iN gene signature of HIV revealing mechanisms of neurocognitive impairment in PLWH.
Authors
Philipp N. Ostermann, Youjun Wu, Scott Bowler, Samuel Martínez-Meza, Mohammad A. Siddiqui, David H. Meyer, Alberto Herrera, Brandon A. Sealy, Mega Sidharta, Kiran Ramnarine, Leslie Ann St. Bernard, Desiree Byrd, R. Jones, Masahiro Yamashita, Douglas F. Nixon, Lishomwa C. Ndhlovu, Ting Zhou, Teresa H. Evering
Abstract
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a fatal genetic muscle-wasting disease characterized by loss of dystrophin protein. Therapeutic attempts to restore a functional copy of dystrophin to striated muscle are under active development, and many utilize adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors. However, the limited cargo capacity of AAVs precludes delivery of full-length dystrophin, a 427 kDa protein, to target tissues. Recently, we developed a novel method to express large dystrophin constructs using the protein trans-splicing (PTS) mechanism mediated by split inteins and myotropic AAV vectors. The efficacy of this approach to restore muscle function in mdx4cv mice was previously assessed using histology, dystrophin immunolabeling, and western blotting. Here, we expand our molecular characterization of dystrophin constructs with variable lengths using a mass spectrometry-based proteomics approach, providing insight into unique protein expression profiles in skeletal muscles of wild-type, dystrophic mdx4cv, and AAV-treated mdx4cv. Our data reveal several affected cellular processes in mdx4cv skeletal muscles with changes in the expression profiles of key proteins to muscle homeostasis, whereas successful expression of dystrophin constructs results in an intermediate to complete restoration. This study highlights several biomarkers that could be used in future preclinical or clinical studies to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic strategies.
Authors
Erynn E. Johnson, Theodore R. Reyes, Jeffrey S. Chamberlain, James M. Ervasti, Hichem Tasfaout
Abstract
The two main subgroups of autoimmune myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular junction disorder associated with muscle weakness, are the early and late-onset forms, defined by onset before or after 50 years of age. Both carry acetylcholine-receptor autoantibodies, but differ in sex ratios, genetics and occurrence of disease-specific thymus inflammation. By applying multimodal techniques, including deep spectral cytometric phenotyping and single cell sequencing to peripheral blood and thymic lymphocyte samples we explored the possibility to discriminate the two forms by cellular immune phenotyping. Analyzing two independent cohorts we identified distinct immunological differences driven by three main lymphocyte populations. Lower frequencies of mucosa-associated invariant T cells and naïve CD8 T cells were observed in late-onset myasthenia, suggesting enhanced immune senescence. Further, a highly differentiated, canonical natural killer cell population was reduced in early-onset myasthenia, which was negatively correlated with the degree of thymic inflammation. Using only the frequency of these three populations, correct myasthenia subgroup assignment could be predicted with an accuracy of 90%. The NK cell population negatively associated to early-onset disease had a similar association to thymic hyperlasia, whereas the two T-cell populations point to enhanced immune senescence in late-onset myasthenia gravis. These distinct immunocellular endophenotypes for early- and late onset disease suggest differences in the immunopathogenic processes. Together with demographic factors and other disease subgroup-specific features, the frequency of the identified cell subpopulations may improve clinical classification, in turn of relevance for channeling to interventions.
Authors
Jakob Theorell, Nicolas Ruffin, Andrew Fower, Chiara Sorini, Philip Ambrose, Valentina Damato, Lahiru Handunnetthi, Isabel Leite, Sarosh R. Irani, Susanna Brauner, Adam E. Handel, Fredrik Piehl
Abstract
Over 95% of head and neck cancers are squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). HNSCC is mostly diagnosed late, causing a poor prognosis despite the application of invasive treatment protocols. Tumor-educated platelets (TEPs) have been shown to hold promise as a molecular tool for early cancer diagnosis. We sequenced platelet mRNA isolated from blood of 101 HNSCC patients and 101 propensity-score matched non-cancer controls. Two independent machine learning classification strategies were employed using a training and validation approach to identify a cancer predictor: a particle swarm optimized support vector machine (PSO-SVM) and a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression model. The best performing PSO-SVM predictor consisted of 245 platelet transcripts and reached a maximum area under the curve (AUC) of 0.87. For the LASSO-based prediction model 1,198 mRNAs were selected, resulting in an median AUC of 0.84, independent of HPV status. Our data show that TEP RNA classification by different AI tools is promising in the diagnosis of HNSCC.
Authors
N.E. Wondergem, J.B. Poell, S.G.J.G In 't Veld, E. Post, S.W. Mes, M.G. Best, W.N. van Wieringen, T. Klausch, R.J. Baatenburg de Jong, C.H.J. Terhaard, R.P. Takes, J.A. Langendijk, I.M. Verdonck-de Leeuw, F. Lamers, C.R. Leemans, E. Bloemena, T. Würdinger, R.H Brakenhoff