Linked List Operations17 Nov 2025 | 47 min read Linked lists are fundamental data structures that support a range of operations for managing collections of data. The basic operations of linked list are including:
InsertionThis operation is performed to add an element to the list. There are various types of insertion on the basis of the position where the new node is going to be inserted:
Insert a Node at the Front/Beginning of the Linked ListFor inserting a new node at the beginning, we make a new node and its next pointer points to the current head of the linked list. After that, we update the head pointer to point to this new node. Insertion in the beginning is very efficient as it only requires the adjustment of a few pointers. 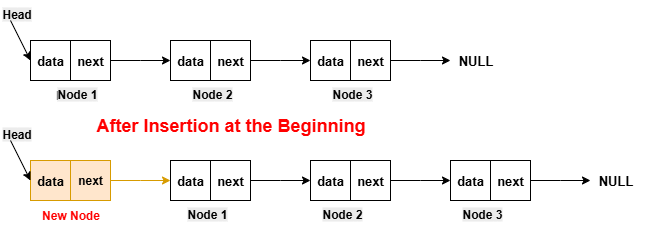 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before insertion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 After insertion, the updated linked list is: 11 -> 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 Insert a Node After a Given Node of the Linked ListFor inserting a new node at the beginning, we make a new node and its next pointer points to the current head of the linked list. After that, we update the head pointer to point to this new node. Insertion in the beginning is very efficient as it only requires the adjustment of a few pointers. 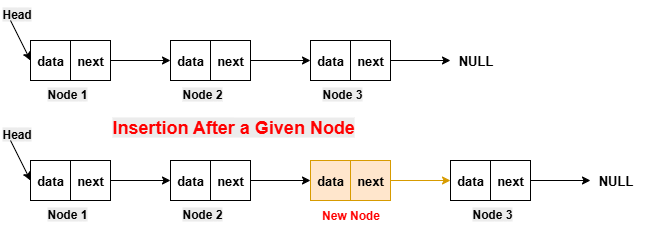 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before insertion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 15 -> 16 After insertion, the updated linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 Insert Node at the End of the Linked ListIn order to insert a new node at the beginning, we first make a new node and its next pointer points to NULL. After that, we update the next pointer of the last node of the linked list to point to the new node. Insertion at the end is also very efficient, as it only requires the adjustment of the next pointer of the last node. 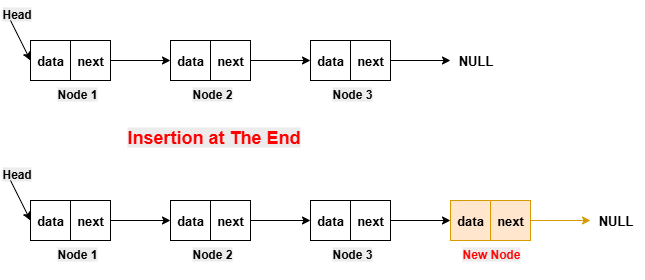 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before insertion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 After insertion, the updated linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 DeletionThis operation is performed to remove a node from the linked list. There are various types of insertion on the basis of the position where the new node is going to be inserted:
Deleting the First Node of the Linked ListFor deleting the first node of the linked list, we put the head node in a temporary variable. After that, we shift the head node to point to the second node of the linked list. After that, we delete the node stored in the temporary variable and then return the head pointer. 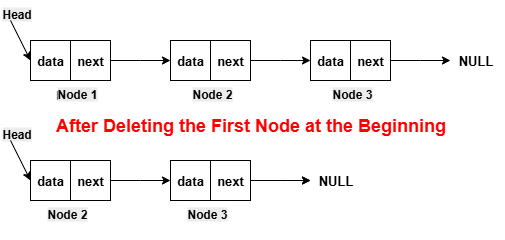 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before deletion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 After deletion, the updated linked list is: 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 Deleting a Node at a Specific Position in the Linked ListFor deleting the node at a specific position in the linked list, we do the traversal of the linked list to reach the node, which is just before the given position. After that, we do the adjustment of the next of the previous node to point to the next node of the next nodes. 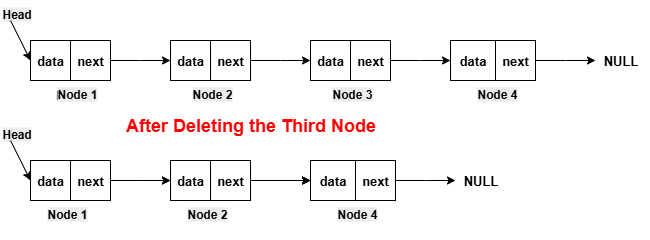 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before deletion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 After deletion, the updated linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 15 -> 16 Deleting The Last Node of the Linked ListFor deleting the last node of the linked list, we do the traversal of the linked list to reach the penultimate node, which is just before the last node. After that, we set the NULL value to the next pointer of the penultimate node. 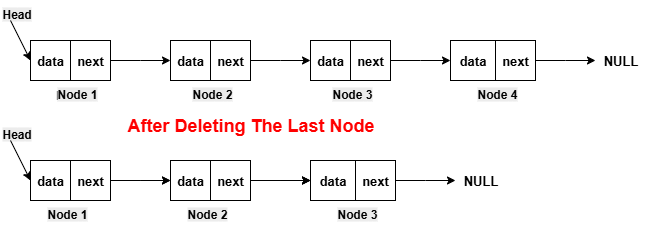 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: Before deletion, the linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 After deletion, the updated linked list is: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 Traversal of Linked ListThis operation is performed to traverse the elements of the list. 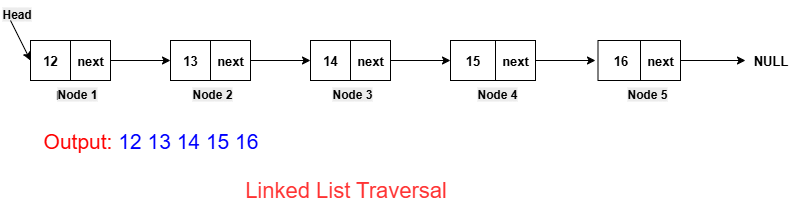 Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: The elements of the linked list are: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 Search in a Linked ListThis operation is performed to search for an element in the list using the given key.  Key = 13 (element to be searched) Output: The key 13 is found. Implementation in PythonExecute NowImplementation in JavaCompile and RunImplementation in C++Compile and RunImplementation in CCompile and RunImplementation in C#Compile and RunOutput: The elements of the linked list are: 12 -> 13 -> 14 -> 15 -> 16 The key 13 is found. Complexity of Linked ListNow, let's see the time and space complexity of the linked list.
Linked List Operations MCQs1. How many pointers are affected when we insert a node in the middle of the singly linked list?
Answer: b) Explanation: Inserting a node in the middle effects only two pointers: one is the next pointer of the node after which the insertion is going to happen, and the other is the next pointer of the new node. 2. What is the time complexity of deleting the last node of the linked list?
Answer: a) Explanation: For deleting the last node of the linked list, one has to traverse all the nodes from the beginning to the end, leading to O(n) time complexity. 3. What is the time complexity of deleting the first node of the linked list?
Answer: d) Explanation: For deleting the first node of the linked list, one deletes the first node of the linked list. Hence, traversing the linked list is not required, leading to O(1) time complexity. 4. How many pointers are affected when we delete a node in the middle of the singly linked list?
Answer: d) Explanation: Only one pointer is affected when one deletes a node in the middle of a singly linked list: the next pointer of the node before the one being deleted. 5. Which one of the following has O(n) time complexity?
Answer: d) Explanation: Inserting a node at the middle, and end, and deleting the node at the middle takes O(n) time. |
Subscribe to Tpoint Tech
We request you to subscribe our newsletter for upcoming updates.


