Types of Hash Functions in C17 Mar 2025 | 5 min read Hashing is the technique/ process of mapping key: value pairs by calculating a Hash code using the Hash Function. When given a (key: value) pair, the Hash Function calculates a small integer value from the key. The obtained integer is called the Hash value/ Hash code and acts as the index to store the corresponding value inside the Hash Table.  If for two (key: value) pairs, the same index is obtained after applying the Hash Function, this condition is called Collision. We need to choose a Hash Function such that Collision doesn't occur. Terminology:
This article explains different types of Hash Functions programmers frequently use. These are the four Hash Functions we can choose based on the key being numeric or alphanumeric:
1. Division Method:Say that we have a Hash Table of size 'S', and we want to store a (key, value) pair in the Hash Table. The Hash Function, according to the Division method, would be:
Let us now take an example to understand the cons of this method: Size of the Hash Table = 5 (M, S) Key: Value pairs: {10: "Sudha", 11: "Venkat", 12: "Jeevani"} For every pair:
Observe that the Hash values were consecutive. This is the disadvantage of this type of Hash Function. We get consecutive indexes for consecutive keys, leading to poor performance due to decreased security. Sometimes, we need to analyze many consequences while choosing the Hash Table size. A simple program to demonstrate the mechanism of the division method:Output: Enter the size of the Hash Table: 5 The indexes of the values in the Hash Table: 0 1 2 2. Mid Square Method:It is a two-step process of computing the Hash value. Given a {key: value} pair, the Hash Function would be calculated by:
We should choose the number of digits to extract based on the size of the Hash Table. Suppose the Hash Table size is 100; indexes will range from 0 to 99. Hence, we should select 2 digits from the middle. Suppose the size of the Hash Table is 10 and the key: value pairs are: {10: "Sudha, 11: "Venkat", 12: "Jeevani"} Number of digits to be selected: Indexes: (0 - 9), so 1 H(10) = 10 * 10 = 100 = 0 H(11) = 11 * 11 = 121 = 2 H(12) = 12 * 12 = 144 = 4
A simple program to demonstrate the mechanism of the mid-square method:3. Folding MethodGiven a {key: value} pair and the table size is 100 (0 - 99 indexes), the key is broken down into 2 segments each except the last segment. The last segment can have less number of digits. Now, the Hash Function would be:
For suppose "k" is a 10-digit key and the size of the table is 100(0 - 99), k is divided into: sum = (k1k2) + (k3k4) + (k5k6) + (k7k8) + (k9k10) Now, H(x) = sum % 100 Let us now take an example: The {key: value} pairs: {1234: "Sudha", 5678: "Venkat"} Size of the table: 100 (0 - 99) For {1234: "Sudha"}: 1234 = 12 + 34 = 46 46 % 100 = 46 For {5678: "Venkat"}: 5678 = 56 + 78 = 134 134 % 99 = 35 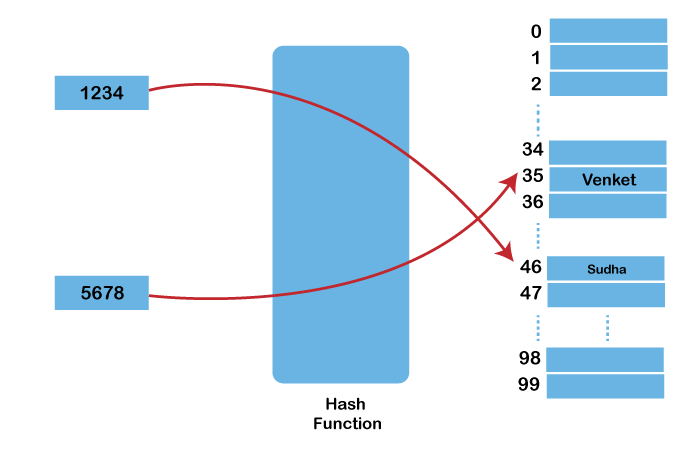 4. Multiplication methodUnlike the three methods above, this method has more steps involved:
So, the Hash Function under this method will be: For example: {Key: value} pairs: {1234: "Sudha", 5678: "Venkat"} Size of the table: 100 A = 0.56 For {1234: "Sudha"}: H(1234) = floor(size(1234*0.56 mod 1)) = floor(100 * 0.04) = floor(4) = 4 For {5678: "Venkat"}: H(5678) = floor(size(5678*0.56 mod 1)) = floor(99 * 0.68) = floor(67.32) = 67 
What after computing the Hash value? After computing the Hash value using the hash Function, this value is used as an index in the Hash table. Whenever the user wants to access a value, the corresponding key is hashed using the Hash Function, which gives the index of the key's value in the Hash Table with less cost than regular arrays and linked lists. Hence, Hashing is used to reduce the Time as well as space complexity of the program. |
We request you to subscribe our newsletter for upcoming updates.