How to Migrate from Java 8 to Java 17+ Using Amazon Q Developer
Learn how Amazon Q developer is speeding up application modernization and other benefits it offers to enterprises and developers
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeReplatforming from Java 8 to the newer Java versions has proven to be a huge challenge due to potential compatibility issues and changes in language specifications. The Spring Framework, which provides a programming and configuration model for modern Java applications, has just released its latest major version, Spring Framework 6.2.10, and it requires a baseline of Java 17 or higher. Because of this, migrating from an older version like Java 8 would involve code modifications, which take considerable effort and rigorous testing.
Before diving deep into version upgrades for Java applications, let us first discuss what Amazon Q developer is and how it helps developers with application modernization.
Updating Software Through Amazon Q Developer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here are the usual steps to follow when updating software using Amazon Q developer.
1. Plan the application update and version changes: Define the scope of the version upgrade, identify affected components, and outline necessary changes based on new language or framework specifications.
2. Draft basic use cases in natural language: Write core use cases in plain English. This helps Amazon Q understand the application's logic and aids in generating relevant code.
3. Generate code for the new application (30–40%): Use Amazon Q to auto-generate a portion of the application code based on the defined use cases and existing structure.
4. Write and run unit tests: Develop or auto-generate unit test cases with Amazon Q to validate functionality and support ongoing development.
5. Scan for vulnerabilities: Use Amazon Q to scan the codebase for security vulnerabilities, deprecated practices, and potential issues.
6. Perform code remediation: Address the issues identified during the vulnerability scan. Refactor code to align with best practices and new platform requirements.
7. Migrate code to target platform/version: Begin the code migration process, ensuring compatibility with the updated Java version or other framework changes.
8. Troubleshoot errors and business logic issues: If you encounter errors or logic conflicts, use Amazon Q’s assistance to debug and resolve issues efficiently.
Considering the extent of what Amazon Q developer can do, it plays a big role in Java software upgrades. But it's not the only way to do application modernization. To migrate from Java 8 to Java 17+ or upgrade to the latest Java version like Java 21, one has two options:
- Use Amazon Q Developer to migrate the application from Java 8 to Java 17.
- Manually upgrade from JDK 17 to JDK 21. The application is updated incrementally, reducing the risk of compatibility issues.
How to Migrate to Java 21
Should you decide to migrate to the recent version of Java 21, below are the steps you can follow.
Step 1: Build code
Build and verify existing code, then execute transformations one by one to update deprecated code, APIs, libraries, frameworks, and other dependencies.
IDE integration: Amazon Q developer’s transformation feature can be accessed directly within the IDE (e.g., IntelliJ IDEA). Once the transformation process is initiated, Amazon Q Developer will identify the necessary updates to upgrade the code to Java 17, including modifications to libraries and frameworks compatible with the new Java version.
Dependency management: Amazon Q will handle updating the project’s dependencies to ensure compatibility with Java 17.
Here is how end-to-end migration is usually done:
1. Environment setup: Install the Amazon Q Developer extension in your IDE or set up the CLI and configurations
2. Transformation source to target: Specify the source (Java 8) and target (Java 21) versions.
3. Changes review and confirmation: Amazon Q will analyse the code and generate a transformation plan, including dependency updates and code modifications. Review the proposed changes and update in IDE.
4. Changes confirmation: Accept the suggested changes to apply the code transformation.
5. Finishing touches: Build and test the migrated application to ensure it functions correctly with Java 17 and check for any runtime errors. Finalize the migration by validating the application in a staging or production environment.
Step 2: Upgrade to Java 21
Amazon Q Developer currently supports upgrades up to Java 17. Upgrading to Java 21 requires manual intervention. Most code and libraries should work on JDK 21 without any changes, but there may be some libraries that need to be upgraded.
Key considerations that may impact cthe urrent code include the following:
(a) Understanding changes in the SDK per v21
(b) Implementing security updates
(c) Identifying removed APIs
(d) Identifying removed tools and components
Other things to keep in mind in relation to the migration process to Java 21:
(a) Java 21 is considered since all the LTS open-source version of Oracle JDK are out of support.
(b) Business logic as part of applications, interfaces, and any dependent application code will remain as is.
(c) It is necessary to upgrade the libraries/frameworks used within application to make sure it is compatible with Java 21.
Advantages of Using Amazon Q Developer
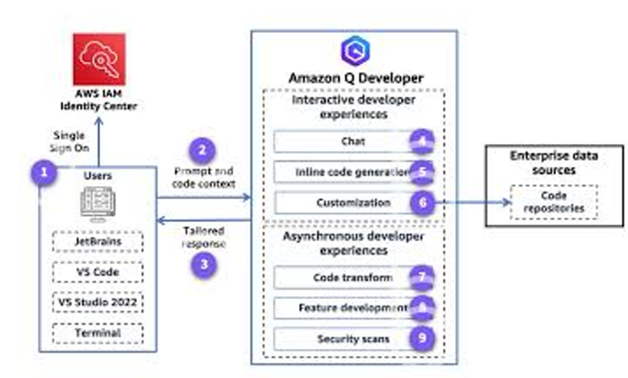
- It provides familiar security and access controls and can understand and respect your existing AWS IAM Identity Center governance identities, roles, and permissions to personalize its interactions.
- It is available with other languages like .NET.
- It connects with GitHub, scans your git code, and provides suggestions. It integrates seamlessly with developer IDE like Visual Studio, Eclipse, and JetBrains, among others.
- It offers flexible pricing options.
- It is built to handle large enterprise projects, Amazon Q Developer works alongside you from idea to production code
- It integrates with a plethora of AI tools.
- It is available in MS Teams and Slack to help you monitor operational events, troubleshoot issues, and operate AWS resources.
Conclusion
Using AWS Amazon Q developer significantly reduces manual effort by allowing you to automatically identify dependencies and fix the code. This tool not only accelerates our migration plan but also ensures a seamless transition from legacy open-source Java versions to the new Java 21 version. It is scalable, fast, and supports various other programming languages such as Java, .NET, and more.
In a nutshell, Amazon Q developer is proving to be extremely helpful during the migration of our enterprise project from Java 8 to Java 21, making the entire process more efficient and less time-consuming.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments