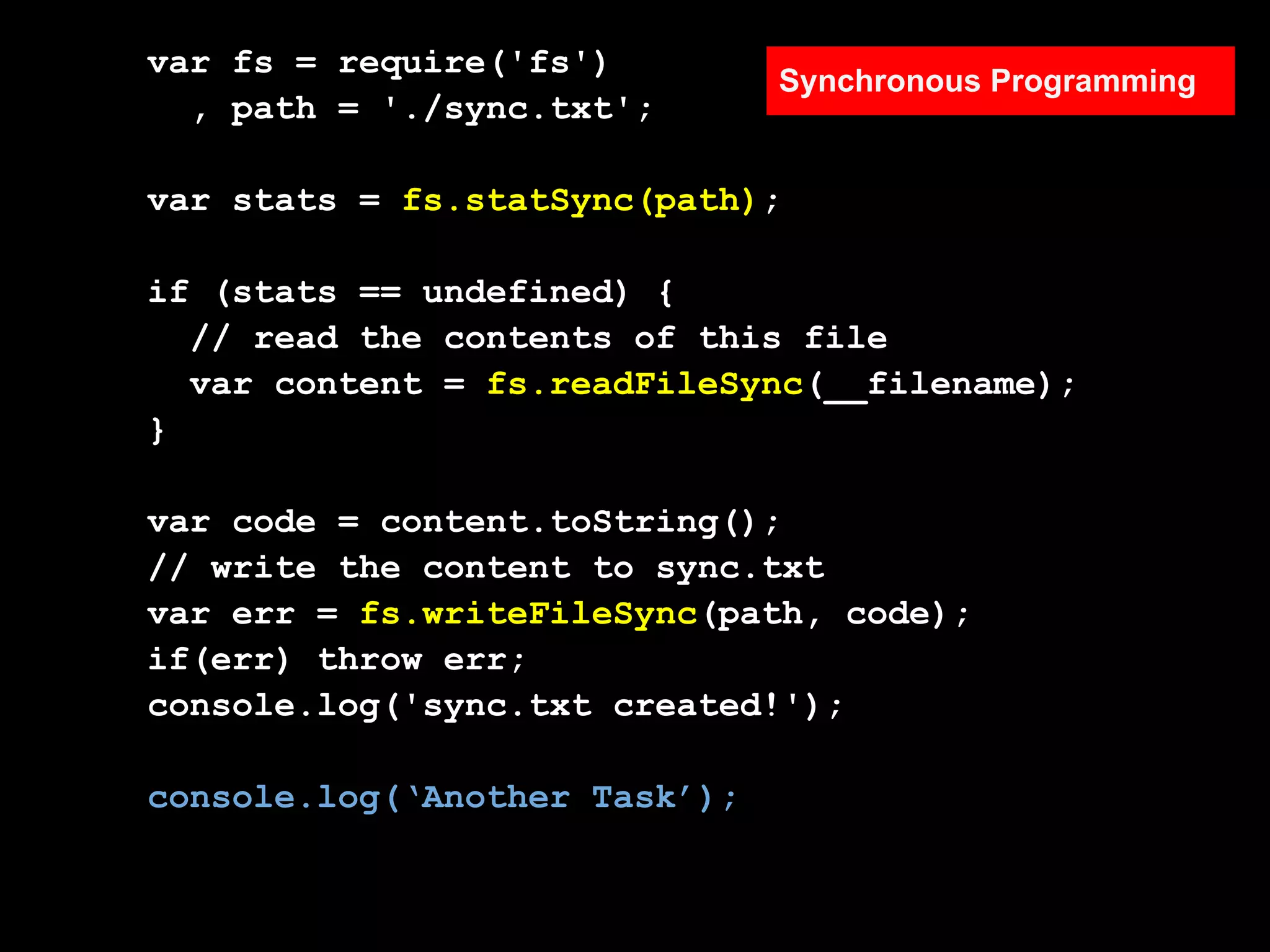
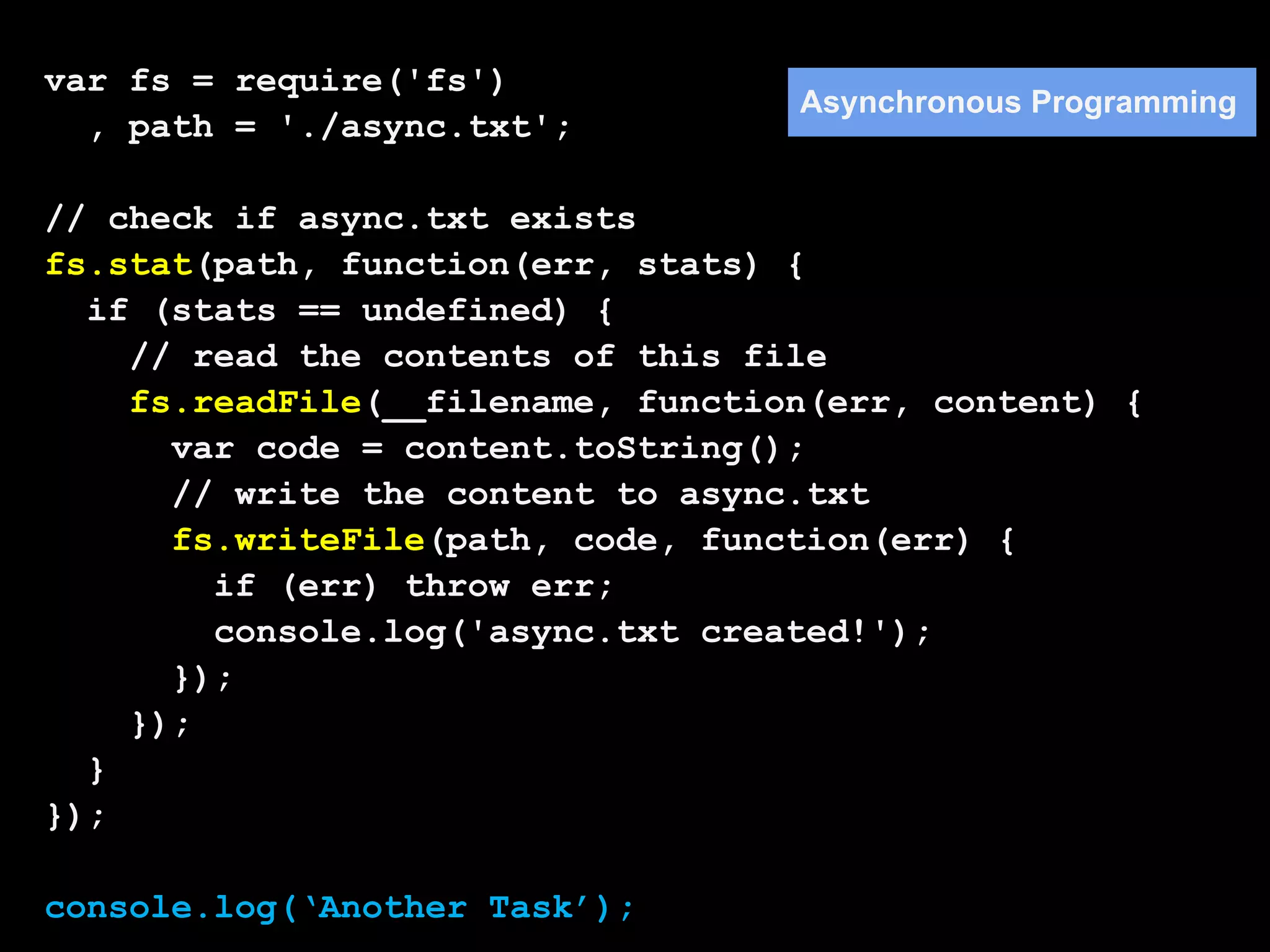
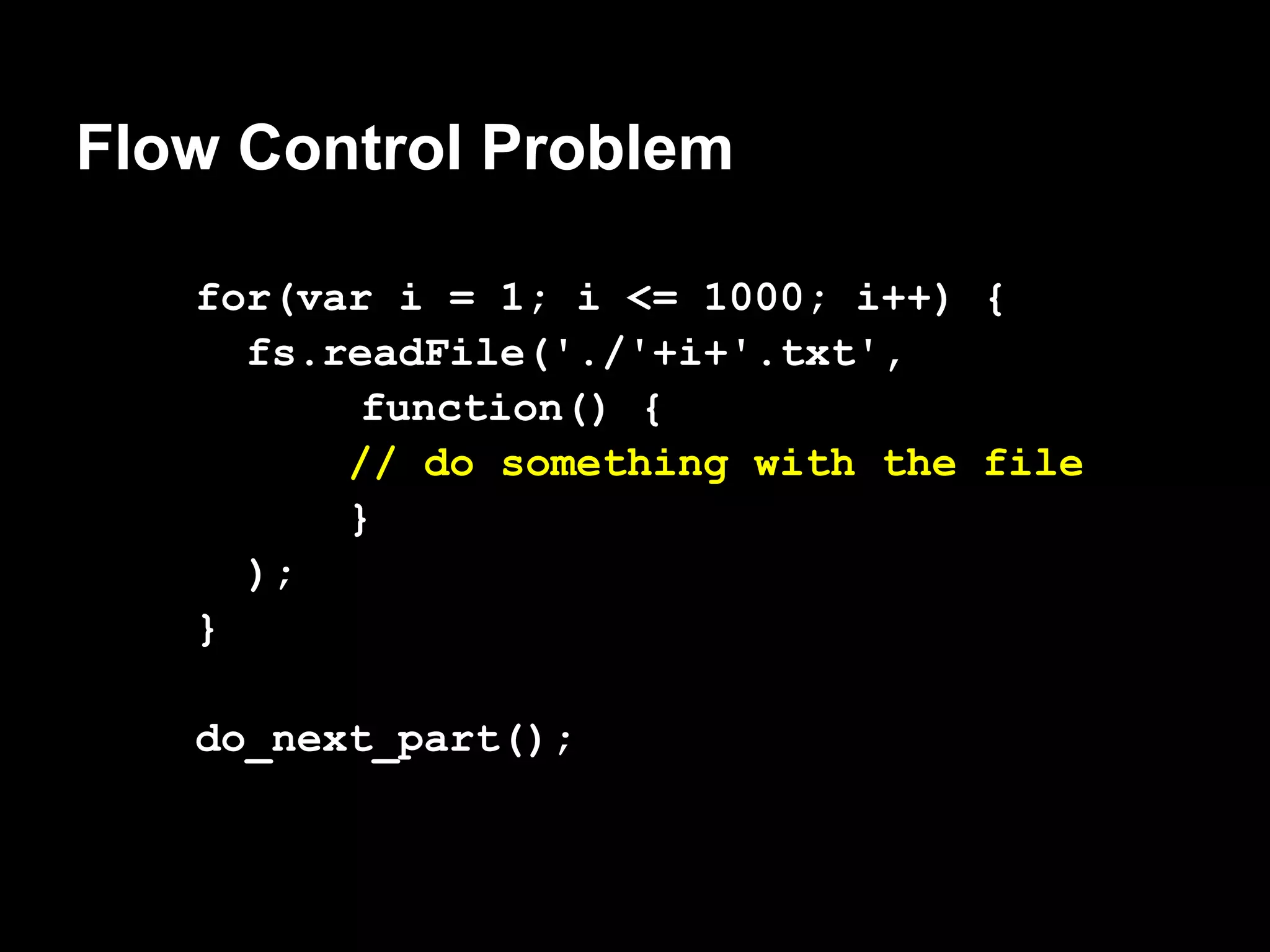
1. Flow control is important in Node.js for asynchronous programming to handle tasks that must execute in a specific order or to collect results.
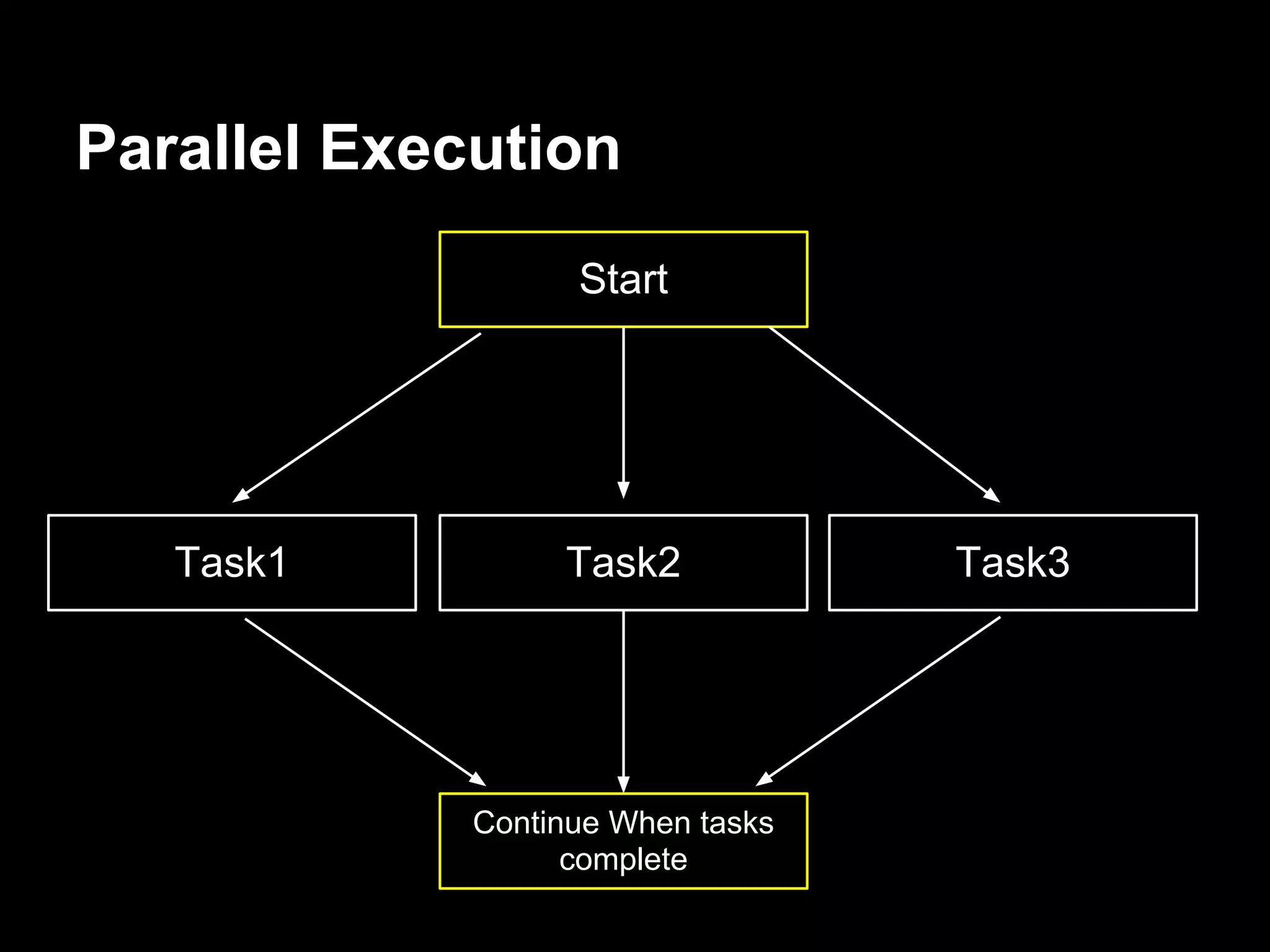
2. Common patterns include serial execution where tasks run one after another, parallel execution where multiple tasks run concurrently, and limited parallel execution where a subset of tasks run at a time.
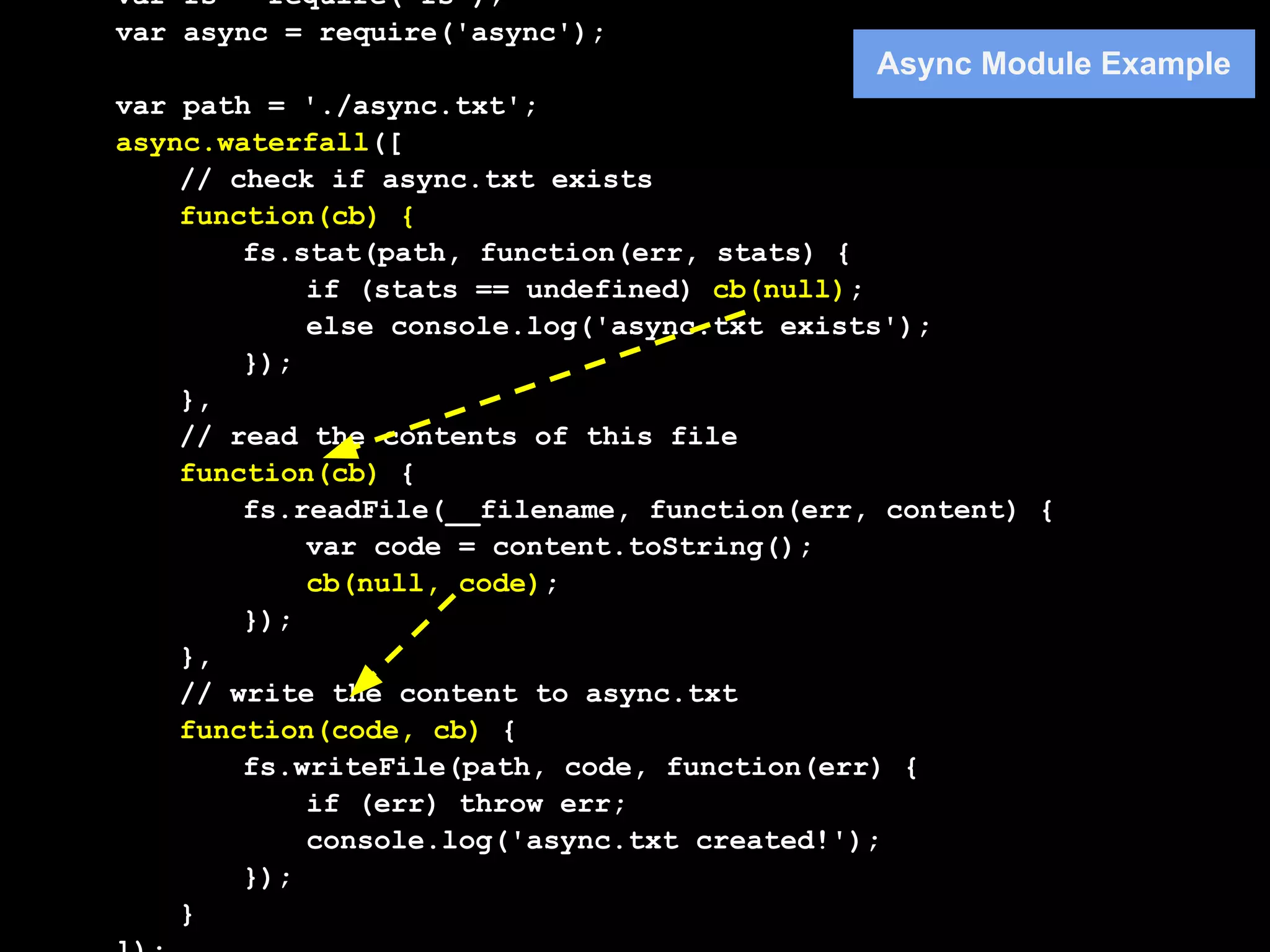
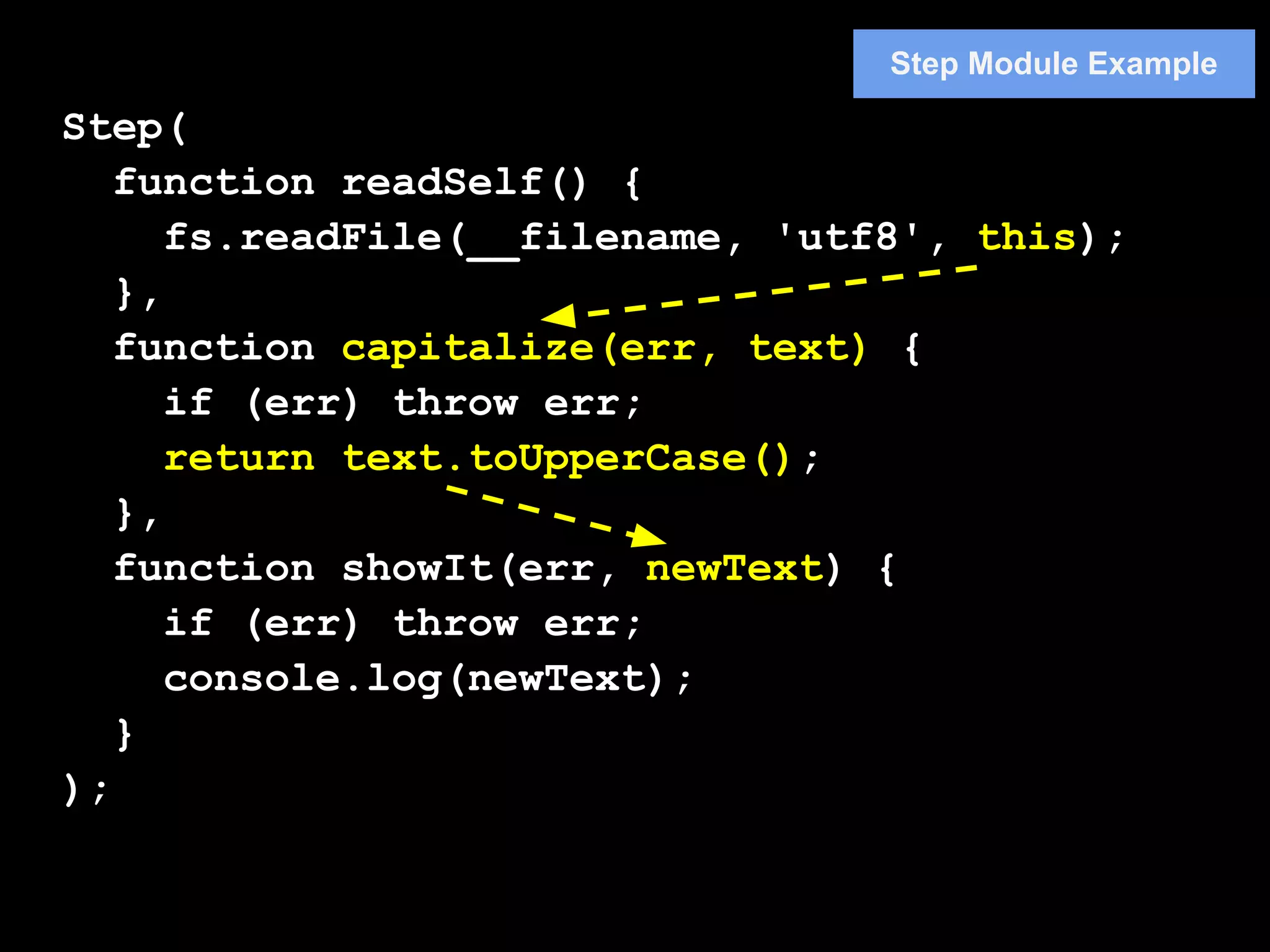
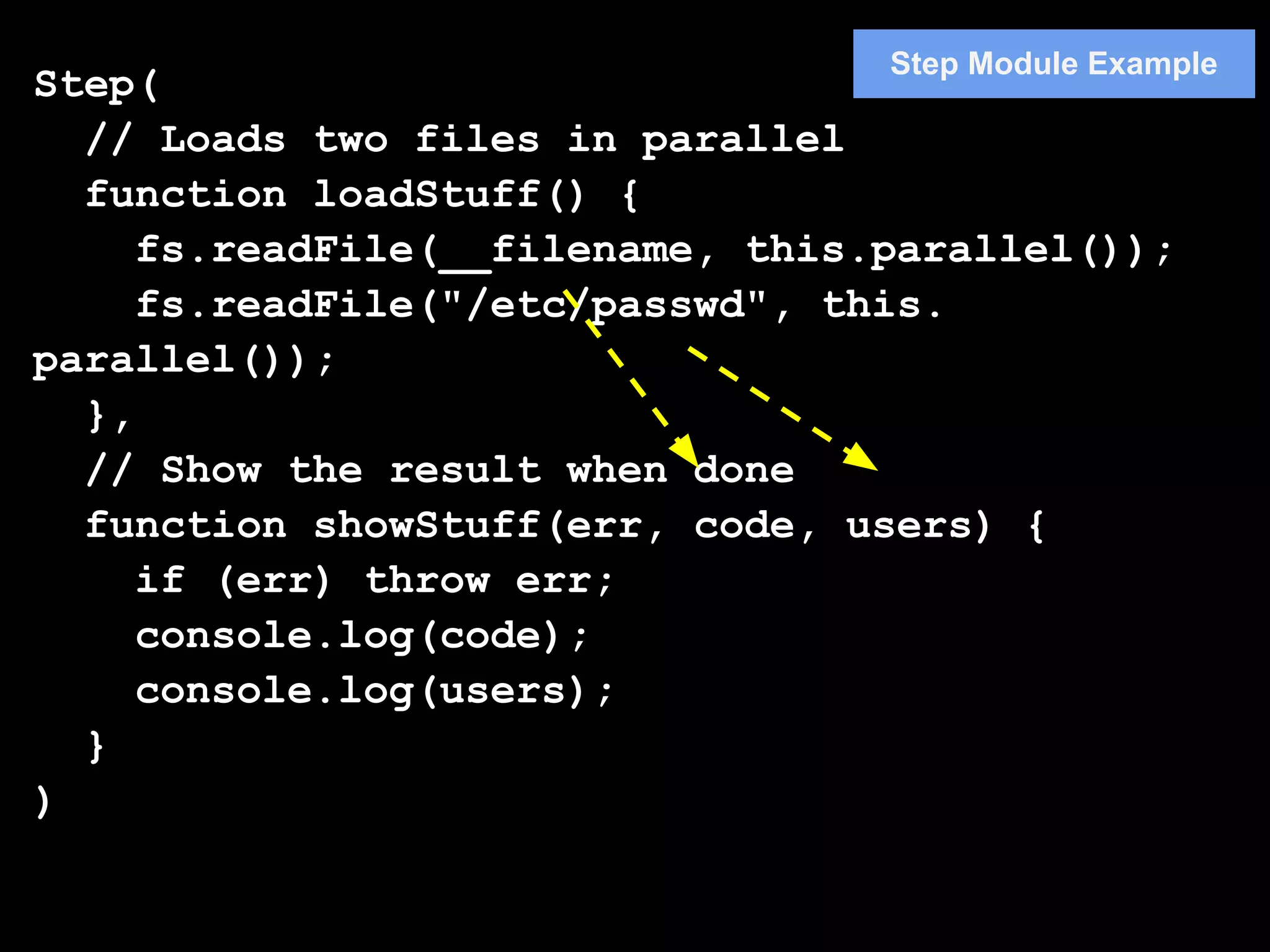
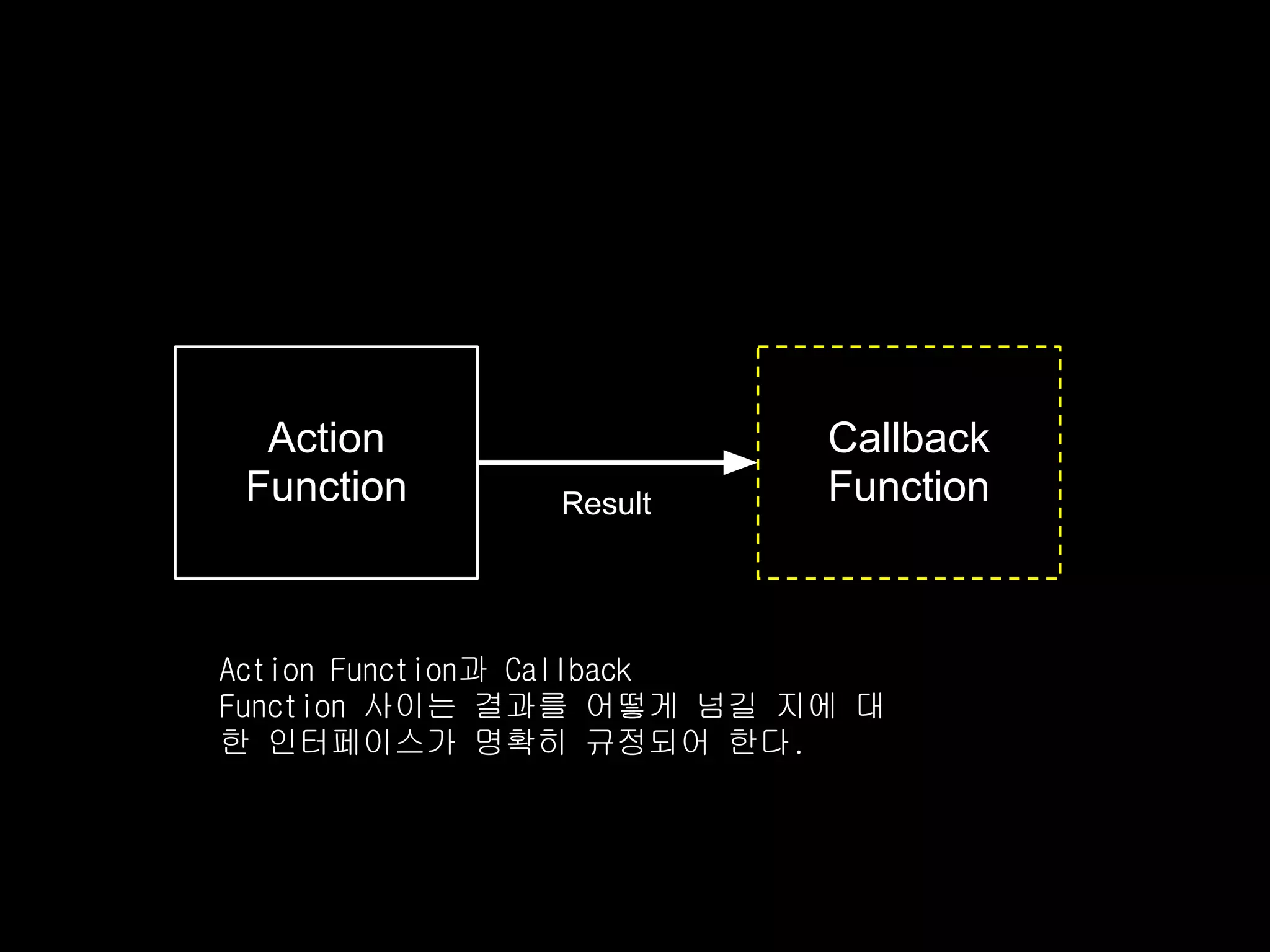
3. Popular flow control libraries like Async, Step, and Slide provide functions to implement patterns like serial execution with waterfall and parallelMap. This allows complex asynchronous code to be written in a readable, synchronous-looking style.









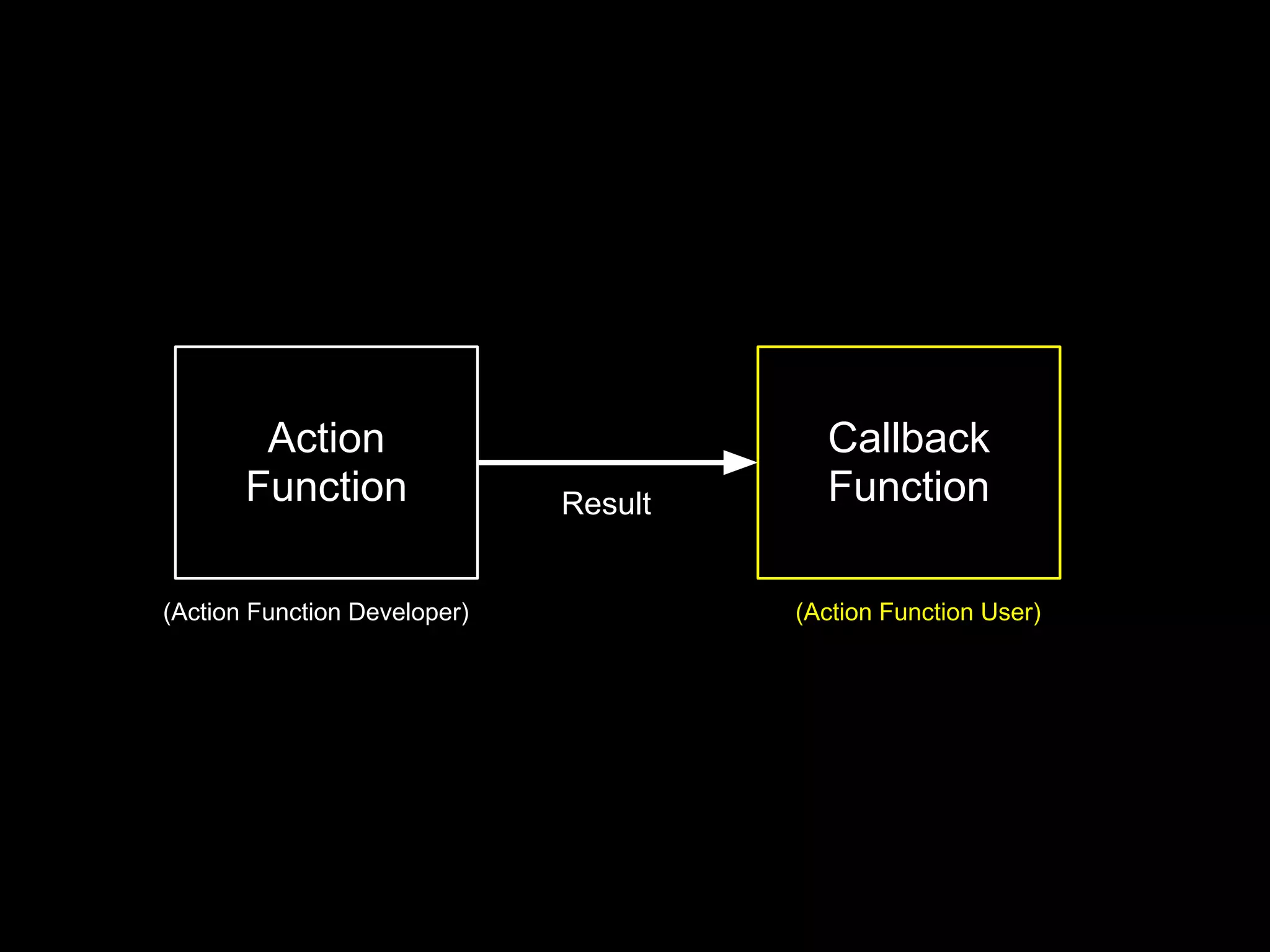
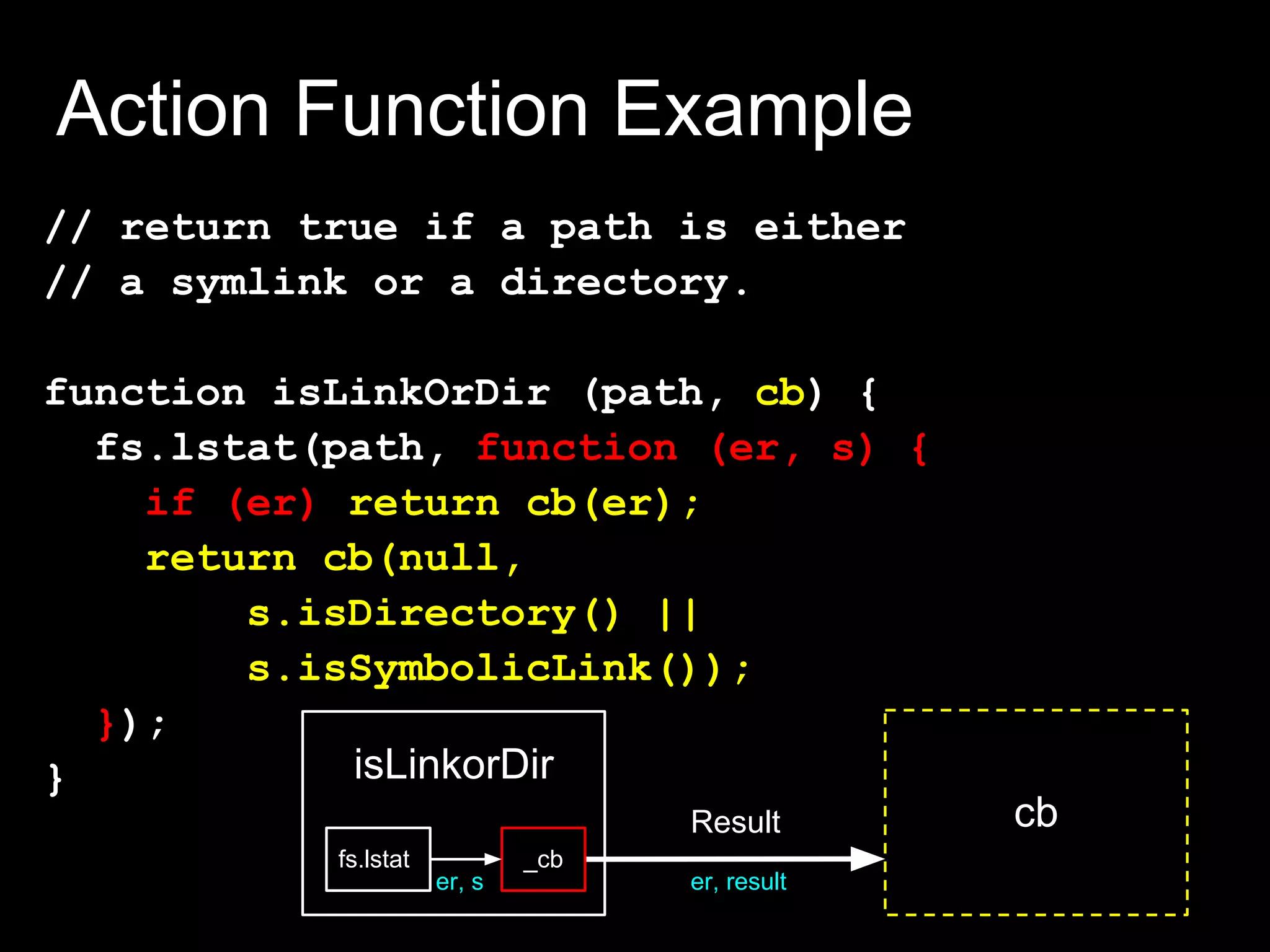
![Action Function Example
function actor (some, args, cb) {
// last argument is callback
// optional args:
if (!cb && typeof(args) === "function")
cb = args, args = [];
// do something, and then:
if (failed) cb(new Error("failed!"))
else cb(null, optionalData)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-15-2048.jpg)

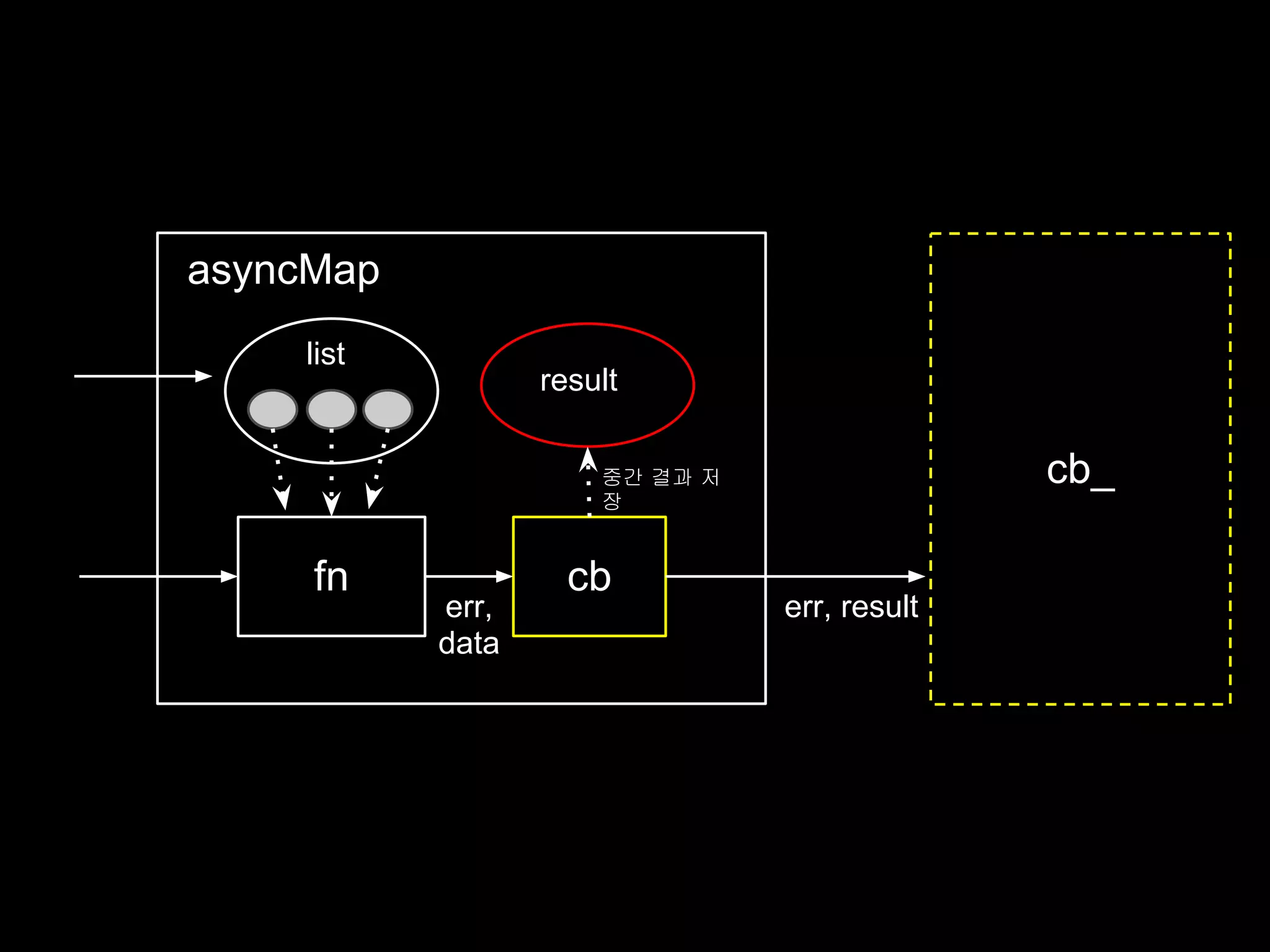
![function asyncMap (list, fn, cb_) {
var n = list.length
, results = []
, errState = null;
function cb (er, data) {
if (errState) return;
if (er) return cb(errState = er);
results.push(data);
if (--n === 0) // 모든 리스트 처리 완료시
return cb_(null, results);
}
// action code
list.forEach(function (l) {
fn(l, cb);
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-19-2048.jpg)
![Usecases : AsyncMap
function writeFiles (files, what, cb) {
asyncMap(files,
function (f, cb_) {
fs.writeFile(f,what,cb_);
}, cb_는 asyncMap의 내부 함수임
cb
);
}
writeFiles([my,file,list], "foo", cb);
writeFiles
asyncMap
files cb
list
fn cb_
err](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-21-2048.jpg)

![function asyncMap(list, fn, cb_) {
var n = list.length
, results = []
, errState = null;
function cbGen (i) {
return function cb(er, data) {
if (errState) return;
if (er)
return cb(errState = er);
results[i] = data;
if (-- n === 0)
return cb_(null, results);
}
}
list.forEach(function (l, i) {
fn(l, cbGen(i));
});
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-23-2048.jpg)

 {
if (er)
return cb(er);
LOOP(i + 1, len)
})
})(0, things.length)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-25-2048.jpg)
![chain
things
LOOP,0
things[0] LOOP,1
things[1] LOOP,2
things[2] LOOP, 3 cb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowcontrolinnode-js-120515173359-phpapp02/75/Flow-control-in-node-js-26-2048.jpg)