This presentation explains the essentials of Data Privacy and Protection in today’s digital world. As individuals and organizations increasingly rely on online services, mobile apps, cloud platforms, and connected devices, understanding how personal data is collected, stored, and used has become more important than ever.
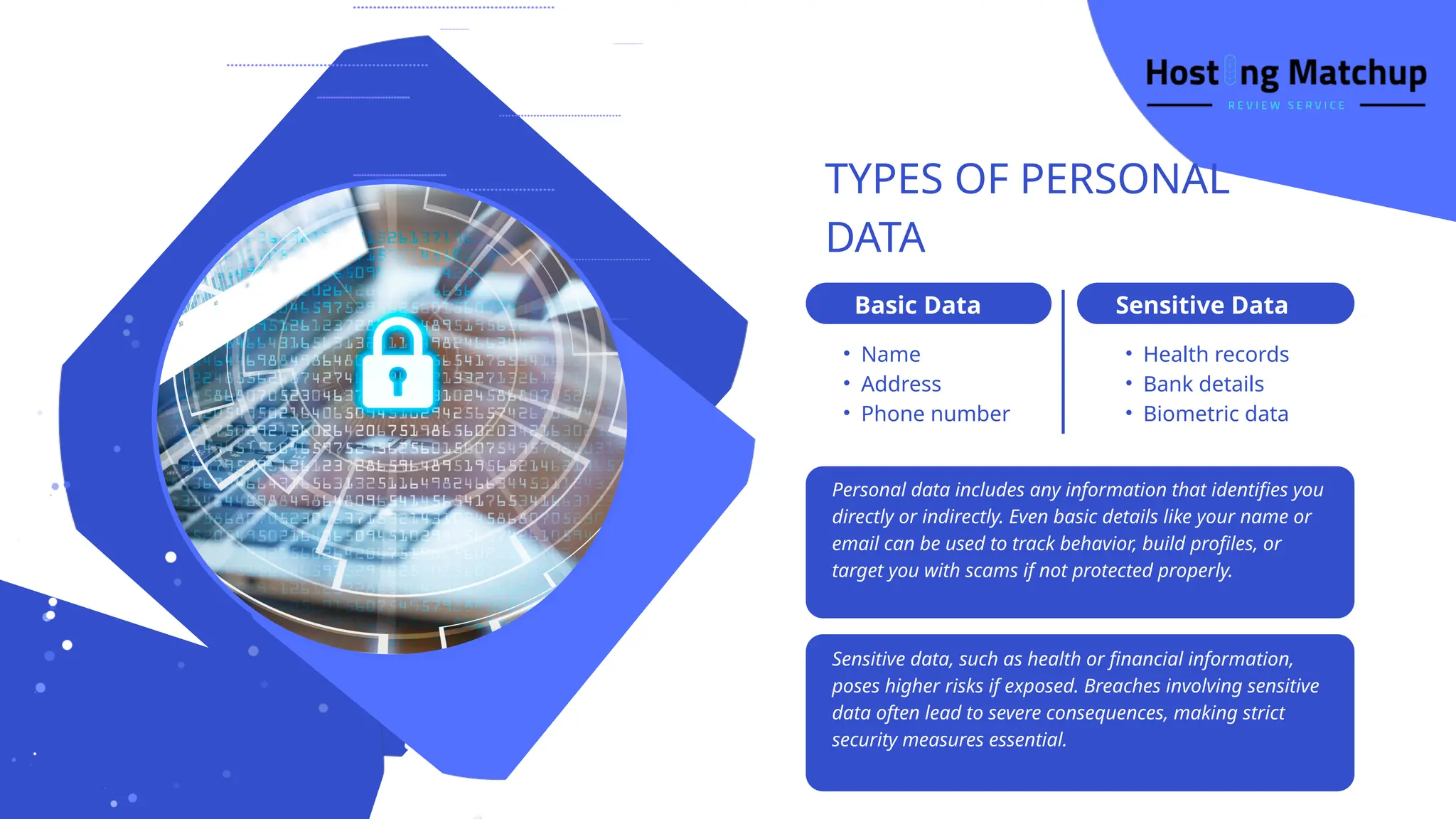
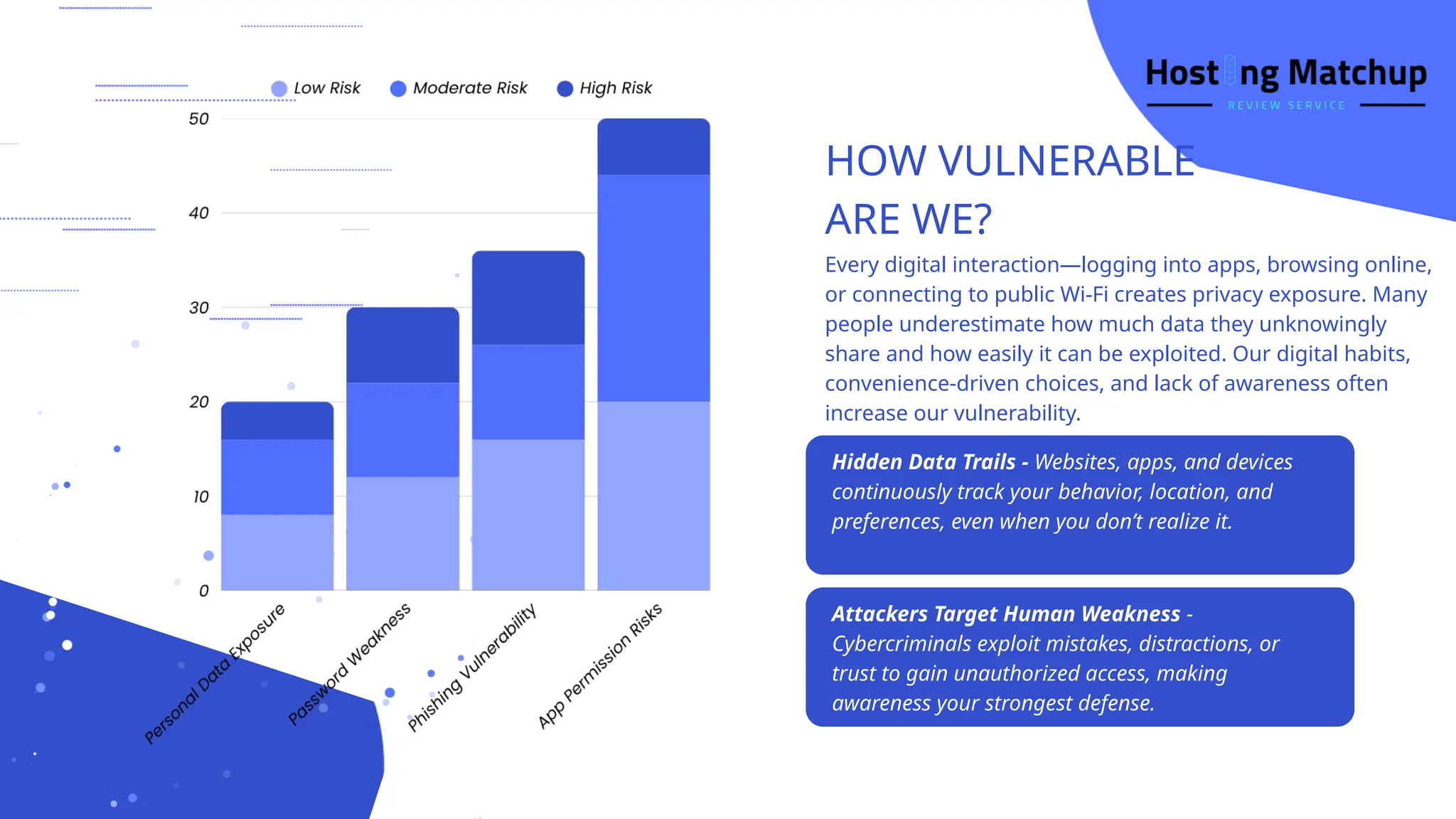
The deck covers why data privacy matters, the different types of personal and sensitive data, and the common privacy threats users face — including data breaches, phishing attacks, ransomware, and misuse of information by apps or services. It also highlights how vulnerable people and organizations are due to hidden data trails, weak digital habits, and lack of awareness.
A complete section on best practices provides practical actions to protect your personal and organizational data, such as strong authentication, secure device practices, privacy settings, and safe internet habits. The presentation also addresses privacy risks on social media, explaining how oversharing, poor privacy settings, and fake profiles expose users to long-term threats and how simple preventative actions can make a big difference.
The deck includes an overview of your data rights, such as the right to access, correct, delete, or restrict the use of your personal information under modern privacy laws. It also emphasizes the critical role of digital education in helping people understand risks, adopt safe online habits, and make informed choices.
This presentation is ideal for:
– Students and general users
– Employees and workplace teams
– Small businesses
– Public sector organizations
– Anyone concerned about digital safety and privacy
Keywords: Data privacy, personal data protection, privacy threats, social media risks, cyber awareness, safe internet habits, data breaches, sensitive data, privacy rights, information security, online protection, digital education, cybersecurity basics, data misuse, privacy best practices.