There is no command to create a pie chart in gnuplot. To plot a pie chart we need to play some tricks.
A pie chart is made up of some sectors with different colors. First we come to see how to plot a sector.
Sectors are parts of a sphere symmetrical plane, so it easy to plot a sector in parametric mode using splot command. For example, commands
set term png set output "sector.png" set parametric set urange [0:pi/3] set vrange [0:1] set view map set size square unset border unset tics unset colorbox splot cos(u)*v,sin(u)*v,1 w pm3d notitle
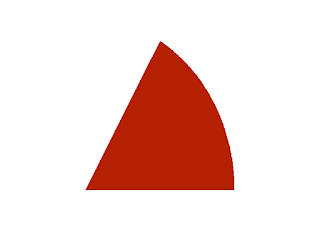 |
| Sector plotted using gnuplot |
England 0.2 France 0.1 Canada 0.3 America 0.2 Japan 0.1 China 0.1
import os
import math
def sign(x):
'''
Sign function.
sign(x)=1 when x >=0
sign(x)=1 when else.
'''
if (x>=0):
return 1
else:
return -1
input=file("data.txt","r") #open data file
plot=file("pie.gnuplot","w") #open plot script file
#Some plot commands
plotcommand='''
reset
set term png #terminal and output file
set output "pie.png"
set size square #square size
set isosample 50,50 #samples
set parametric #parametric mode on
set xrange [-1:1] #x,y,v range
set yrange [-1:1]
set vrange [0:1]
unset border #no border, tics and colorbox
unset xtics
unset ytics
unset colorbox
set view map #the view point
set palette defined(0 "red",1 "green",2 "blue",\\
3 "yellow",4 "cyan",5 "brown",6 "greenyellow",\\
7 "gray",8"bisque",9"violet",10"black")
#The color palette
set cbrange [0:10]
set multiplot #multiplot mode
'''
plot.write(plotcommand)
#output the commands to plot script file
u_begin=0.
#The begin value of u(dummy variable in parametric plot)
i=0. #The item indicate
while True:
##Read data
data=input.readline()
if len(data)==0: #if end of data file, break
break
data=data.split()
##Caculate some parameters
u_end=u_begin+float(data[1]) #end value of u
ang=(u_begin+u_end)*math.pi #the angle lables will be rotated
x=math.cos(ang)
x=x+sign(x)*0.2 #x value of label position
y=math.sin(ang)
y=y+sign(y)*0.2 #y value of label position
##Output some plot commands
plot.write("set urange [%f*2*pi:%f*2*pi]\n" \
%(u_begin,u_end)) #command set the range of variable u
plot.write('set label %d center "%s" at %f,%f rotate \
by %f*180/pi\n' %(int(i+1),data[0],x,y,ang))
#command set the labels
plot.write("splot cos(u)*v,sin(u)*v,%f w pm3d \
notitle\n" %i)
#command plot a sector
u_begin=u_end #the next begin value of u
i=i+1
plot.write("unset multiplot") #plot command
input.close() #close files
plot.close()
os.system("gnuplot plot.gplt") #execute the plot script
Run this python script we get a gnuplot script named pie.gnuplot and the following pie chart.
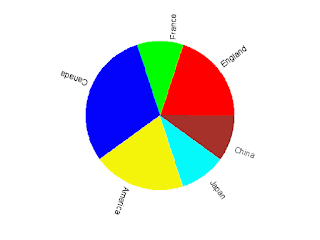 |
| Fig.1 Pie chart created by gnuplot with assistance of python |