Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

Source code for a computer program written in the JavaScript language. It demonstrates the appendChild method. The method adds a new child node to an existing parent node. It is commonly used to dynamically modify the structure of an HTML document.
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. It is one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter written for the language.
If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. (Full article...) -
Image 2In computer systems a loader is the part of an operating system that is responsible for loading programs and libraries. It is one of the essential stages in the process of starting a program, as it places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. Loading a program involves either memory-mapping or copying the contents of the executable file containing the program instructions into memory, and then carrying out other required preparatory tasks to prepare the executable for running. Once loading is complete, the operating system starts the program by passing control to the loaded program code.
All operating systems that support program loading have loaders, apart from highly specialized computer systems that only have a fixed set of specialized programs. Embedded systems typically do not have loaders, and instead, the code executes directly from ROM or similar. In order to load the operating system itself, as part of booting, a specialized boot loader is used. In many operating systems, the loader resides permanently in memory, though some operating systems that support virtual memory may allow the loader to be located in a region of memory that is pageable.
In the case of operating systems that support virtual memory, the loader may not actually copy the contents of executable files into memory, but rather may simply declare to the virtual memory subsystem that there is a mapping between a region of memory allocated to contain the running program's code and the contents of the associated executable file. (See memory-mapped file.) The virtual memory subsystem is then made aware that pages with that region of memory need to be filled on demand if and when program execution actually hits those areas of unfilled memory. This may mean parts of a program's code are not actually copied into memory until they are actually used, and unused code may never be loaded into memory at all. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Yoshua Bengio OC FRS FRSC (born March 5, 1964) is a Canadian-French computer scientist, and a pioneer of artificial neural networks and deep learning. He is a professor at the Université de Montréal and scientific director of the AI institute MILA.
Bengio received the 2018 ACM A.M. Turing Award, often referred to as the "Nobel Prize of Computing", together with Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun, for their foundational work on deep learning. Bengio, Hinton, and LeCun are sometimes referred to as the "Godfathers of AI". Bengio is the most-cited computer scientist globally (by both total citations and by h-index), and the most-cited living scientist across all fields (by total citations). In 2024, TIME Magazine included Bengio in its yearly list of the world's 100 most influential people. (Full article...) -
Image 4Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...) -
Image 5The Antikythera mechanism (/ˌæntɪkɪˈθɪərə/ AN-tik-ih-THEER-ə, US also /ˌæntaɪkɪˈ-/ AN-ty-kih-) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery (model of the Solar System). It is the oldest known example of an analogue computer. It could be used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games similar to an Olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games.
The artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. In 1902, during a visit to the National Archaeological Museum in Athens, it was noticed by Greek politician Spyridon Stais as containing a gear, prompting the first study of the fragment by his cousin, Valerios Stais, the museum director. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size 34 cm × 18 cm × 9 cm (13.4 in × 7.1 in × 3.5 in), was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is about 13 cm (5 in) in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. All these fragments of the mechanism are kept at the National Archaeological Museum, Athens, along with reconstructions and replicas, to demonstrate how it may have looked and worked.
In 2005, a team from Cardiff University led by Mike Edmunds used computer X-ray tomography and high resolution scanning to image inside fragments of the crust-encased mechanism and read the faintest inscriptions that once covered the outer casing. These scans suggest that the mechanism had 37 meshing bronze gears enabling it to follow the movements of the Moon and the Sun through the zodiac, to predict eclipses and to model the irregular orbit of the Moon, where the Moon's velocity is higher in its perigee than in its apogee. This motion was studied in the 2nd century BC by astronomer Hipparchus of Rhodes, and he may have been consulted in the machine's construction. There is speculation that a portion of the mechanism is missing and it calculated the positions of the five classical planets. The inscriptions were further deciphered in 2016, revealing numbers connected with the synodic cycles of Venus and Saturn. (Full article...) -
Image 6Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced /ˌɛsˌkjuˈɛl/ S-Q-L; or alternatively as /ˈsiːkwəl/ ⓘ "sequel")
is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
Introduced in the 1970s, SQL offered two main advantages over older read–write APIs such as ISAM or VSAM. Firstly, it introduced the concept of accessing many records with one single command. Secondly, it eliminates the need to specify how to reach a record, i.e., with or without an index.
Originally based upon relational algebra and tuple relational calculus, SQL consists of many types of statements, which may be informally classed as sublanguages, commonly: data query language (DQL), data definition language (DDL), data control language (DCL), and data manipulation language (DML). (Full article...) -
Image 7Programming languages are used for controlling the behavior of a machine (often a computer). Like natural languages, programming languages follow rules for syntax and semantics.
There are thousands of programming languages and new ones are created every year. Few languages ever become sufficiently popular that they are used by more than a few people, but professional programmers may use dozens of languages in a career.
Most programming languages are not standardized by an international (or national) standard, even widely used ones, such as Perl or Standard ML (despite the name). Notable standardized programming languages include ALGOL, C, C++, JavaScript (under the name ECMAScript), Smalltalk, Prolog, Common Lisp, Scheme (IEEE standard), ISLISP, Ada, Fortran, COBOL, SQL, and XQuery. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.
Python is dynamically type-checked and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library.
Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of Python 2. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Haskell (/ˈhæskəl/) is a general-purpose, statically typed, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language features such as type classes, which enable type-safe operator overloading, and monadic input/output (IO). It is named after logician Haskell Curry. Haskell's main implementation is the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC).
Haskell's semantics are historically based on those of the Miranda programming language, which served to focus the efforts of the initial Haskell working group. The last formal specification of the language was made in July 2010, while the development of GHC continues to expand Haskell via language extensions.
Haskell is used in academia and industry. As of May 2021[update], Haskell was the 28th most popular programming language by Google searches for tutorials, and made up less than 1% of active users on the GitHub source code repository. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Kotlin (/ˈkɒtlɪn/) is a cross-platform, statically typed, general-purpose high-level programming language with type inference. Kotlin is designed to interoperate fully with Java, and the JVM version of Kotlin's standard library depends on the Java Class Library,
but type inference allows its syntax to be more concise. Kotlin mainly targets the JVM, but also compiles to JavaScript (e.g., for frontend web applications using React) or native code via LLVM (e.g., for native iOS apps sharing business logic with Android apps). Language development costs are borne by JetBrains, while the Kotlin Foundation protects the Kotlin trademark.
On 7 May 2019, Google announced that the Kotlin programming language had become its preferred language for Android app developers. Since the release of Android Studio 3.0 in October 2017, Kotlin has been included as an alternative to the standard Java compiler. The Android Kotlin compiler emits Java 8 bytecode by default (which runs in any later JVM), but allows targeting Java 9 up to 20, for optimizing, or allows for more features; has bidirectional record class interoperability support for JVM, introduced in Java 16, considered stable as of Kotlin 1.5.
Kotlin has support for the web with Kotlin/JS, through an intermediate representation-based backend which has been declared stable since version 1.8, released December 2022. Kotlin/Native (for e.g. Apple silicon support) has been declared stable since version 1.9.20, released November 2023. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Computer class at Chkalovski Village School No. 2 in 1985–1986
The history of computing in the Soviet Union began in the late 1940s, when the country began to develop its Small Electronic Calculating Machine (MESM) at the Kiev Institute of Electrotechnology in Feofaniya. Initial ideological opposition to cybernetics in the Soviet Union was overcome by a Khrushchev era policy that encouraged computer production.
By the early 1970s, the uncoordinated work of competing government ministries had left the Soviet computer industry in disarray. Due to lack of common standards for peripherals and lack of digital storage capacity the Soviet Union's technology significantly lagged behind the West's semiconductor industry. The Soviet government decided to abandon development of original computer designs and encouraged cloning of existing Western systems (e.g. the 1801 CPU series was scrapped in favor of the PDP-11 ISA by the early 1980s).
Soviet industry was unable to mass-produce computers to acceptable quality standards and locally manufactured copies of Western hardware were unreliable. As personal computers spread to industries and offices in the West, the Soviet Union's technological lag increased. (Full article...) -
Image 12

A computer lab contains a wide range of information technology elements,
including hardware, software and storage systems.
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data and information processing, and storage. Information technology is an application of computer science and computer engineering.
The term is commonly used as a synonym for computers and computer networks, but it also encompasses other information distribution technologies such as television and telephones. Several products or services within an economy are associated with information technology, including computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet, telecom equipment, and e-commerce.
An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a computer system — including all hardware, software, and peripheral equipment — operated by a limited group of IT users, and an IT project usually refers to the commissioning and implementation of an IT system. IT systems play a vital role in facilitating efficient data management, enhancing communication networks, and supporting organizational processes across various industries. Successful IT projects require meticulous planning and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal functionality and alignment with organizational objectives. (Full article...) -
Image 13

PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared towards web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP Group. PHP was originally an abbreviation of Personal Home Page, but it now stands for the recursive backronym PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
PHP code is usually processed on a web server by a PHP interpreter implemented as a module, a daemon or a Common Gateway Interface (CGI) executable. On a web server, the result of the interpreted and executed PHP code—which may be any type of data, such as generated HTML or binary image data—would form the whole or part of an HTTP response. Various web template systems, web content management systems, and web frameworks exist that can be employed to orchestrate or facilitate the generation of that response. Additionally, PHP can be used for many programming tasks outside the web context, such as standalone graphical applications and drone control. PHP code can also be directly executed from the command line.
The standard PHP interpreter, powered by the Zend Engine, is free software released under the PHP License. PHP has been widely ported and can be deployed on most web servers on a variety of operating systems and platforms. (Full article...) -
Image 14

C# (pronounced: C-sharp) (/ˌsiː ˈʃɑːrp/ see SHARP) is a general-purpose high-level programming language supporting multiple paradigms. C# encompasses static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines.
The principal inventors of the C# programming language were Anders Hejlsberg, Scott Wiltamuth, and Peter Golde from Microsoft. It was first widely distributed in July 2000 and was later approved as an international standard by Ecma (ECMA-334) in 2002 and ISO/IEC (ISO/IEC 23270 and 20619) in 2003. Microsoft introduced C# along with .NET Framework and Microsoft Visual Studio, both of which are technically speaking, closed-source. At the time, Microsoft had no open-source products. Four years later, in 2004, a free and open-source project called Microsoft Mono began, providing a cross-platform compiler and runtime environment for the C# programming language. A decade later, Microsoft released Visual Studio Code (code editor), Roslyn (compiler), and the unified .NET platform (software framework), all of which support C# and are free, open-source, and cross-platform. Mono also joined Microsoft but was not merged into .NET.
As of January 2025,[update] the most recent stable version of the language is C# 13.0, which was released in 2024 in .NET 9.0 (Full article...) -
Image 15Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to perceive their environment and use learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals.
High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); generative and creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., chess and Go). However, many AI applications are not perceived as AI: "A lot of cutting edge AI has filtered into general applications, often without being called AI because once something becomes useful enough and common enough it's not labeled AI anymore."
Various subfields of AI research are centered around particular goals and the use of particular tools. The traditional goals of AI research include learning, reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, natural language processing, perception, and support for robotics. To reach these goals, AI researchers have adapted and integrated a wide range of techniques, including search and mathematical optimization, formal logic, artificial neural networks, and methods based on statistics, operations research, and economics. AI also draws upon psychology, linguistics, philosophy, neuroscience, and other fields. Some companies, such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind and Meta, aim to create artificial general intelligence (AGI)—AI that can complete virtually any cognitive task at least as well as a human. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 1A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 2A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
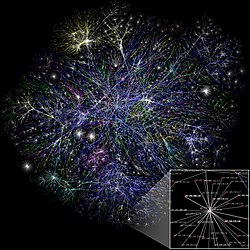
Image 3Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 5Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 6Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 7GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
Image 8Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 9An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
-
Image 11A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 12Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 13This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 14Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 15Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 18Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that Rust has been named the "most loved programming language" every year for seven years since 2016 by annual surveys conducted by Stack Overflow?
- ... that a "hacker" with blog posts written by ChatGPT was at the center of an online scavenger hunt promoting Avenged Sevenfold's album Life Is but a Dream...?
- ... that it took a particle accelerator and machine-learning algorithms to extract the charred text of PHerc. Paris. 4 without unrolling it?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that both Thackeray and Longfellow bought paintings by Fanny Steers?
- ... that a pink skin for Mercy in the video game Overwatch helped raise more than $12 million for breast cancer research?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
- 23 May 2025 –
- Authorities from Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the U.S. announce a joint operation to crack down on malware around the world, which took down over 300 servers, neutralized 650 domains, and seized over €3.5 million (US$3.9 million) of cryptocurrency. (DW)
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus