Since its introduction in 2012, an OS X feature known as Gatekeeper has gone a long way to protecting the Macs of security novices and experts alike. Not only does it help neutralize social engineering attacks that trick less experienced users into installing trojans, code-signing requirements ensure even seasoned users that an installer app hasn't been maliciously modified as it was downloaded over an unencrypted connection.
Now, a security researcher has found a drop-dead simple technique that completely bypasses Gatekeeper, even when the protection is set to its strictest setting. The hack uses a binary file already trusted by Apple to pass through Gatekeeper. Once the Apple-trusted file is on the other side, it executes one or more malicious files that are included in the same folder. The bundled files can install a variety of nefarious programs, including password loggers, apps that capture audio and video, and botnet software.
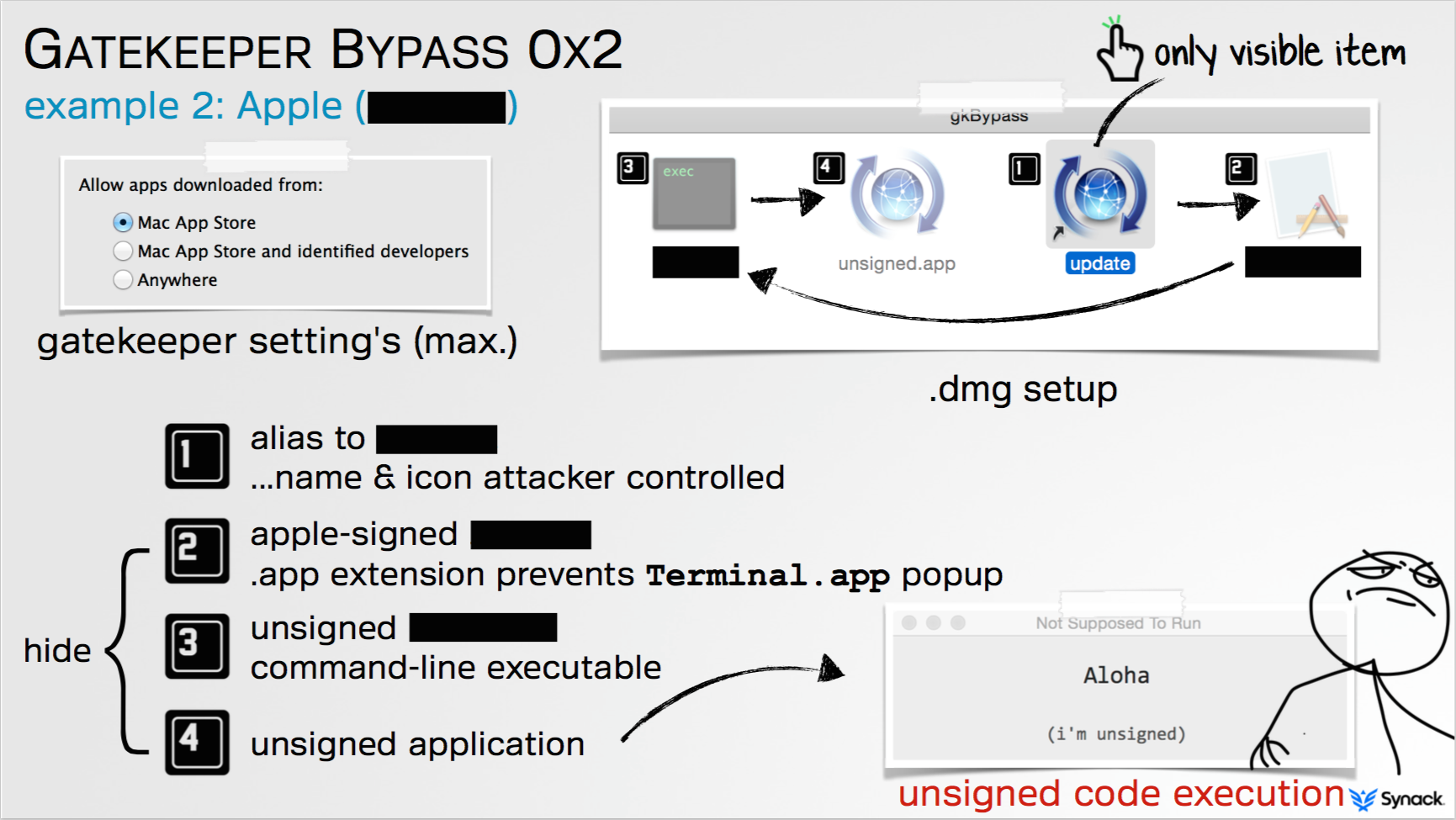
Patrick Wardle, director of research of security firm Synack, said the bypass stems from a key shortcoming in the design of Gatekeeper rather than a defect in the way it operates. Gatekeeper's sole function is to check the digital certificate of a downloaded app before it's installed to see if it's signed by an Apple-recognized developer or originated from the official Apple App Store. It was never set up to prevent apps already trusted by OS X from running in unintended or malicious ways, as the proof-of-concept exploit he developed does.
"If the application is valid—so it was signed by a developer ID or was (downloaded) from the Mac App Store—Gatekeeper basically says 'OK, I'm going to let this run,' and then Gatekeeper essentially exits," Wardle told Ars. "It doesn't monitor what that application is doing. If that application turns around and either loads or executes other content from the same directory... Gatekeeper does not examine those files."
Putting it into practice
Wardle has found a widely available binary that's already signed by Apple. Once executed, the file runs a separate app located in the same folder as the first one. At the request of Apple officials, he and Ars have agreed to withhold the names of the two files, and instead will refer to them only as Binary A and Binary B. His exploit works by renaming Binary A but otherwise making no other changes to it. He then packages it inside an Apple disk image. Because the renamed Binary A is a known file signed by Apple, it will immediately be approved by Gatekeeper and be executed by OS X.

 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
