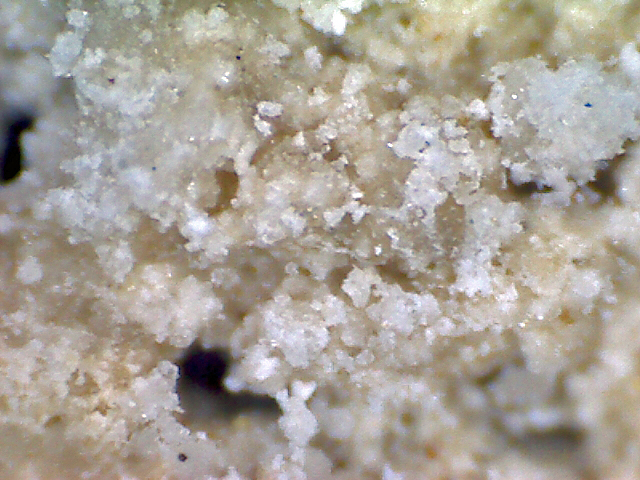
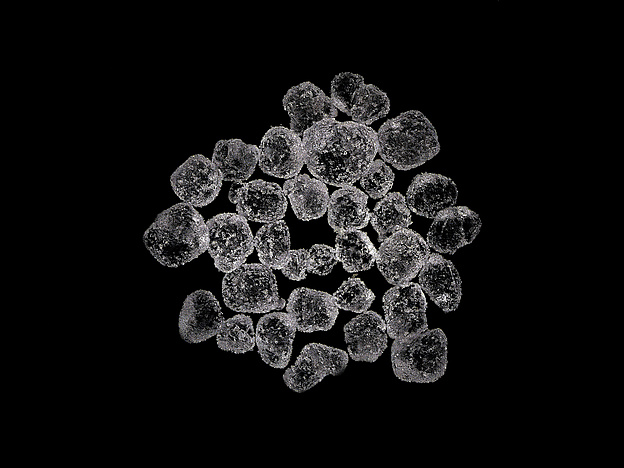
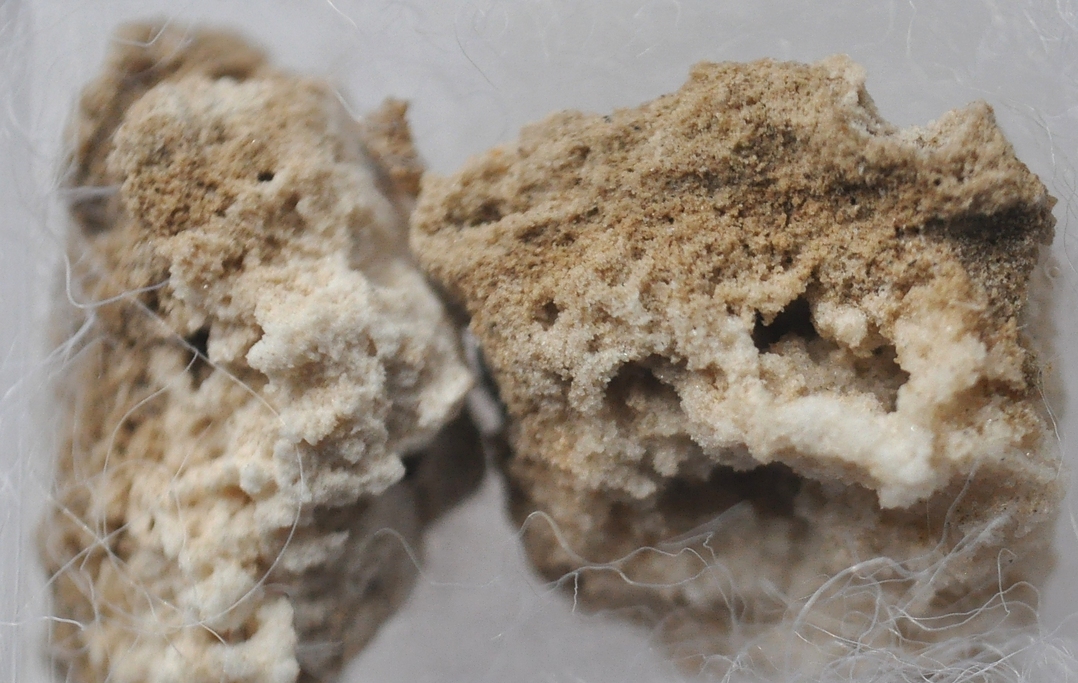
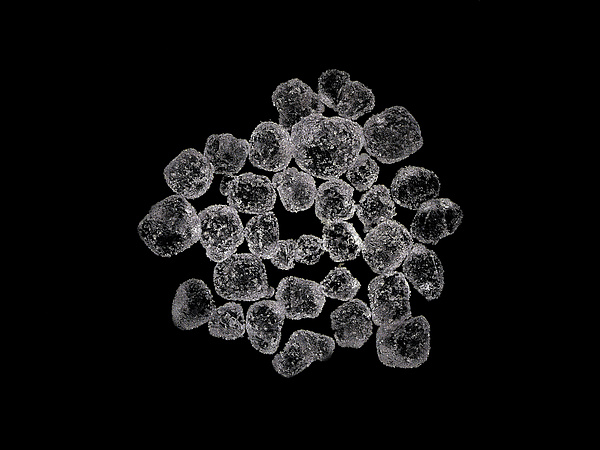
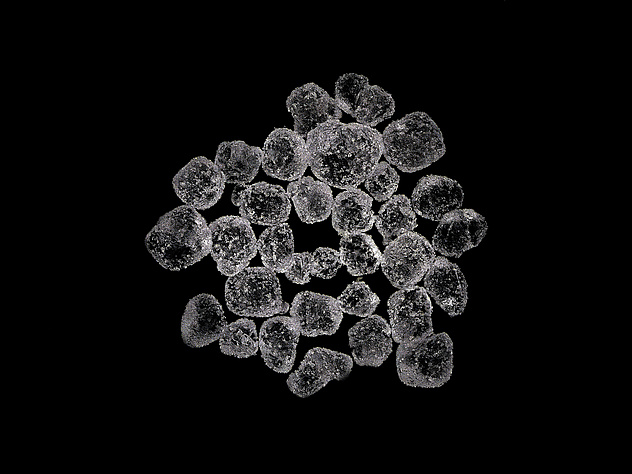
Santite
About Santite
Unique Identifiers
IMA Classification of Santite
Classification of Santite
6 : BORATES
E : Pentaborates
A : Neso-pentaborates
26 : HYDRATED BORATES CONTAINING HYDROXYL OR HALOGEN
5 : Pentaborates
9 : Borates
1 : Borates of the alkalis and boric acid
Mineral Symbols
| Symbol | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Snt | IMA–CNMNC | Warr, L.N. (2021). IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols. Mineralogical Magazine, 85(3), 291-320. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43 |
Physical Properties of Santite
Optical Data of Santite
Based on recorded range of RI values above.
The colours simulate birefringence patterns seen in thin section under crossed polars. They do not take into account mineral colouration or opacity.
Michel-Levy Bar The default colours simulate the birefringence range for a 30 µm thin-section thickness. Adjust the slider to simulate a different thickness.
Grain Simulation You can rotate the grain simulation to show how this range might look as you rotated a sample under crossed polars.
Chemistry of Santite
Crystallography of Santite
Crystal Structure
Unit Cell | Unit Cell Packed
2x2x2 | 3x3x3 | 4x4x4
Big Balls | Small Balls | Just Balls | Spacefill
Polyhedra Off | Si Polyhedra | All Polyhedra
Remove metal-metal sticks
Black Background | White Background
Perspective On | Perspective Off
2D | Stereo | Red-Blue | Red-Cyan
CIF File Best | x | y | z | a | b | c
Stop | Start
Console Off | On | Grey | Yellow
| ID | Species | Reference | Link | Year | Locality | Pressure (GPa) | Temp (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0010569 | Santite | Zachariasen W H (1937) The crystal structure of potassium acid dihydronium pentaborate KH2(H3O)2B5O10, (potassium pentaborate tetrahydrate) Zeitschrift fur Kristallographie 98 266-274 |  | 1937 | synthetic | 0 | 293 |
| 0018018 | Santite | Zachariasen W (1938) The crystal structure of potassium acid dihydronium pentaborate K H2 (H3 O)2 B5 O10, (potassium pentaborate tetrahydrate) _cod_database_code 1011124 Zeitschrift fur Kristallographie 98 266-274 |  | 1938 | 0 | 293 |
X-Ray Powder Diffraction
| d-spacing | Intensity |
|---|---|
| 3.36 Å | (100) |
| 3.52 Å | (84) |
| 5.60 Å | (71) |
| 2.767 Å | (50) |
| 2.181 Å | (21) |
| 3.28 Å | (18) |
| 5.93 Å | (15) |
Geological Environment
| Paragenetic Mode | Earliest Age (Ga) |
|---|---|
| Near-surface Processes | |
| 25 : Evaporites (prebiotic) | |
| Stage 7: Great Oxidation Event | <2.4 |
| 45b : [Other oxidized fumarolic minerals] |
Type Occurrence of Santite
Synonyms of Santite
Other Language Names for Santite
Relationship of Santite to other Species
| Sborgite | Na[B5O6(OH)4] · 3H2O | Mon. 2/m : B2/b |
Common Associates
| 1 photo of Santite associated with Thénardite | Na2SO4 |
Related Minerals - Strunz-mindat Grouping
| 6.EA.05 | Sborgite | Na[B5O6(OH)4] · 3H2O |
| 6.EA.05 | Leucostaurite | Pb2[B5O9]Cl · 0.5H2O |
| 6.EA.10 | Ramanite-(Rb) | Rb[B5O6(OH)4] · 2H2O |
| 6.EA.10 | Ramanite-(Cs) | Cs[B5O6(OH)4] · 2H2O |
| 6.EA.15 | Ammonioborite | (NH4)2[B5O6(OH)4]2 · H2O |
| 6.EA.25 | Ulexite | NaCa[B5O6(OH)6] · 5H2O |
Radioactivity
| Element | % Content | Activity (Bq/kg) | Radiation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uranium (U) | 0.0000% | 0 | α, β, γ |
| Thorium (Th) | 0.0000% | 0 | α, β, γ |
| Potassium (K) | 13.3346% | 4,134 | β, γ |
For comparison:
- Banana: ~15 Bq per fruit
- Granite: 1,000–3,000 Bq/kg
- EU exemption limit: 10,000 Bq/kg
Note: Risk is shown relative to daily recommended maximum exposure to non-background radiation of 1000 µSv/year. Note that natural background radiation averages around 2400 µSv/year so in reality these risks are probably extremely overstated! With infrequent handling and safe storage natural radioactive minerals do not usually pose much risk.
Note: The mass selector refers to the mass of radioactive mineral present, not the full specimen, also be aware that the matrix may also be radioactive, possibly more radioactive than this mineral!
Activity: –
| Distance | Dose rate | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cm | ||
| 10 cm | ||
| 1 m |
The external dose rate (D) from a radioactive mineral is estimated by summing the gamma radiation contributions from its Uranium, Thorium, and Potassium content, disregarding daughter-product which may have a significant effect in some cases (eg 'pitchblende'). This involves multiplying the activity (A, in Bq) of each element by its specific gamma ray constant (Γ), which accounts for its unique gamma emissions. The total unshielded dose at 1 cm is then scaled by the square of the distance (r, in cm) and multiplied by a shielding factor (μshield). This calculation provides a 'worst-case' or 'maximum risk' estimate because it assumes the sample is a point source and entirely neglects any self-shielding where radiation is absorbed within the mineral itself, meaning actual doses will typically be lower. The resulting dose rate (D) is expressed in microsieverts per hour (μSv/h).
D = ((AU × ΓU) + (ATh × ΓTh) + (AK × ΓK)) / r2 × μshield
Other Information
Internet Links for Santite
Please feel free to link to this page.
References for Santite
Localities for Santite
Locality List
 - This locality has map coordinates listed.
- This locality has map coordinates listed.
 - This locality has estimated coordinates.
ⓘ - Click for references and further information on this occurrence.
? - Indicates mineral may be doubtful at this locality.
- This locality has estimated coordinates.
ⓘ - Click for references and further information on this occurrence.
? - Indicates mineral may be doubtful at this locality.
 - Good crystals or important locality for species.
- Good crystals or important locality for species.
 - World class for species or very significant.
(TL) - Type Locality for a valid mineral species.
(FRL) - First Recorded Locality for everything else (eg varieties).
- World class for species or very significant.
(TL) - Type Locality for a valid mineral species.
(FRL) - First Recorded Locality for everything else (eg varieties).
All localities listed without proper references should be considered as questionable.
Italy | |
| Campostrini I. et al - Vulcano: ein ... |
| Merlino et al. (1970) +1 other reference |
Kazakhstan | |
| Коротченкова et al. (2016) |
USA | |
| a spectroscopic exploration. Economic ... +1 other reference |






 symbol to view information about a locality.
The
symbol to view information about a locality.
The
Eagle Borax Spring, Inyo County, California, USA