Types of Network Firewall
Last Updated :
12 Dec, 2025
A network firewall is a security system that protects private networks from unauthorized access. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
- Acts as a barrier between internal (trusted) and external (untrusted) networks
- Can be hardware-based, software-based, or both
- Filters traffic using rules, policies, and inspection methods
- Main goal: prevent attacks, malware, and unauthorized access
Types of Network Firewalls
Here are the main types of network firewalls, organized by how they function and where they're deployed:
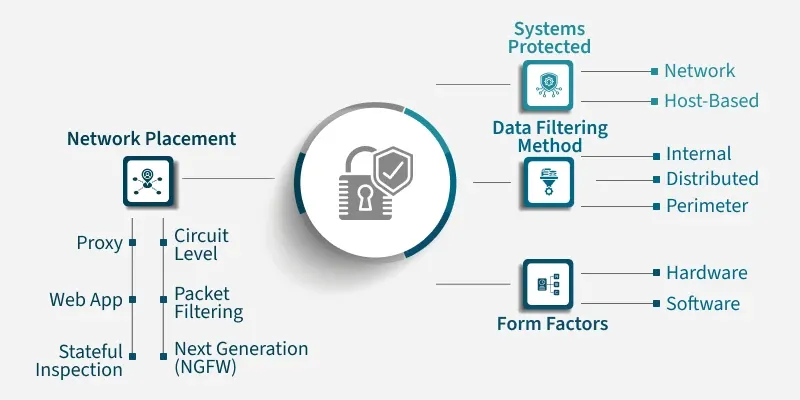
1) Based on Function (How They Filter Traffic)
Network Security is the process of protecting networks, systems, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage.
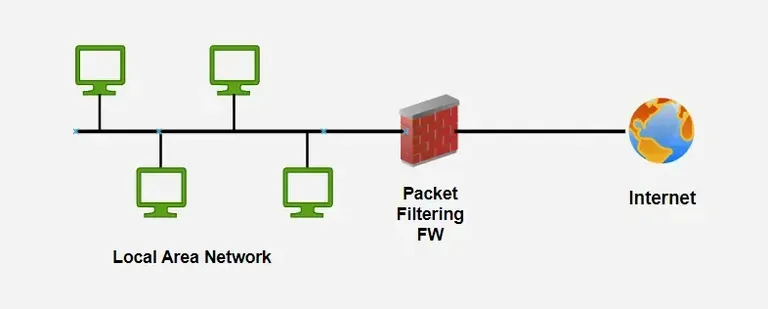
a. Packet Filtering Firewall
A basic firewall that checks packet headers like IP, port, and protocol.
- Very fast and lightweight
- Does not inspect data inside packets
- Provides basic security only
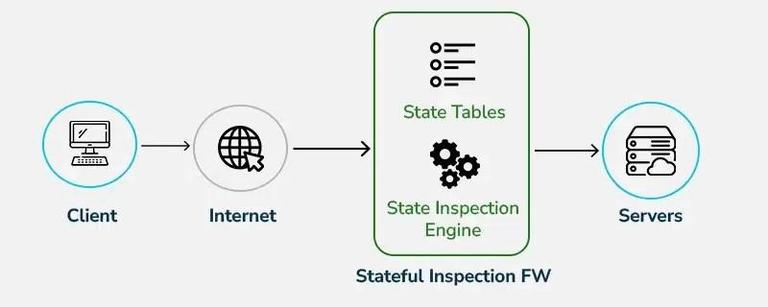
b. Stateful Inspection Firewall
Tracks active connections and makes decisions based on traffic context.
- More secure than packet filtering
- Remembers past traffic (state table)
- Blocks suspicious or unexpected packets
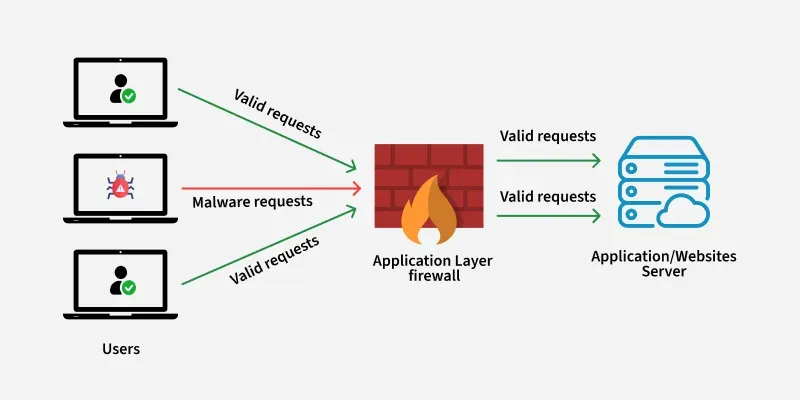
c. Proxy (Application-Level) Firewall
Acts as a middleman between user and destination server.
- Filters data at the application layer
- Hides internal network details
- Can block malicious content before it reaches the user
d. Circuit-Level Gateway
Validates session creation (like TCP handshake) without inspecting data.
- Ensures only legitimate sessions start
- Low processing overhead
- Does not detect internal packet threats
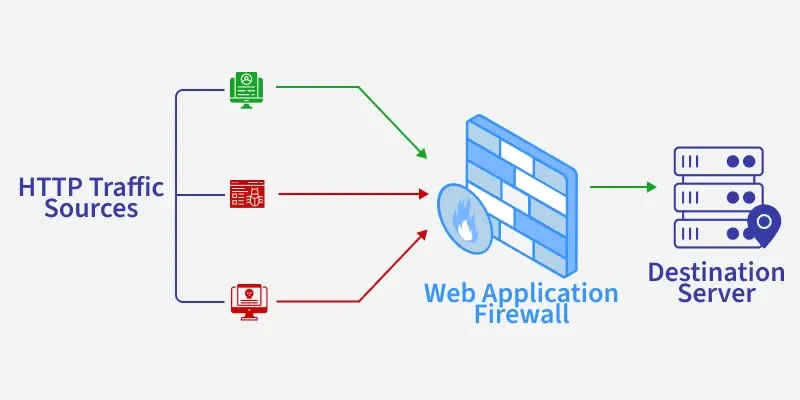
e. Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
Advanced firewall combining multiple security features.
- Includes intrusion prevention, malware detection
- Can inspect encrypted traffic
- Provides app-level filtering
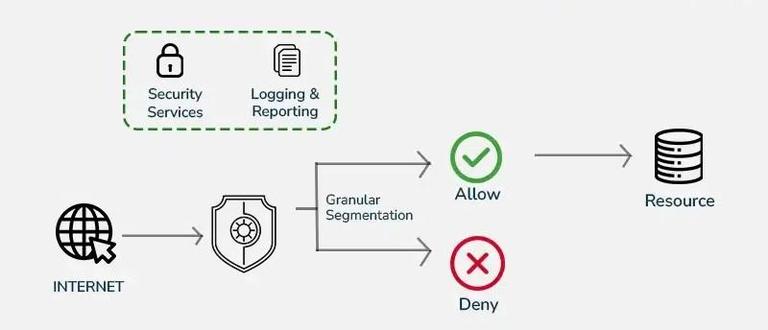
2) Network Firewall
A Network Firewall secures the perimeter, while a host-based firewall protects the endpoint.
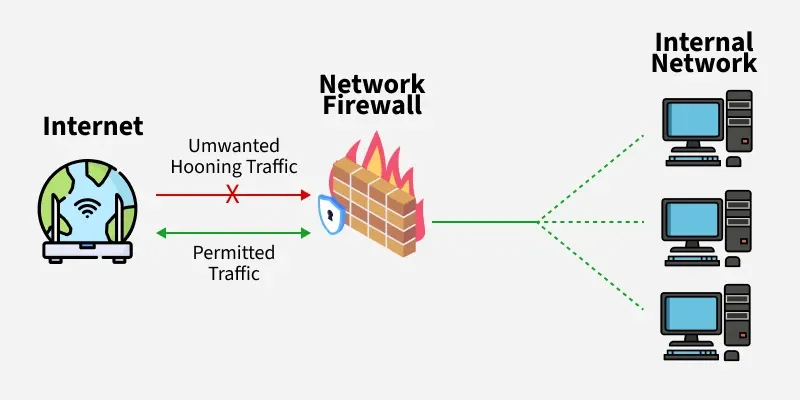
a. Network Firewall
Placed at the network perimeter to protect the whole network.
- Controls inbound & outbound traffic
- First line of defense
- Ideal for organizations
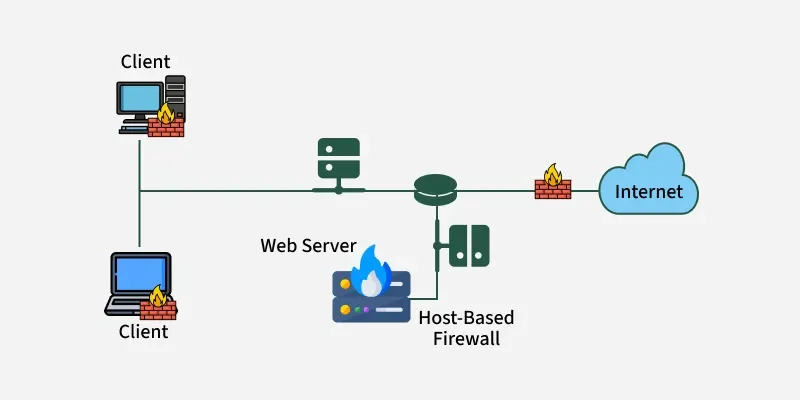
b. Host-Based Firewall
Installed on individual PCs, laptops, or servers.
- Protects a single device
- Monitors local application traffic
- Useful for personal or endpoint security
3) Data Filtering Method
All three of these firewall types work to control network access, but they differ in their placement and scope.
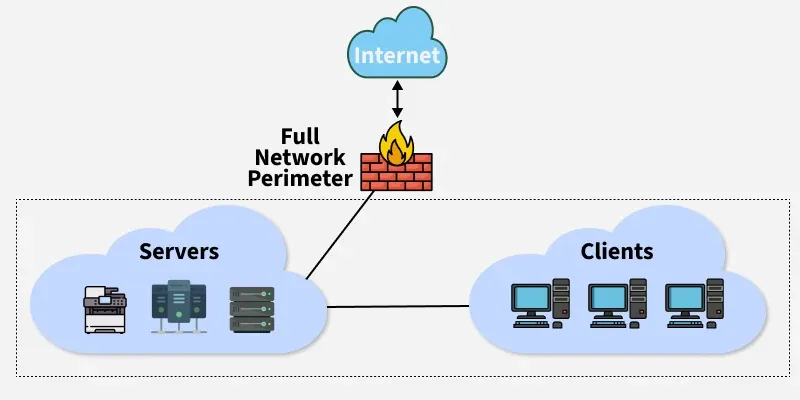
a. Perimeter Firewall
Placed at the edge to filter traffic between internet and internal network.
- Central security control
- Blocks external attacks
- Common in corporate environments
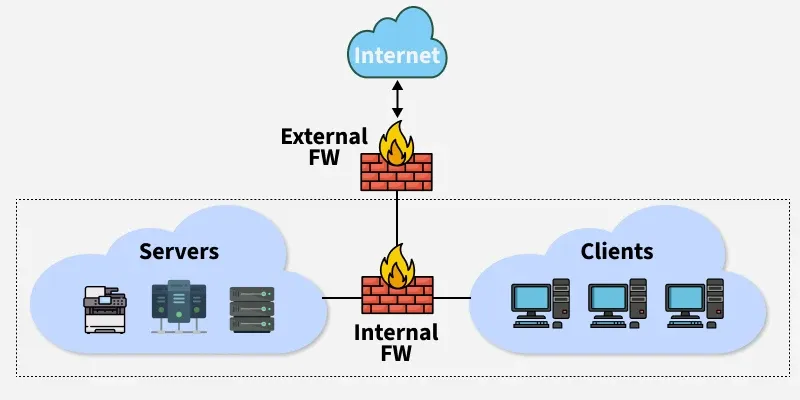
b. Internal Firewall
Placed between internal network segments (e.g., departments).
- Prevents insider threats
- Protects sensitive areas (HR, finance)
- Provides micro-segmentation
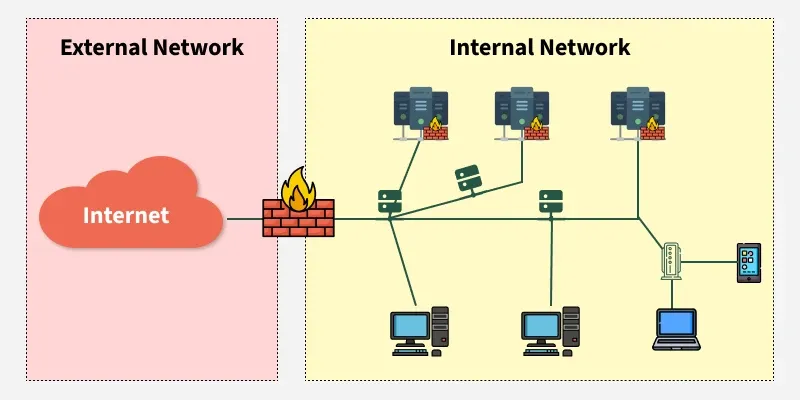
c. Distributed Firewall
Firewall policies applied on multiple endpoints across the network.
- No single point of failure
- Consistent security across devices
- Good for large, distributed networks
A program installed on a computer or server that protects it from network threats.
a. Hardware Firewall
A physical device installed on the network.
- Strong performance, high reliability
- Best for offices or enterprise networks
- More expensive than software firewalls
b. Software Firewall
Installed as a program on computers or servers.
- Easy to configure
- Ideal for individuals and virtual environments
- Lower cost compared to hardware solutions

Working of Firewalls
Firewalls inspect packets entering or leaving the network and decide whether to allow or block them. They compare traffic against rules to keep malicious data out.
- Analyze packet headers and sometimes packet content
- Block viruses, malware, and unauthorized access
- Monitor traffic patterns to detect anomalies
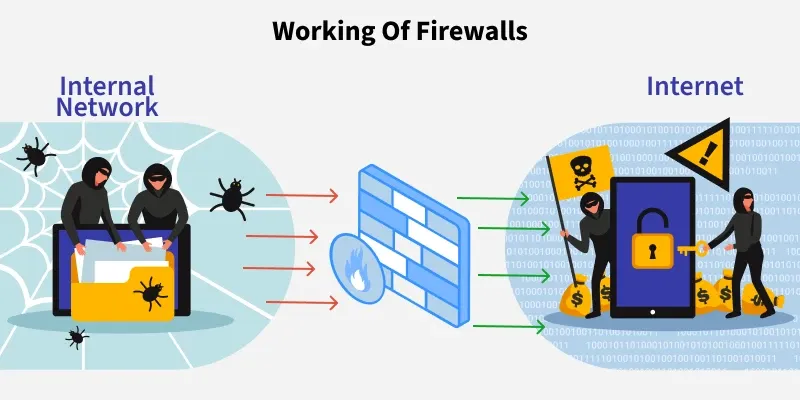 Working of Firewall
Working of FirewallPros and Cons of Network Firewall
Here are some pros and cons of network firewall:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|
| Protects network from unauthorized access | Can reduce network speed due to inspection |
| Prevents malware, attacks, and suspicious traffic | Hardware firewalls can be expensive |
| Easy to enforce security policies | May block legitimate tasks by mistake |
| Works with other security tools | Requires ongoing updates & maintenance |
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice
My Profile