An array is a collection of elements of the same type stored in a single variable. It allows you to access each element using an index. Arrays make it easy to store and manage multiple values together.
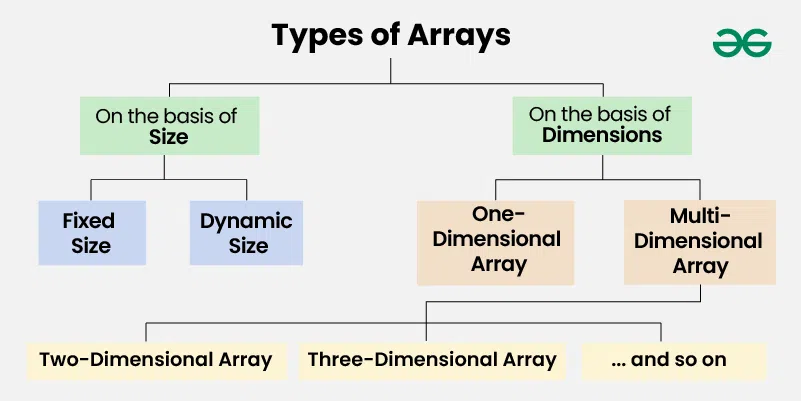
On the basis of Size:
1. Fixed Sized Arrays:
- The size of a fixed-size array cannot be changed after creation.
- Memory is allocated only for the size mentioned in square brackets [].
- Declaring a larger size than needed wastes memory.
- Declaring a smaller size than needed is not enough to store all elements.
- Fixed-size arrays are not preferred when the number of elements is unknown.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// fixed-size array of 5 integers
int arr[5];
// storing values in the array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
// printing array elements
cout << "Array elements are: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// fixed-size array of 5 integers
int arr[5];
int i;
// storing values in the array
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
// printing array elements
printf("Array elements are: ");
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// fixed-size array of 5 integers
int[] arr= new int[5];
// storing values in the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1; // storing 1,2,3,4,5
}
// printing array elements
System.out.print("Array elements are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
# creating a fixed-size list of 5 elements
arr = [0] * 5
# storing values in the list
for i in range(5):
arr[i] = i + 1
# printing list elements
print("Array elements are:", arr)
using System;
class Program {
static void Main()
{
// fixed-size array of 5 integers
int[] arr = new int[5];
// storing values in the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
// printing array elements
Console.Write("Array elements are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
OutputArray elements are: 1 2 3 4 5
2. Dynamic Sized Arrays:
- The size of a dynamic array can change during program execution.
- Elements can be added or removed as needed.
- Memory is allocated and de-allocated automatically.
- Don’t need to worry about the array size in advance.
- Dynamic arrays are flexible and useful when the number of elements is unknown.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// dynamic array
vector<int> arr;
// adding elements
arr.push_back(10);
arr.push_back(20);
arr.push_back(30);
// printing array elements
cout << "Array elements are: ";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// removing last element
arr.pop_back();
cout << "\nAfter removing last element: ";
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// pointer for dynamic array
int *arr = NULL;
int size = 0;
// adding elements dynamically
size++;
arr = (int *)realloc(arr, size * sizeof(int));
arr[size - 1] = 10;
size++;
arr = (int *)realloc(arr, size * sizeof(int));
arr[size - 1] = 20;
size++;
arr = (int *)realloc(arr, size * sizeof(int));
arr[size - 1] = 30;
// printing array elements
printf("Array elements are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// removing last element
size--;
printf("\nAfter removing last element: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
free(arr); // free memory
return 0;
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// dynamic array
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
// adding elements
arr.add(10);
arr.add(20);
arr.add(30);
// printing array elements
System.out.print("Array elements are: ");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
// removing last element
arr.remove(arr.size() - 1);
System.out.print("\nAfter removing last element: ");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
# dynamic array
arr = []
# adding elements
arr.append(10)
arr.append(20)
arr.append(30)
# printing array elements
print("Array elements are:", arr)
# removing last element
arr.pop()
print("After removing last element:", arr)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program {
static void Main()
{
// dynamic array
List<int> arr = new List<int>();
// adding elements
arr.Add(10);
arr.Add(20);
arr.Add(30);
// printing array elements
Console.Write("Array elements are: ");
foreach(int num in arr)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
// removing last element
arr.RemoveAt(arr.Count - 1);
Console.Write("\nAfter removing last element: ");
foreach(int num in arr)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
}
}
OutputArray elements are: 10 20 30
After removing last element: 10 20
Note: In C, there is no built-in dynamic array like in other languages, but you can create one using pointers and malloc/realloc.
On the basis of Dimensions
1. One-dimensional Array :
- A 1-D array is a single row of elements stored in a sequence under one name.
- Each element can be accessed using an index starting from 0.
- It is used to store multiple values of the same type in a linear manner.
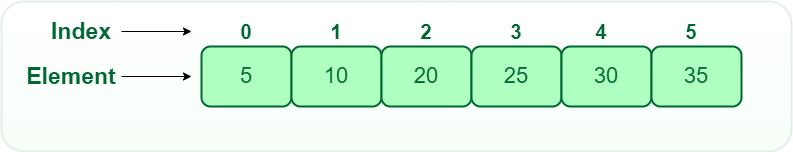 C++
C++
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// printing array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
2. Two-dimensional (2D) array:
- A 2-D array is like a table or grid with rows and columns.
- Each element is accessed using two indices: one for the row and one for the column.
- It is used to store multiple values of the same type in a matrix-like structure.
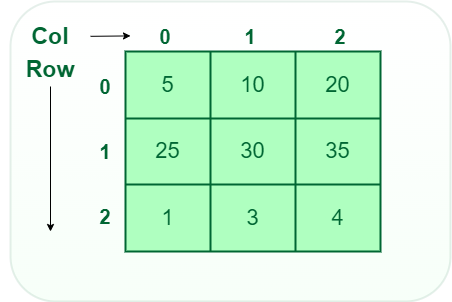 C++
C++
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[2][3] = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}}; // 2 rows and 3 columns
// printing array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. Three-dimensional array:
- A 3-D array is like a stack of 2-D arrays, forming rows, columns, and layers.
- Each element is accessed using three indices: for layer, row, and column.
- It is used to store multiple values of the same type in a 3-dimensional structure.
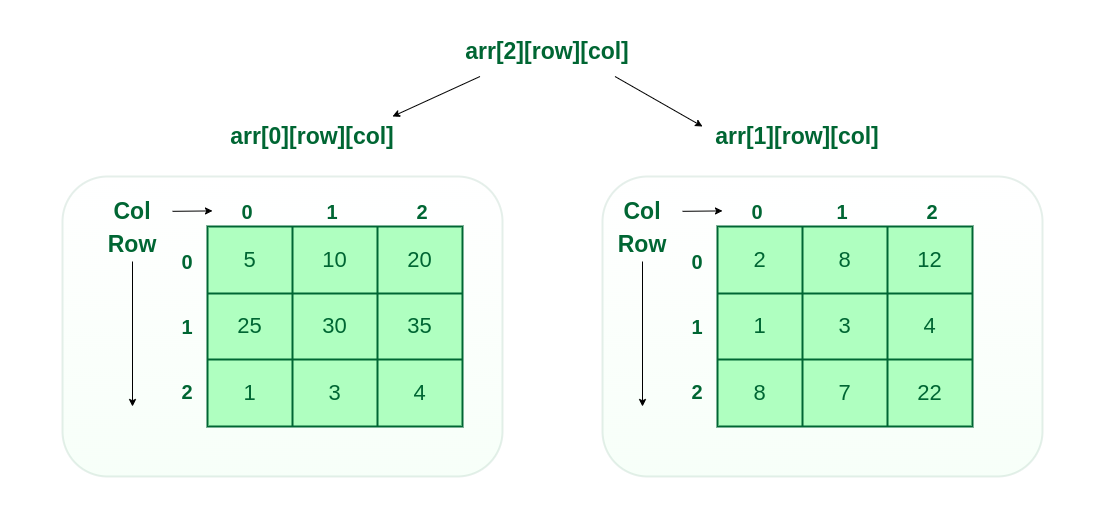 C++
C++
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// 3-D array: 2 layers, 2 rows, 3 columns
int arr[2][2][3] = {{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}}, {{7, 8, 9}, {10, 11, 12}}};
// printing array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
// layer
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
// row
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
// column
printf("%d ", arr[i][j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
10 11 12
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile