In Java, the StringBuilder class is a part of the java.lang package that provides a mutable sequence of characters. Unlike String (which is immutable), StringBuilder allows in-place modifications, making it memory-efficient and faster for frequent string operations.
Declaration:
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Initial String");
Key points of the StringBuilder class:
The key features of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- StringBuilder in Java represents a mutable sequence of characters.
- String Class in Java creates an immutable sequence of characters, whereas StringBuilder creates a mutable sequence of characters, offering an alternative.
- The functionality of StringBuilder is similar to the StringBuffer class, as both provide mutable sequences of characters.
- StringBuilder does not guarantee synchronization, while StringBuffer does. It is a high-performance and low-overhead non thread non-thread-safe alternative to StringBuffer, suitable for single-threaded applications, while StringBuffer is used for synchronization in multithreaded applications.
- StringBuilder is faster than StringBuffer in most implementations.
Example: Demonstration of a StringBuilder class in Java.
Java
// Demonstrating the usage of StringBuilder class
public class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new StringBuilder with the
// initial content "GeeksforGeeks"
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks");
System.out.println("Initial StringBuilder: " + sb);
// Append a string to the StringBuilder
sb.append(" is awesome!");
System.out.println("After append: " + sb);
}
}
OutputInitial StringBuilder: GeeksforGeeks
After append: GeeksforGeeks is awesome!
Explanation:
- In the above code, we first create a StringBuilder with the object sb and put the initial string as "GeeksforGeeks"
- Then we use the append() method from StringBuilder class to add the " is awesome!" string in end of current StringBuilder object.
Syntax of Java StringBuilder Class
The syntax of the StringBuilder class is listed below:
public final class StringBuilder extends Object implements Serializable, CharSequence
StringBuilder Class Hierarchy
java.lang.Object
↳ java.lang
↳ Class StringBuilder
Why Use StringBuilder in Java?
Using the StringBuilder class in Java has many benefits, which are listed below:
- Mutable: Unlike String, which creates a new object every time it's modified, StringBuilder allows you to change the string without creating new objects. This makes it more efficient for repeated modifications.
- Faster than String: StringBuilder doesn't create new objects for every change, it avoids unnecessary memory allocations, which makes it faster than String when performing many string manipulations.
- More Efficient than StringBuffer: In single-threaded environments, StringBuilder is more efficient than StringBuffer because it doesn't have the overhead of thread safety, which makes StringBuilder a better choice when we don't need synchronization.
StringBuilder vs String vs StringBuffer
The table below demonstrates the difference between String, StringBuilder and StringBuffer:
Features | String | StringBuilder | StringBuffer |
|---|
Mutability | String are immutable(creates new objects on modification) | StringBuilder are mutable(modifies in place) | StringBuffer are mutable (modifies in place) |
|---|
Thread-Safe | It is thread-safe | It is not thread-safe | It is thread-safe |
|---|
Performance | It is slow because it creates an object each time | It is faster (no object creation) | it is slower due to synchronization overhead |
|---|
use Case | Fixed, unchanging strings | Single-threaded string manipulation | Multi-threaded string manipulation |
|---|
StringBuilder Constructors
The StringBuilder class provides several constructors, which are listed below:
| Constructor | Description | Example |
|---|
| StringBuilder() | Creates an empty StringBuilder with a default initial capacity of 16. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder(); |
| StringBuilder(int capacity) | Creates a StringBuilder with the specified initial capacity. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder(50); |
| StringBuilder(String str) | Creates a StringBuilder initialized with the contents of the given string. | StringBuilder strbldr = new StringBuilder("Geeks"); |
| StringBuilder(CharSequence cs) | Creates a StringBuilder initialized with the contents of the given CharSequence object. | CharSequence strbldr = "Geeks"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(cs); |
Example: Creating a string using the StringBuilder Constructor StringBuilder(String str).
Java
// Creating a String using StringBuilder constructor
// StringBuilder(String str)
public class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a String using StringBuilder constructor
// StringBuilder(String str)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks");
// Converting StringBuilder to String
String str = sb.toString();
// Printing the String
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Methods of StringBuilder class
The StringBuilder class provides several methods for creating and manipulating strings, which are listed below:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|
| append(String str) | Appends the specified string to the end of the StringBuilder. | sb.append("Geeks"); |
| insert(int offset, String) | Inserts the specified string at the given position in the StringBuilder. | sb.insert(5, " Geeks"); |
| replace(int start, int end, String) | Replaces characters in a substring with the specified string. | sb.replace(6, 11, "Geeks"); |
| delete(int start, int end) | Removes characters in the specified range. | sb.delete(5, 11); |
| reverse() | Reverses the sequence of characters in the StringBuilder. | sb.reverse(); |
| capacity() | Returns the current capacity of the StringBuilder. | int cap = sb.capacity(); |
| length() | Returns the number of characters in the StringBuilder. | int len = sb.length(); |
| charAt(int index) | Returns the character at the specified index. | char ch = sb.charAt(4); |
| setCharAt(int index, char) | Replaces the character at the specified position with a new character. | sb.setCharAt(0, 'G'); |
| substring(int start, int end) | Returns a new String that contains characters from the specified range. | String sub = sb.substring(0, 5); |
| ensureCapacity(int minimum) | Ensures the capacity of the StringBuilder is at least equal to the specified minimum. | sb.ensureCapacity(50); |
| deleteCharAt(int index) | Removes the character at the specified position. | sb.deleteCharAt(3); |
| indexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified string. | int idx = sb.indexOf("Geeks"); |
| lastIndexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified string. | int idx = sb.lastIndexOf("Geeks"); |
| toString() | Converts the StringBuilder object to a String. | String result = sb.toString(); |
Example: Performing different String manipulation operations using StringBuilder methods such as appending, inserting, replacing, deleting, reversing, and accessing characters.
Java
// Demonstrating the usage of multiple StringBuilder methods like
// append(), insert(), replace(), delete(), reverse(),
public class Geeks
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new StringBuilder with the
// initial content "GeeksforGeeks"
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("GeeksforGeeks");
System.out.println("Initial StringBuilder: " + sb);
// 1. Append a string to the StringBuilder
sb.append(" is awesome!");
System.out.println("After append: " + sb);
// 2. Insert a substring at a specific position
sb.insert(13, " Java");
System.out.println("After insert: " + sb);
// 3. Replace a substring with another string
sb.replace(0, 5, "Welcome to");
System.out.println("After replace: " + sb);
// 4. Delete a substring from the StringBuilder
sb.delete(8, 14);
System.out.println("After delete: " + sb);
// 5. Reverse the content of the StringBuilder
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("After reverse: " + sb);
// 6. Get the current capacity of the StringBuilder
int capacity = sb.capacity();
System.out.println("Current capacity: " + capacity);
// 7. Get the length of the StringBuilder
int length = sb.length();
System.out.println("Current length: " + length);
// 8. Access a character at a specific index
char charAt5 = sb.charAt(5);
System.out.println("Character at index 5: " + charAt5);
// 9. Set a character at a specific index
sb.setCharAt(5, 'X');
System.out.println("After setCharAt: " + sb);
// 10. Get a substring from the StringBuilder
String substring = sb.substring(5, 10);
System.out.println("Substring (5 to 10): " + substring);
// 11. Find the index of a specific substring
sb.reverse(); // Reversing back to original order for search
int indexOfGeeks = sb.indexOf("Geeks");
System.out.println("Index of 'Geeks': " + indexOfGeeks);
// 12. Delete a character at a specific index
sb.deleteCharAt(5);
System.out.println("After deleteCharAt: " + sb);
// 13. Convert the StringBuilder to a String
String result = sb.toString();
System.out.println("Final String: " + result);
}
}
Output:
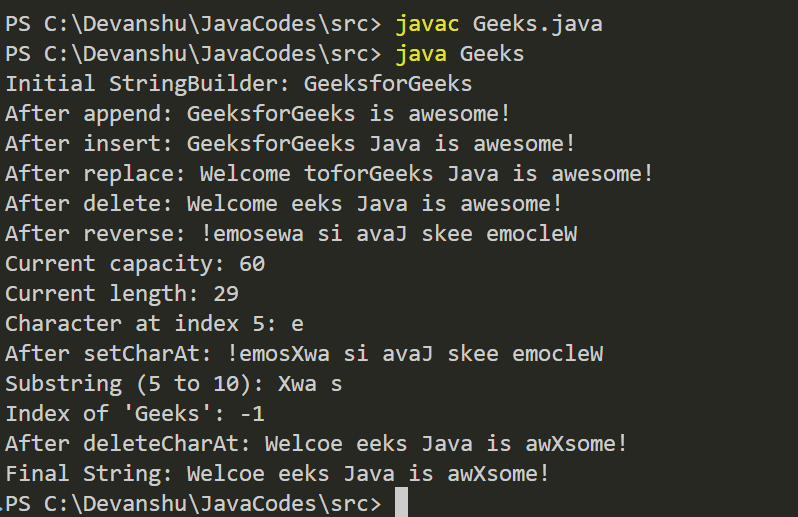
Explanation: In the above program, we use different methods of the StringBuilder class to perform different string manipulation operations such as append(), insert(), reverse(), and delete().
Advantages
The advantages of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- It is more efficient than String when performing multiple string manipulations (like concatenation) since it modifies the string in place.
- It avoids creating new objects on every modification, reducing memory overhead.
- Unlike String, StringBuilder allows the modification of strings without creating new instances.
- It dynamically adjusts its capacity as needed, minimizing the need for resizing.
- Great for scenarios where strings are modified repeatedly inside loops.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the StringBuilder class are listed below:
- It is not synchronized, making it unsuitable for use in multi-threaded environments.
- If not used properly, StringBuilder may allocate excess memory, especially if the initial capacity is set too large.
- For multi-threaded scenarios, you must handle synchronization manually, unlike StringBuffer.
Similar Reads
Basics of Java
Learn Java - A Beginners Guide for 2024If you are new to the world of coding and want to start your coding journey with Java, then this learn Java a beginners guide gives you a complete overview of how to start Java programming. Java is among the most popular and widely used programming languages and platforms. A platform is an environme
10 min read
Introduction to JavaJava is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995. It is platform-independent, which means we can write code once and run it anywhere using the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Java is mostly used for building desktop applications, web applications, Android
4 min read
Similarities and Difference between Java and C++Nowadays Java and C++ programming languages are vastly used in competitive coding. Due to some awesome features, these two programming languages are widely used in industries as well as competitive programming. C++ is a widely popular language among coders for its efficiency, high speed, and dynamic
6 min read
Setting up Environment Variables For Java - Complete Guide to Set JAVA_HOMEIn the journey to learning the Java programming language, setting up environment variables for Java is essential because it helps the system locate the Java tools needed to run the Java programs. Now, this guide on how to setting up environment variables for Java is a one-place solution for Mac, Win
6 min read
Java SyntaxJava is an object-oriented programming language that is known for its simplicity, portability, and robustness. The syntax of Java programming language is very closely aligned with C and C++, which makes it easier to understand. Java Syntax refers to a set of rules that define how Java programs are w
6 min read
Java Hello World ProgramJava is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages and platforms. In this article, we will learn how to write a simple Java Program. This article will guide you on how to write, compile, and run your first Java program. With the help of Java, we can develop web and mobile applicat
6 min read
Differences Between JDK, JRE and JVMUnderstanding the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM plays a very important role in understanding how Java works and how each component contributes to the development and execution of Java applications. The main difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM is:JDK: Java Development Kit is a software develo
3 min read
How JVM Works - JVM ArchitectureJVM (Java Virtual Machine) runs Java applications as a run-time engine. JVM is the one that calls the main method present in a Java code. JVM is a part of JRE (Java Runtime Environment). Java applications are called WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere). This means a programmer can develop Java code on one
7 min read
Java IdentifiersAn identifier in Java is the name given to Variables, Classes, Methods, Packages, Interfaces, etc. These are the unique names used to identify programming elements. Every Java Variable must be identified with a unique name.Example:public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 2
2 min read
Variables & DataTypes in Java
Java VariablesIn Java, variables are containers that store data in memory. Understanding variables plays a very important role as it defines how data is stored, accessed, and manipulated.Key Components of Variables in Java:A variable in Java has three components, which are listed below:Data Type: Defines the kind
9 min read
Scope of Variables in JavaThe scope of variables is the part of the program where the variable is accessible. Like C/C++, in Java, all identifiers are lexically (or statically) scoped, i.e., scope of a variable can be determined at compile time and independent of the function call stack. In this article, we will learn about
7 min read
Java Data TypesJava is statically typed and also a strongly typed language because each type of data, such as integer, character, hexadecimal, packed decimal etc. is predefined as part of the programming language, and all constants or variables defined for a given program must be declared with the specific data ty
14 min read
Operators in Java
Java OperatorsJava operators are special symbols that perform operations on variables or values. These operators are essential in programming as they allow you to manipulate data efficiently. They can be classified into different categories based on their functionality. In this article, we will explore different
15 min read
Java Arithmetic Operators with ExamplesOperators constitute the basic building block to any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they
6 min read
Java Assignment Operators with ExamplesOperators constitute the basic building block of any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they
7 min read
Java Unary Operator with ExamplesOperators constitute the basic building block to any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they p
8 min read
Java Relational Operators with ExamplesOperators constitute the basic building block to any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they
10 min read
Java Logical Operators with ExamplesLogical operators are used to perform logical "AND", "OR", and "NOT" operations, i.e., the functions similar to AND gate and OR gate in digital electronics. They are used to combine two or more conditions/constraints or to complement the evaluation of the original condition under particular consider
8 min read
Java Ternary OperatorOperators constitute the basic building block of any programming language. Java provides many types of operators that can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provi
5 min read
Bitwise Operators in JavaIn Java, Operators are special symbols that perform specific operations on one or more than one operands. They build the foundation for any type of calculation or logic in programming.There are so many operators in Java, among all, bitwise operators are used to perform operations at the bit level. T
6 min read
Packages in Java
Flow Control in Java
Loops in Java
Jump Statements in Java
Arrays in Java
Arrays in JavaArrays in Java are one of the most fundamental data structures that allow us to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. They are useful for storing and managing collections of data. Arrays in Java are objects, which makes them work differently from arrays in C/C++ in terms of me
15+ min read
Java Multi-Dimensional ArraysMultidimensional arrays are used to store the data in rows and columns, where each row can represent another individual array are multidimensional array. It is also known as array of arrays. The multidimensional array has more than one dimension, where each row is stored in the heap independently. T
10 min read
Jagged Array in JavaIn Java, a Jagged array is an array that holds other arrays. When we work with a jagged array, one thing to keep in mind is that the inner array can be of different lengths. It is like a 2D array, but each row can have a different number of elements.Example:arr [][]= { {10,20}, {30,40,50,60},{70,80,
6 min read
Strings in Java
Java StringsIn Java, a String is the type of object that can store a sequence of characters enclosed by double quotes, and every character is stored in 16 bits, i.e., using UTF 16-bit encoding. A string acts the same as an array of characters. Java provides a robust and flexible API for handling strings, allowi
9 min read
String Class in JavaA string is a sequence of characters. In Java, objects of the String class are immutable, which means they cannot be changed once created. In this article, we are going to learn about the String class in Java.Example of String Class in Java:Java// Java Program to Create a String import java.io.*; cl
7 min read
StringBuffer Class in JavaThe StringBuffer class in Java represents a sequence of characters that can be modified, which means we can change the content of the StringBuffer without creating a new object every time. It represents a mutable sequence of characters.Features of StringBuffer ClassThe key features of StringBuffer c
11 min read
Java StringBuilder ClassIn Java, the StringBuilder class is a part of the java.lang package that provides a mutable sequence of characters. Unlike String (which is immutable), StringBuilder allows in-place modifications, making it memory-efficient and faster for frequent string operations.Declaration:StringBuilder sb = new
7 min read
OOPS in Java
Java OOP(Object Oriented Programming) ConceptsJava Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) is a fundamental concept in Java that every developer must understand. It allows developers to structure code using classes and objects, making it more modular, reusable, and scalable.The core idea of OOPs is to bind data and the functions that operate on it,
13 min read
Classes and Objects in JavaIn Java, classes and objects are basic concepts of Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) that are used to represent real-world concepts and entities. The class represents a group of objects having similar properties and behavior, or in other words, we can say that a class is a blueprint for objects, wh
11 min read
Java MethodsJava Methods are blocks of code that perform a specific task. A method allows us to reuse code, improving both efficiency and organization. All methods in Java must belong to a class. Methods are similar to functions and expose the behavior of objects.Example: Java program to demonstrate how to crea
8 min read
Access Modifiers in JavaIn Java, access modifiers are essential tools that define how the members of a class, like variables, methods, and even the class itself can be accessed from other parts of our program. They are an important part of building secure and modular code when designing large applications. Understanding de
7 min read
Wrapper Classes in JavaA Wrapper class in Java is one whose object wraps or contains primitive data types. When we create an object in a wrapper class, it contains a field, and in this field, we can store primitive data types. In other words, we can wrap a primitive value into a wrapper class object. Let's check on the wr
6 min read
Need of Wrapper Classes in JavaFirstly the question that hits the programmers is when we have primitive data types then why does there arise a need for the concept of wrapper classes in java. It is because of the additional features being there in the Wrapper class over the primitive data types when it comes to usage. These metho
3 min read