Multithreading in OS - Different Models
Last Updated :
29 Aug, 2025
Multithreading is a technique where a process is divided into smaller execution units called threads that run concurrently.
- A thread is also called a lightweight process. Concurrency or Parallelism within a process is achieved by dividing a process into multiple threads.
- Multithreading improves system performance and responsiveness by allowing multiple threads to share CPU, memory and I/O resources of a single process.
- Example: In a browser, each tab can be a thread. In MS Word, one thread formats text while another processes inputs.
How are User Threads Mapped with Kernel Threads?
Multithreading model are of three types.
- Many to many model.
- Many to one model.
- One to one model.
Many to Many Model
In this model, we have multiple user threads multiplex to same or lesser number of kernel level threads. Number of kernel level threads are specific to the machine, advantage of this model is if a user thread is blocked we can schedule others user thread to other kernel thread. Thus, System doesn't block if a particular thread is blocked.
It is the best multi threading model.
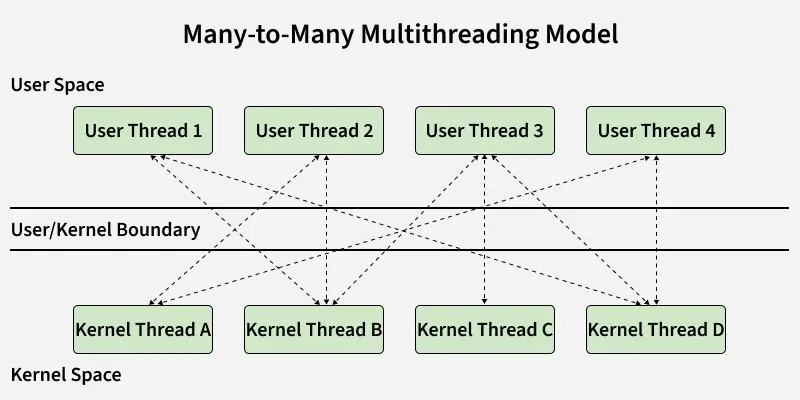 Many-to-Many Multithreading Model
Many-to-Many Multithreading Model Many to One Model
In this model, we have multiple user threads mapped to one kernel thread. In this model when a user thread makes a blocking system call entire process blocks. As we have only one kernel thread and only one user thread can access kernel at a time, so multiple threads are not able access multiprocessor at the same time.
The thread management is done on the user level so it is more efficient.
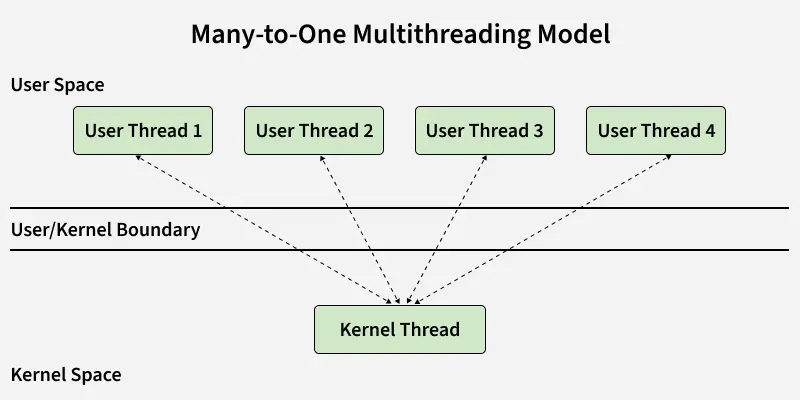 Many-to-Many Multithreading Model
Many-to-Many Multithreading Model One to One Model
In this model, one to one relationship between kernel and user thread. In this model multiple thread can run on multiple processor. Problem with this model is that creating a user thread requires the corresponding kernel thread.
As each user thread is connected to different kernel , if any user thread makes a blocking system call, the other user threads won't be blocked.
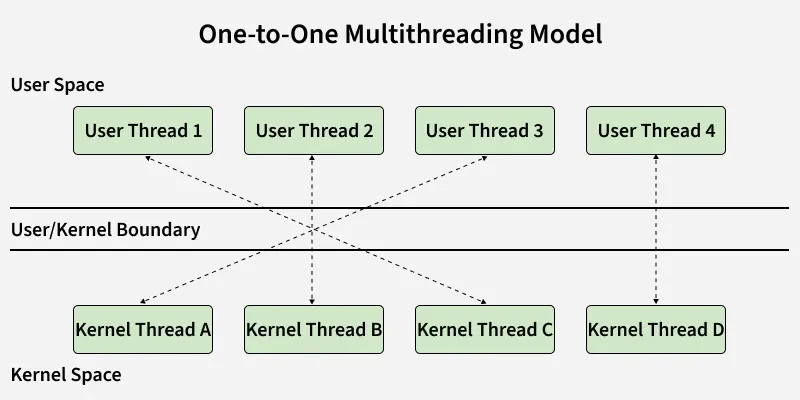 One-to-One Multithreading Model
One-to-One Multithreading Model Which of the above Model is used in Practice?
One to one This model is usually preferred because:
- True Parallelism: Since each user thread is backed by a kernel thread, the operating system can schedule them on multiple CPUs/cores at the same time. This means multiple threads from the same process can actually run in parallel, unlike the many-to-one model (where all user threads run on a single kernel thread).
- Blocking System Calls Don’t Stop Others: In the many-to-one model, if one user thread makes a blocking system call (like waiting for I/O), the whole process is stuck. In the one-to-one model, only that thread blocks; other threads of the same process keep running.
- Better Utilization of Multiprocessor Systems: Modern systems are multicore. One-to-one allows full usage of available cores, which improves performance.
- OS Support and Management: The operating system manages kernel threads directly, so scheduling, context switching, and resource allocation are efficient and handled at the kernel level.
Is Multithreading Possible Without OS Support?
- Multithreading can be done without OS support, as seen in Java’s model.
- Threads are managed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), not the OS.
- The application manages thread creation, scheduling, and context switching using a thread library.
- The OS is unaware of these threads and treats the process as single-threaded.
Applications
1. Transaction Processing
- Widely used in banking, online payments, and mobile recharges.
- Multiple transactions can be processed simultaneously without delays.
2. Web and Internet Applications
- Threads handle multiple client requests at the same time (e.g., web servers, chat servers).
- Improves responsiveness and efficiency of online platforms.
3. Banking & Financial Systems
- Online fund transfers, balance updates, and background verification tasks run in parallel.
- Prevents bottlenecks during high traffic (e.g., during salary credits or sales).
- Multiple recharge or service requests are processed concurrently.
- Ensures quick response and smooth functioning for millions of users.
Explore
OS Basics
Process Management
Memory Management
I/O Management
Important Links