A relation in Mathematics is defined as the relationship between two sets. If we are given two sets, set A and set B, and set A has a relation with set B, then each value of set A is related to a value of set B through some unique relation. Here, set A is called the domain of the relation, and set B is called the range of the relation.
Example of a Relation
Suppose there are two sets X = {4, 36, 49, 50} and Y = {1, -2, -6, -7, 7, 6, 2}. A relation R states that
"(x, y) is in the relation R if x is a square of y" can be represented using ordered pairs,
- R = {(4, -2), (4, 2), (36, -6), (36, 6), (49, -7), (49, 7)}
Also, the image added below shows two sets, A and B, and the relation between them.
- Set A = {x, y, z}
- Set B = {1, 2, 3}

Representation of Relations
In mathematics or set theory we can represent the relation using different techniques, and the two important ways to represent the set are,
Set Builder Notation
If a relation between two sets is represented using the logical formula, then this type of representation is called the set builder notation.
For example, if we are given two sets, set X = {2, 4, 6} and set Y = {4, 8, 12}. Then, on observing clearly, we can see that each element of set Y is twice each element of set X the relation between them is,
R {(a, b): b is twice of a, a ∈ X, b ∈ Y}
Roaster form is another way of representing a relation. In roaster form, we use ordered pairs to represent the relation.
For example, if we are given two sets, set X = {2, 4, 6} and set Y = {4, 8, 12}. Then the relation between set X and set Y is represented using the relation R such that,
R = {(2, 4), (4, 8), (6, 12)}
Types of Relation
Graphing Relations
Relations can be easily represented on the graphs, and representing them on graphs is an easy way of explaining them. The ordered pair in a relation represents a coordinate that can be plotted on the Cartesian coordinate system. We can easily graph the relation by following the steps added below.
- Substitute x with random numerical values in the relation.
- Find the corresponding y value of the respective x value.
- Write the ordered pair such that, {(x, y)}
- Plot these points and join them to find the required curve.
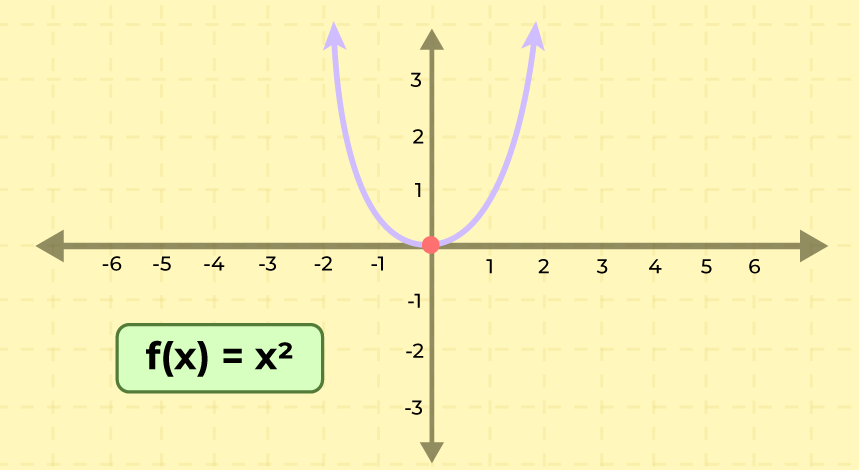
The graph of the relation y = x2 is added below,
Importance in Computer Science
Relations are widely used in computer science, often without explicitly calling them “relations.” Some key applications include:
Databases (Relational Model)
- The term relational database comes directly from the mathematical concept of a relation.
- A database table is a set of tuples — exactly what a relation is in set theory.
Graphs and Networks
- A graph can be seen as a relation between vertices.
- In an undirected graph, the relation is symmetric.
- In a directed graph, the relation is not necessarily symmetric.
State Machines
- In automata theory, the transition function is a relation between states and inputs to next states.
Other Applications
- Data Structures: Adjacency matrices and adjacency lists in graphs are ways to store relations between nodes.
- Information Retrieval: Search engines model the relation between documents and keywords.
Solved Examples of Relations
Question 1: Find the inverse relation of R = {(1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Solution:
Inverse relation is defined as R-1 = {(y, x): (x, y) ∈ R}
Given,
R = {(1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Inverse relation of R is R-1 then,
R-1 = {(3, 1), (4, 2), (5, 3)}
Question 2: Find the inverse relation of R = {(a, x), (b, y), (c, z)}
Solution:
Inverse relation is defined as R-1 = {(y, x): (x, y) ∈ R}
Given,
R = {(a, x), (b, y), (c, z)}
Inverse relation of R is R-1 then,
R-1 = {(x, a), (y, b), (z, c)}
Question 3: Is the relation R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3, 2)} on set A = {1, 2, 3} an equivalence relation?
Solution:
No, it's not an equivalence relation. It's reflexive and symmetric, but not transitive.
Question 4: Find the domain and range of the relation R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5)}.
Solution:
Domain = {1, 2, 3, 4}, Range = {2, 3, 4, 5}
Question 5: Is the relation R = {(x, y) | x² + y² = 25} on the set of real numbers a function?
Solution:
No, it's not a function. For example, (0, 5) and (0, -5) are both in the relation.
Question 6: Find the inverse of the relation R = {(1,1), (2,4), (3,9), (4,16)}.
Solution:
R⁻¹ = {(1, 1), (4, 2), (9, 3), (16, 4)}
Question 7: Determine if the relation R = {(x, y) | x - y is even} on the set of integers is an equivalence relation.
Solution:
Yes, it's an equivalence relation. It's reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Question 8: Find the composition R ∘ S for R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)} and S = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4)}.
Solution:
R ∘ S = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)}
Question 9: Is the relation R = {(a, b) | a is a multiple of b} on the set of positive integers transitive?
Solution:
Yes, it's transitive.
Question 10: Find the reflexive closure of R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1)} on set A = {1, 2, 3}.
Solution:
Reflexive closure = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1)}
Unsolved Examples of Relations
Question 1: Find the inverse relation of R = {(2, 5), (3, 6), (4, 7)}.
Question 2: Find the inverse relation of R = {(p, q), (r, s), (t, u)}.
Question 3: Determine whether the relation R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3)} on the set A = {1, 2, 3} is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Question 4: Find the domain and range of R = {(2, 4), (3, 9), (4, 16), (5, 25)}.
Question 5: Find the inverse of the relation R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5)}.
Question 7: Check whether the relation R = {(x, y)∣x + y is even} on the set of integers is an equivalence relation.
Question 9: Determine whether the relation R = {(a, b)∣a divides b} on the set of positive integers is transitive.
Question 6: Find the inverse of the relation R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5)}.
Question 8: Find the composition of relations R∘S, where R = {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1)} and S = {(1, 3), (2, 1), (3, 2)}.
Question 10: Find the reflexive closure of R = {(a, b), (b, c)} on the set A={a, b, c}.
Related Articles
Explore
Basic Arithmetic
Algebra
Geometry
Trigonometry & Vector Algebra
Calculus
Probability and Statistics
Practice
My Profile