Julia is a high-level open-source programming language developed by a group of four at MIT. Julia is a dynamic, high-performance programming language used to perform scientific computing operations. Like the R programming language, Julia is used for statistical computing and data analysis. Julia was developed primarily for the speed of programming. It runs much faster than Python or R. analysis.
Before learning how to program in Julia, let's see where to download the necessary software and programs. Julia can be downloaded from the official website, see how to install Julia on Windows and Linux. Must be installed.
Finally, you'll need a text editor to write your code. Feel free to use a text editor like VS Code, Sublime Text or Notepad++.
Hello World Program
Hello World is the simplest program used to demonstrate the basic syntax of a programming language. Julia offers several ways to write and run code:
Interactive sessions with Julia:
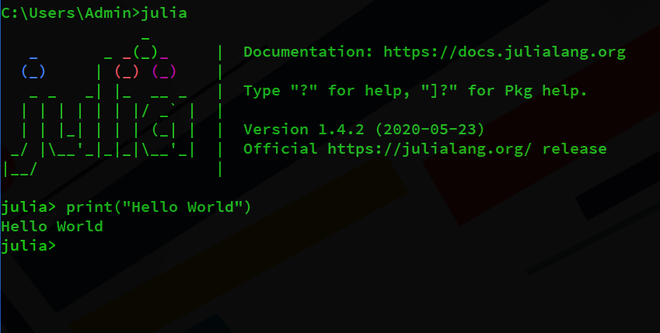
The easiest way to get started with Julia is through an interactive session (aka Read-Eval-Print -loop or "REPL "). ") Double-click the Julia executable or run Julia from the command line:
I want to print a string, so I need to enclose it in double quotes.
Julia
Output:
"Hello World"

You can also use the print() function. The print function is used to print data to the output screen. Just pass the string "Hello World" as an argument to the print() function.
Julia
The difference between writing "Hello World" directly and using the print function is that writing "Hello World" directly prints the quotes (" ") along with the text, but the print function only prints the text.
Output:
Hello World
Creating a helloworld.jl File:
In order for Julia to print Hello World as output, you need to create a file named helloworld.jl. Then you can use the print function above to print Hello World as output. All we need to do is pass the string "Hello World" as an argument to the print function.
Julia
Then run the file from a command prompt or terminal with the following command:
julia helloworld.jl.
Output:
Hello World

You can also use the println() function to print Hello World as output. The only difference is that the output ends on a new line after being printed to the screen.
Julia
Output:
Hello World

Similar Reads
else keyword in Julia Keywords in Julia are reserved words that have a specific meaning and operation to the compiler. These keywords can not be used as a variable name, doing the same will stop the execution process and an error will be raised. 'else' keyword in Julia is used to execute a block of code when the 'if' con
2 min read
For loop in Julia For loops are used to iterate over a set of values and perform a set of operations that are given in the body of the loop. For loops are used for sequential traversal. In Julia, there is no C style for loop, i.e., for (i = 0; i Syntax: for iterator in range statements(s) end Here, 'for' is the keywo
2 min read
Vectors in Julia Vectors in Julia are a collection of elements just like other collections like Array, Sets, Dictionaries, etc. Vector are different from Sets because vectors are ordered collections of elements, and can hold duplicate values, unlike sets which require all the elements to be unique. Vectors are one-d
5 min read
Variables in Julia Variables are some names given to the memory location to which they are assigned. These memory locations are used to store values that can be accessed by using the name of the location, i.e. Variable. Unlike C and Java, variables in Julia need not to be written with a Datatype. Julia auto-assigns th
4 min read
Regular Expressions in Julia Julia has Perl-compatible regular expressions (regexes), as provided by the PCRE library. Regular expressions can be used to find regular patterns in strings and in Julia regular expressions are themselves input as strings which are parsed into a state machine that can be used to efficiently search
3 min read