Given an n × m grid[][] consisting of 'L' (land) and 'W' (water), we need to count the total number of islands present in the grid without modifying the original grid.
An island is defined as a group of connected 'L' cells that are adjacent horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, and surrounded by water or the boundary of the grid.
Examples:
Input: grid[][] = [['L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']]
Output: 4
Explanation: The image below shows all the 4 islands.

Input: grid[][] = [['W', 'L', 'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W', 'L', 'W']]
Output: 2
Explanation: The image below shows all the 2 islands in the graph
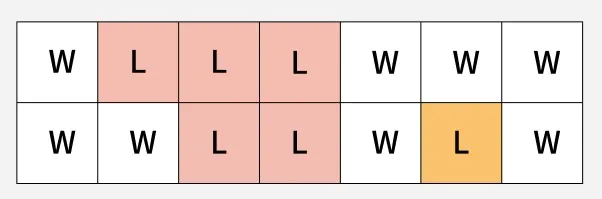 Two islands in the matrix
Two islands in the matrix
[Approach 1] Using DFS and Additional Matrix - O(n*m) Time and O(n*m) Space
The main idea is to explore each land cell ('L') using DFS and mark all connected land cells that belong to the same island. To avoid modifying the original grid, we maintain a separate visited matrix that keeps track of which cells have already been explored. The DFS explores all 8 possible directions (up, down, left, right, and 4 diagonals), marking every connected 'L' cell as visited. This ensures that all parts of the current island are counted once.
Each time we encounter an unvisited land cell, it represents the start of a new island, and we perform DFS to mark all cells of that island. By the end, the total count represents the number of distinct islands in the grid.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// Checks if the given cell (r, c) can be visited
bool isSafe(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int r, int c, vector<vector<bool>> &visited)
{
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
// Cell is within bounds, contains land ('L'), and is not yet visited
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Performs DFS to mark all connected land cells
void dfs(vector<vector<char>> &grid, int r, int c, vector<vector<bool>> &visited)
{
// Mark current cell as visited
visited[r][c] = true;
// All 8 possible directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
vector<int> dr = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
vector<int> dc = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
// Explore all connected neighbours
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int nr = r + dr[k];
int nc = c + dc[k];
if (isSafe(grid, nr, nc, visited))
dfs(grid, nr, nc, visited);
}
}
// finding number of distinct islands in the grid
int countIslands(vector<vector<char>> &grid)
{
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
// Matrix to track visited cells
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int islands = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// Start a new DFS when an unvisited land cell is found
if (grid[i][j] == 'L' && !visited[i][j])
{
dfs(grid, i, j, visited);
islands++;
}
}
}
return islands;
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main()
{
vector<vector<char>> grid = {
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
{'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}};
// printing the number of islands
cout << countIslands(grid) << endl;
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
//Driver Code Ends
// Checks if the given cell (r, c) can be visited
static boolean isSafe(char[][] grid, int r, int c, boolean[][] visited) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// Cell is within bounds, contains land ('L'), and is not yet visited
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Performs DFS to mark all connected land cells
static void dfs(char[][] grid, int r, int c, boolean[][] visited) {
// Mark current cell as visited
visited[r][c] = true;
// All 8 possible directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
int[] dr = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int[] dc = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
// Explore all connected neighbours
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int nr = r + dr[k];
int nc = c + dc[k];
if (isSafe(grid, nr, nc, visited))
dfs(grid, nr, nc, visited);
}
}
// finding number of distinct islands in the grid
static int countIslands(char[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// Matrix to track visited cells
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int islands = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// Start a new DFS when an unvisited land cell is found
if (grid[i][j] == 'L' && !visited[i][j]) {
dfs(grid, i, j, visited);
islands++;
}
}
}
return islands;
}
//Driver Code Starts
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] grid = {
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
{'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
// printing the number of islands
System.out.println(countIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
# Checks if the given cell (r, c) can be visited
def isSafe(grid, r, c, visited):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
# Cell is within bounds, contains land ('L'), and is not yet visited
return (0 <= r < n and 0 <= c < m and grid[r][c] == 'L' and not visited[r][c])
# Performs DFS to mark all connected land cells
def dfs(grid, r, c, visited):
# Mark current cell as visited
visited[r][c] = True
# All 8 possible directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
dr = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]
dc = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1]
# Explore all connected neighbours
for k in range(8):
nr = r + dr[k]
nc = c + dc[k]
if isSafe(grid, nr, nc, visited):
dfs(grid, nr, nc, visited)
# finding number of distinct islands in the grid
def countIslands(grid):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
# Matrix to track visited cells
visited = [[False for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)]
islands = 0
# Traverse every cell in the grid
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
# Start a new DFS when an unvisited land cell is found
if grid[i][j] == 'L' and not visited[i][j]:
dfs(grid, i, j, visited)
islands += 1
return islands
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid = [
['L', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']
]
# printing the number of islands
print(countIslands(grid))
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
//Driver Code Ends
// Checks if the given cell (r, c) can be visited
static bool IsSafe(char[][] grid, int r, int c, bool[][] visited)
{
int n = grid.Length;
int m = grid[0].Length;
// Cell is within bounds, contains land ('L'), and is not yet visited
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Performs DFS to mark all connected land cells
static void Dfs(char[][] grid, int r, int c, bool[][] visited)
{
// Mark current cell as visited
visited[r][c] = true;
// All 8 possible directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
int[] dr = { -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 };
int[] dc = { -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1 };
// Explore all connected neighbours
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int nr = r + dr[k];
int nc = c + dc[k];
if (IsSafe(grid, nr, nc, visited))
Dfs(grid, nr, nc, visited);
}
}
// finding number of distinct islands in the grid
static int CountIslands(char[][] grid)
{
int n = grid.Length;
int m = grid[0].Length;
// Matrix to track visited cells
bool[][] visited = new bool[n][];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
visited[i] = new bool[m];
int islands = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// Start a new DFS when an unvisited land cell is found
if (grid[i][j] == 'L' && !visited[i][j])
{
Dfs(grid, i, j, visited);
islands++;
}
}
}
return islands;
}
//Driver Code Starts
static void Main()
{
char[][] grid = new char[][]
{
new char[] {'L', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
new char[] {'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
new char[] {'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
new char[] {'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
new char[] {'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
// printing the number of islands
Console.WriteLine(CountIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
// Checks if the given cell (r, c) can be visited
function isSafe(grid, r, c, visited) {
const n = grid.length;
const m = grid[0].length;
// Cell is within bounds, contains land ('L'), and is not yet visited
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] === 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Performs DFS to mark all connected land cells
function dfs(grid, r, c, visited) {
// Mark current cell as visited
visited[r][c] = true;
// All 8 possible directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal)
const dr = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1];
const dc = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1];
// Explore all connected neighbours
for (let k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
const nr = r + dr[k];
const nc = c + dc[k];
if (isSafe(grid, nr, nc, visited))
dfs(grid, nr, nc, visited);
}
}
// finding number of distinct islands in the grid
function countIslands(grid) {
const n = grid.length;
const m = grid[0].length;
// Matrix to track visited cells
const visited = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(false));
let islands = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// Start a new DFS when an unvisited land cell is found
if (grid[i][j] === 'L' && !visited[i][j]) {
dfs(grid, i, j, visited);
islands++;
}
}
}
return islands;
}
//Driver Code Starts
const grid = [
['L', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']
];
// printing the number of islands
console.log(countIslands(grid));
//Driver Code Ends
[Approach 2] Using Breadth First Search - O(n*m) time and O(n*m) space
The idea is to use Breadth First Search (BFS) to explore all connected land cells for each island. We traverse the entire grid, and whenever we encounter an unvisited land cell ('L'), we perform a BFS starting from that cell to explore its entire connected component. During BFS, we visit all cells connected horizontally, vertically, or diagonally to the current land cell.
To ensure we don’t revisit the same cell multiple times, we maintain a separate boolean matrix to mark visited cells instead of modifying the original grid. Each BFS traversal explores one complete island, after which we increment the island counter. Repeating this for all cells ensures that every island is counted exactly once, and the final counter gives the total number of islands in the grid.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// Check if the cell (r, c) is valid for BFS traversal
// It must lie within grid bounds, contain land ('L'), and not be visited yet
bool isSafe(vector<vector<char>>& grid, int r, int c, vector<vector<bool>>& visited) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Perform BFS to traverse all connected land cells (forming one island)
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int startR, int startC) {
// Possible 8 directions (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal)
vector<int> dRow = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
vector<int> dCol = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({startR, startC});
visited[startR][startC] = true;
// Explore all reachable land cells for this island
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [r, c] = q.front();
q.pop();
// Check all 8 neighbors of the current cell
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int newR = r + dRow[k];
int newC = c + dCol[k];
if (isSafe(grid, newR, newC, visited)) {
visited[newR][newC] = true;
q.push({newR, newC});
}
}
}
}
// Count the total number of islands in the grid
int countIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int islandCount = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
// If an unvisited land cell is found, start BFS for that island
if (grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]) {
bfs(grid, visited, r, c);
islandCount++;
}
}
}
return islandCount;
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main() {
vector<vector<char>> grid = {
{'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
{'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
cout << countIslands(grid) << endl;
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
//Driver Code Ends
// Check if the cell (r, c) is valid for BFS traversal
// It must lie within grid bounds, contain land ('L'), and not be visited yet
static boolean isSafe(char[][] grid, int r, int c, boolean[][] visited) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Perform BFS to traverse all connected land cells (forming one island)
static void bfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int startR, int startC) {
// Possible 8 directions (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal)
int[] dRow = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int[] dCol = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new int[]{startR, startC});
visited[startR][startC] = true;
// Explore all reachable land cells for this island
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = q.poll();
int r = cell[0];
int c = cell[1];
// Check all 8 neighbors of the current cell
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int newR = r + dRow[k];
int newC = c + dCol[k];
if (isSafe(grid, newR, newC, visited)) {
visited[newR][newC] = true;
q.add(new int[]{newR, newC});
}
}
}
}
// Count the total number of islands in the grid
static int countIslands(char[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int islandCount = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
// If an unvisited land cell is found, start BFS for that island
if (grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]) {
bfs(grid, visited, r, c);
islandCount++;
}
}
}
return islandCount;
}
//Driver Code Starts
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[][] grid = {
{'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
{'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
System.out.println(countIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
#Driver Code Starts
from collections import deque
#Driver Code Ends
# Check if the cell (r, c) is valid for BFS traversal
# It must lie within grid bounds, contain land ('L'), and not be visited yet
def isSafe(grid, r, c, visited):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
return (0 <= r < n and 0 <= c < m and grid[r][c] == 'L' and not visited[r][c])
# Perform BFS to traverse all connected land cells (forming one island)
def bfs(grid, visited, startR, startC):
# Possible 8 directions (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal)
dRow = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]
dCol = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1]
q = deque()
q.append((startR, startC))
visited[startR][startC] = True
# Explore all reachable land cells for this island
while q:
r, c = q.popleft()
# Check all 8 neighbors of the current cell
for k in range(8):
newR = r + dRow[k]
newC = c + dCol[k]
if isSafe(grid, newR, newC, visited):
visited[newR][newC] = True
q.append((newR, newC))
# Count the total number of islands in the grid
def countIslands(grid):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
islandCount = 0
# Traverse every cell in the grid
for r in range(n):
for c in range(m):
# If an unvisited land cell is found, start BFS for that island
if grid[r][c] == 'L' and not visited[r][c]:
bfs(grid, visited, r, c)
islandCount += 1
return islandCount
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid = [
['L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']
]
print(countIslands(grid))
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
//Driver Code Ends
// Check if the cell (r, c) is valid for BFS traversal
// It must lie within grid bounds, contain land ('L'), and not be visited yet
static bool IsSafe(char[][] grid, int r, int c, bool[][] visited)
{
int n = grid.Length;
int m = grid[0].Length;
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Perform BFS to traverse all connected land cells (forming one island)
static void Bfs(char[][] grid, bool[][] visited, int startR, int startC)
{
// Possible 8 directions (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal)
int[] dRow = { -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 };
int[] dCol = { -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1 };
Queue<(int, int)> q = new Queue<(int, int)>();
q.Enqueue((startR, startC));
visited[startR][startC] = true;
// Explore all reachable land cells for this island
while (q.Count > 0)
{
var (r, c) = q.Dequeue();
// Check all 8 neighbors of the current cell
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int newR = r + dRow[k];
int newC = c + dCol[k];
if (IsSafe(grid, newR, newC, visited))
{
visited[newR][newC] = true;
q.Enqueue((newR, newC));
}
}
}
}
// Count the total number of islands in the grid
static int CountIslands(char[][] grid)
{
int n = grid.Length;
int m = grid[0].Length;
bool[][] visited = new bool[n][];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
visited[i] = new bool[m];
int islandCount = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++)
{
// If an unvisited land cell is found, start BFS for that island
if (grid[r][c] == 'L' && !visited[r][c])
{
Bfs(grid, visited, r, c);
islandCount++;
}
}
}
return islandCount;
}
//Driver Code Starts
static void Main()
{
char[][] grid = new char[][]
{
new char[] {'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
new char[] {'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
new char[] {'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
new char[] {'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
new char[] {'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
Console.WriteLine(CountIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
// Check if the cell (r, c) is valid for BFS traversal
// It must lie within grid bounds, contain land ('L'), and not be visited yet
function isSafe(grid, r, c, visited) {
const n = grid.length;
const m = grid[0].length;
return (r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m && grid[r][c] === 'L' && !visited[r][c]);
}
// Perform BFS to traverse all connected land cells (forming one island)
function bfs(grid, visited, startR, startC) {
// Possible 8 directions (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal)
const dRow = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1];
const dCol = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1];
const q = [];
q.push([startR, startC]);
visited[startR][startC] = true;
// Explore all reachable land cells for this island
while (q.length > 0) {
const [r, c] = q.shift();
// Check all 8 neighbors of the current cell
for (let k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
const newR = r + dRow[k];
const newC = c + dCol[k];
if (isSafe(grid, newR, newC, visited)) {
visited[newR][newC] = true;
q.push([newR, newC]);
}
}
}
}
// Count the total number of islands in the grid
function countIslands(grid) {
const n = grid.length;
const m = grid[0].length;
const visited = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(false));
let islandCount = 0;
// Traverse every cell in the grid
for (let r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < m; c++) {
// If an unvisited land cell is found, start BFS for that island
if (grid[r][c] === 'L' && !visited[r][c]) {
bfs(grid, visited, r, c);
islandCount++;
}
}
}
return islandCount;
}
//Driver Code Starts
const grid = [
['L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']
];
console.log(countIslands(grid));
//Driver Code Ends
[Approach 3] Using Disjoint Set - O(n*m) time and O(n*m) space
The idea is to model the grid as a graph where each land cell acts as a node. Using the Disjoint Set (Union-Find) structure, we initially treat every land cell as its own parent.
Then, for each land cell, we check all eight neighboring directions — if a neighbor is also land, we perform a union operation to merge their sets.
After all unions are done, each unique parent in the Disjoint Set represents one distinct island.
Counting these unique parents gives the total number of islands in the grid.
C++
//Driver Code Starts
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
//Driver Code Ends
// Disjoint Set Union (Union-Find) class
class DisjointSet {
vector<int> parent, rank;
public:
// Initialize DSU with each node as its own parent
DisjointSet(int n) {
parent.resize(n);
rank.assign(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Find operation with path compression
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
// Union operation by rank
void unite(int x, int y) {
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
else if (rank[yRoot] < rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else {
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
rank[xRoot]++;
}
}
};
// Count total islands in the grid using DSU
int countIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
int m = grid[0].size();
DisjointSet ds(n * m);
// Directions for 8-connected neighbors
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {
{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1},
{-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}
};
auto getIndex = [&](int r, int c) {
return r * m + c;
};
// Perform union for all connected 'L' (land) cells
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L') {
for (auto [dr, dc] : directions) {
int nr = r + dr, nc = c + dc;
if (nr >= 0 && nr < n && nc >= 0 && nc < m && grid[nr][nc] == 'L')
ds.unite(getIndex(r, c), getIndex(nr, nc));
}
}
}
}
// Use a set to count unique root parents representing islands
unordered_set<int> uniqueIslands;
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L')
uniqueIslands.insert(ds.find(getIndex(r, c)));
}
}
return uniqueIslands.size();
}
//Driver Code Starts
int main() {
vector<vector<char>> grid = {
{'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'},
{'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'},
{'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'},
{'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W'}
};
cout << countIslands(grid) << endl;
return 0;
}
//Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
import java.util.*;
//Driver Code Ends
class DisjointSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
// Initialize DSU with each node as its own parent
public DisjointSet(int n)
{
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Find operation with path compression
public int find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
// Union operation by rank
public void unite(int x, int y)
{
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
else if (rank[yRoot] < rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else {
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
rank[xRoot]++;
}
}
}
// Count total islands in the grid using DSU
public class Main {
public static int countIslands(char[][] grid)
{
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
DisjointSet ds = new DisjointSet(n * m);
// Directions for 8-connected neighbors
int[][] directions = { { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 },
{ 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 },
{ -1, -1 }, { -1, 1 },
{ 1, -1 }, { 1, 1 } };
// Perform union for all connected 'L' (land) cells
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L') {
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int nr = r + dir[0], nc
= c + dir[1];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < n && nc >= 0
&& nc < m
&& grid[nr][nc] == 'L')
ds.unite(r * m + c,
nr * m + nc);
}
}
}
}
// Use a set to count unique root parents
// representing islands
Set<Integer> uniqueIslands = new HashSet<>();
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L')
uniqueIslands.add(ds.find(r * m + c));
}
}
return uniqueIslands.size();
}
//Driver Code Starts
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char[][] grid = { { 'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W' },
{ 'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L' },
{ 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L' },
{ 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W' },
{ 'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W' } };
System.out.println(countIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
class DisjointSet:
# Initialize DSU with each node as its own parent
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = list(range(n))
self.rank = [0] * n
# Find operation with path compression
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
# Union operation by rank
def unite(self, x, y):
xRoot = self.find(x)
yRoot = self.find(y)
if xRoot == yRoot:
return
if self.rank[xRoot] < self.rank[yRoot]:
self.parent[xRoot] = yRoot
elif self.rank[yRoot] < self.rank[xRoot]:
self.parent[yRoot] = xRoot
else:
self.parent[yRoot] = xRoot
self.rank[xRoot] += 1
def countIslands(grid):
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
ds = DisjointSet(n * m)
# Directions for 8-connected neighbors
directions = [
(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1),
(-1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1)
]
# Perform union for all connected 'L' (land) cells
for r in range(n):
for c in range(m):
if grid[r][c] == 'L':
for dr, dc in directions:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= nr < n and 0 <= nc < m and grid[nr][nc] == 'L':
ds.unite(r * m + c, nr * m + nc)
# Use a set to count unique root parents representing islands
uniqueIslands = set()
for r in range(n):
for c in range(m):
if grid[r][c] == 'L':
uniqueIslands.add(ds.find(r * m + c))
return len(uniqueIslands)
#Driver Code Starts
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid = [
['L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L'],
['L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L'],
['W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W'],
['L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W']
]
print(countIslands(grid))
#Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
//Driver Code Ends
class DisjointSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
// Initialize DSU with each node as its own parent
public DisjointSet(int n)
{
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
// Find operation with path compression
public int Find(int x)
{
if (parent[x] != x)
parent[x] = Find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
// Union operation by rank
public void Unite(int x, int y)
{
int xRoot = Find(x);
int yRoot = Find(y);
if (xRoot == yRoot)
return;
if (rank[xRoot] < rank[yRoot])
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
else if (rank[yRoot] < rank[xRoot])
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
else {
parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
rank[xRoot]++;
}
}
}
class Program {
// Count total islands in the grid using DSU
static int CountIslands(char[][] grid)
{
int n = grid.Length;
int m = grid[0].Length;
DisjointSet ds = new DisjointSet(n * m);
// Directions for 8-connected neighbors
int[][] directions
= { new int[] { -1, 0 }, new int[] { 1, 0 },
new int[] { 0, -1 }, new int[] { 0, 1 },
new int[] { -1, -1 }, new int[] { -1, 1 },
new int[] { 1, -1 }, new int[] { 1, 1 } };
// Perform union for all connected 'L' (land) cells
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L') {
foreach(var dir in directions)
{
int nr = r + dir[0], nc
= c + dir[1];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < n && nc >= 0
&& nc < m
&& grid[nr][nc] == 'L')
ds.Unite(r * m + c,
nr * m + nc);
}
}
}
}
// Use a set to count unique root parents
// representing islands
HashSet<int> uniqueIslands = new HashSet<int>();
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] == 'L')
uniqueIslands.Add(ds.Find(r * m + c));
}
}
return uniqueIslands.Count;
}
//Driver Code Starts
static void Main()
{
char[][] grid
= { new char[] { 'L', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'W' },
new char[] { 'W', 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L' },
new char[] { 'L', 'W', 'W', 'L', 'L' },
new char[] { 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W', 'W' },
new char[] { 'L', 'W', 'L', 'L', 'W' } };
Console.WriteLine(CountIslands(grid));
}
}
//Driver Code Ends
class DisjointSet {
constructor(n)
{
this.parent = Array.from({length : n}, (_, i) => i);
this.rank = new Array(n).fill(0);
}
// Find operation with path compression
find(x)
{
if (this.parent[x] !== x)
this.parent[x] = this.find(this.parent[x]);
return this.parent[x];
}
// Union operation by rank
unite(x, y)
{
let xRoot = this.find(x);
let yRoot = this.find(y);
if (xRoot === yRoot)
return;
if (this.rank[xRoot] < this.rank[yRoot]) {
this.parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
}
else if (this.rank[yRoot] < this.rank[xRoot]) {
this.parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
}
else {
this.parent[yRoot] = xRoot;
this.rank[xRoot]++;
}
}
}
// Count total islands in the grid using DSU
function countIslands(grid)
{
let n = grid.length;
let m = grid[0].length;
let ds = new DisjointSet(n * m);
// Directions for 8-connected neighbors
let directions = [
[ -1, 0 ], [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, -1 ], [ 0, 1 ],
[ -1, -1 ], [ -1, 1 ], [ 1, -1 ], [ 1, 1 ]
];
// Perform union for all connected 'L' (land) cells
for (let r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === "L") {
for (let [dr, dc] of directions) {
let nr = r + dr, nc = c + dc;
if (nr >= 0 && nr < n && nc >= 0
&& nc < m && grid[nr][nc] === "L")
ds.unite(r * m + c, nr * m + nc);
}
}
}
}
// Use a set to count unique root parents representing
// islands
let uniqueIslands = new Set();
for (let r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < m; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === "L")
uniqueIslands.add(ds.find(r * m + c));
}
}
return uniqueIslands.size;
}
//Driver Code Starts
// Example usage
let grid = [
[ "L", "L", "W", "W", "W" ],
[ "W", "L", "W", "W", "L" ],
[ "L", "W", "W", "L", "L" ],
[ "W", "W", "W", "W", "W" ], [ "L", "W", "L", "L", "W" ]
];
console.log(countIslands(grid));
//Driver Code Ends
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile