Given a string s representing an infix expression ("operand1 operator operand2" ), Convert it into its prefix notation ("operator operand1 operand2").
Note: The precedence order is as follows: (^) has the highest precedence and is evaluated from right to left, (* and /) come next with left to right associativity, and (+ and -) have the lowest precedence with left to right associativity.
Examples:
Input: s = "a*(b+c)/d"
Output: /*a+bcd
Explanation: The infix expression is a*(b+c)/d. First, inside the brackets, b + c becomes +bc. Now the expression looks like a*(+bc)/d. Next, multiply a with (+bc), so it becomes *a+bc. Finally, divide this result by d, so it becomes /*a+bcd.
[Approach 1] Using Stack - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to scan the expression from right to left, directly placing operands (a, b, c…) into the result as they appear. Operators (+, -, *, /, ^) are handled using a stack so that precedence and associativity are maintained.
How to Maintain Precedence and Associativity?
To maintain precedence and associativity, when a new operator appears, compare it with the operator on top of the stack. Pop operators from the stack if they have higher precedence, or if they have equal precedence and the new operator is right-associative (^). Left-associative operators (+, -, *, /) do not cause a pop. Push the new operator onto the stack. For parentheses (when scanning right to left), push ')' onto the stack, and when '(' is encountered, pop operators until a ')' is found.
At the end, pop all remaining operators from the stack and add them to the result. Finally, reverse the result to obtain the correct prefix expression.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// function to return precedence of operators
int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if operator is right-associative
bool isRightAssociative(char c) {
return c == '^';
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
bool isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// function to convert infix expression to prefix
string infixToPrefix(string s) {
stack<char> st;
string result = "";
// scan from right to left
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char c = s[i];
if (isalnum(c)) {
result += c;
}
else if (c == ')') {
st.push(c);
}
else if (c == '(') {
while (!st.empty() && st.top() != ')') {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
// pop ')'
if (!st.empty()) st.pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (!st.empty() && isOperator(st.top()) &&
(precedence(st.top()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st.top()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.push(c);
}
}
// pop remaining operators
while (!st.empty()) {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
// reverse at the end to get correct prefix
reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
int main() {
string s = "a*(b+c)/d";
cout << infixToPrefix(s);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// function to return precedence of operators
int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if operator is right-associative
int isRightAssociative(char c) {
return c == '^';
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
int isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// function to convert infix expression to prefix
char* infixToPrefix(char* s) {
int n = strlen(s);
char* result = (char*)malloc(n * 2);
int resIndex = 0;
char st[100];
int top = -1;
// scan from right to left
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char c = s[i];
if (isalnum(c)) {
result[resIndex++] = c;
}
else if (c == ')') {
st[++top] = c;
}
else if (c == '(') {
while (top != -1 && st[top] != ')') {
result[resIndex++] = st[top--];
}
if (top != -1) top--; // pop ')'
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (top != -1 && isOperator(st[top]) &&
(precedence(st[top]) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st[top]) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result[resIndex++] = st[top--];
}
st[++top] = c;
}
}
// pop remaining operators
while (top != -1) {
result[resIndex++] = st[top--];
}
result[resIndex] = '\0';
// reverse at the end to get correct prefix
for (int i = 0; i < resIndex / 2; i++) {
char temp = result[i];
result[i] = result[resIndex - i - 1];
result[resIndex - i - 1] = temp;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
char s[] = "a*(b+c)/d";
char* prefix = infixToPrefix(s);
printf("%s\n", prefix);
return 0;
}
import java.util.Stack;
class GfG {
// function to return precedence of operators
static int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if operator is right-associative
static boolean isRightAssociative(char c) {
return c == '^';
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
static boolean isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// function to convert infix expression to prefix
static String infixToPrefix(String s) {
Stack<Character> st = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
// scan from right to left
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
result.append(c);
}
else if (c == ')') {
st.push(c);
}
else if (c == '(') {
while (!st.isEmpty() && st.peek() != ')') {
result.append(st.pop());
}
if (!st.isEmpty()) st.pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (!st.isEmpty() && isOperator(st.peek()) &&
(precedence(st.peek()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st.peek()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result.append(st.pop());
}
st.push(c);
}
}
// pop remaining operators
while (!st.isEmpty()) {
result.append(st.pop());
}
// reverse to get correct prefix
return result.reverse().toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "a*(b+c)/d";
System.out.println(infixToPrefix(s));
}
}
# function to return precedence of operators
def precedence(c):
if c == '^':
return 3
elif c in ('*', '/'):
return 2
elif c in ('+', '-'):
return 1
else:
return -1
# function to check if operator is right-associative
def isRightAssociative(c):
return c == '^'
# function to check if a character is an operator
def isOperator(c):
return c in "+-*/^"
# function to convert infix expression to prefix
def infixToPrefix(s):
st = []
result = []
# scan from right to left
for c in reversed(s):
if c.isalnum():
result.append(c)
elif c == ')':
st.append(c)
elif c == '(':
while st and st[-1] != ')':
result.append(st.pop())
if st:
st.pop() # remove ')'
elif isOperator(c):
while (st and isOperator(st[-1]) and
(precedence(st[-1]) > precedence(c) or
(precedence(st[-1]) == precedence(c) and isRightAssociative(c)))):
result.append(st.pop())
st.append(c)
# pop remaining operators
while st:
result.append(st.pop())
# reverse at the end to get correct prefix
return ''.join(reversed(result))
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = "a*(b+c)/d"
print(infixToPrefix(s))
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// function to return precedence of operators
static int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
static bool isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// function to check if operator is right-associative
static bool isRightAssociative(char c) {
return c == '^';
}
// function to convert infix expression to prefix
static string infixToPrefix(string s) {
Stack<char> st = new Stack<char>();
string result = "";
// scan from right to left
for (int i = s.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char c = s[i];
if (Char.IsLetterOrDigit(c)) {
result += c;
}
else if (c == ')') {
st.Push(c);
}
else if (c == '(') {
while (st.Count > 0 && st.Peek() != ')') {
result += st.Pop();
}
if (st.Count > 0) st.Pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (st.Count > 0 && isOperator(st.Peek()) &&
(precedence(st.Peek()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st.Peek()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result += st.Pop();
}
st.Push(c);
}
}
// pop remaining operators
while (st.Count > 0) {
result += st.Pop();
}
// reverse at the end to get correct prefix
char[] arr = result.ToCharArray();
Array.Reverse(arr);
return new string(arr);
}
static void Main() {
string s = "a*(b+c)/d";
Console.WriteLine(infixToPrefix(s));
}
}
// function to return precedence of operators
function precedence(c) {
if (c === '^') return 3;
else if (c === '*' || c === '/') return 2;
else if (c === '+' || c === '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
function isOperator(c) {
return ['+', '-', '*', '/', '^'].includes(c);
}
// function to check if operator is right-associative
function isRightAssociative(c) {
return c === '^';
}
// function to convert infix expression to prefix
function infixToPrefix(s) {
let st = [];
let result = [];
// scan from right to left
for (let i = s.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let c = s[i];
if (/[a-zA-Z0-9]/.test(c)) {
result.push(c);
} else if (c === ')') {
st.push(c);
} else if (c === '(') {
while (st.length > 0 && st[st.length - 1] !== ')') {
result.push(st.pop());
}
if (st.length > 0) st.pop();
} else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (
st.length > 0 &&
isOperator(st[st.length - 1]) &&
(precedence(st[st.length - 1]) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st[st.length - 1]) === precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))
) {
result.push(st.pop());
}
st.push(c);
}
}
// pop remaining operators
while (st.length > 0) {
result.push(st.pop());
}
// reverse to get correct prefix
return result.reverse().join('');
}
// Driver Code
let s = "a*(b+c)/d";
console.log(infixToPrefix(s));
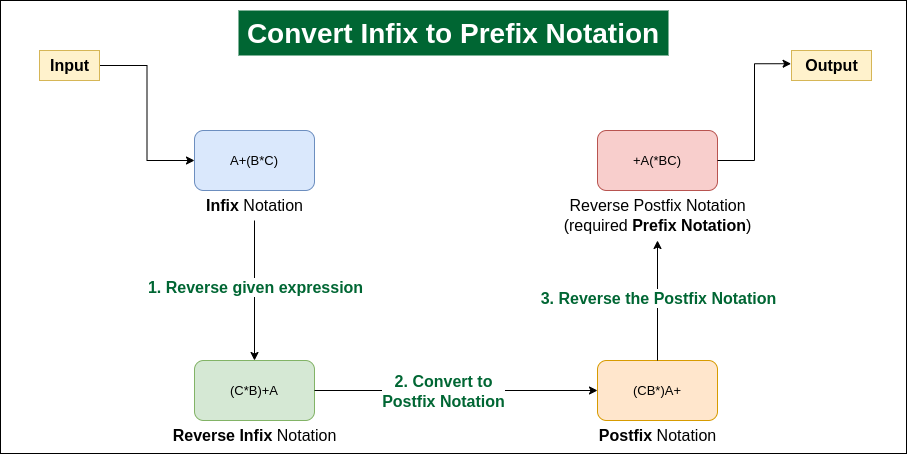
[Approach 2] Using Postfix and Reverse Method - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
To convert an infix expression to prefix, we make use of the infix-to-postfix method with a small modification.
- First, we reverse the infix expression because prefix is evaluated from right to left (opposite of postfix).
- While reversing, we swap '(' with ')' to maintain the correct grouping of subexpressions.
- Now, we convert this modified expression into postfix using the standard stack-based method.
- Finally, we reverse the resulting postfix expression. This gives the correct prefix form.
Note: Prefix = reverse( postfix( reverse(infix) ) )
Illustration:
 C++
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
// function to return precedence of operators
int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// function to check if a character is an operator
bool isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// Function to check if operator is right-associative
bool isRightAssociative(char op) {
return (op == '^');
}
// function to convert infix to prefix
string infixToPrefix(string s) {
// reverse the string
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
// swap '(' and ')'
for (int i = 0; i < (int)s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') s[i] = ')';
else if (s[i] == ')') s[i] = '(';
}
stack<char> st;
string result = "";
// convert to postfix (on reversed expression)
for (int i = 0; i < (int)s.length(); i++) {
char c = s[i];
if (isalnum(c)) {
result += c;
}
else if (c == '(') {
st.push(c);
}
else if (c == ')') {
while (!st.empty() && st.top() != '(') {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
if (!st.empty()) st.pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (!st.empty() && st.top() != '(' &&
((precedence(st.top()) > precedence(c)) ||
(precedence(st.top()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.push(c);
}
}
// pop all remaining operators
while (!st.empty()) {
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
// reverse the result to prefix
reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
int main() {
string s = "a*(b+c)/d";
cout << infixToPrefix(s);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
// stack implementation
char stack[100];
int top = -1;
void push(char c) { stack[++top] = c; }
char pop() { return stack[top--]; }
char peek() { return stack[top]; }
int isEmpty() { return top == -1; }
// precedence of operators
int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
// check if operator
int isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// check if operator is right-associative
int isRightAssociative(char c) {
return (c == '^');
}
// function to convert infix to prefix using reverse-trick
void infixToPrefix(char s[]) {
int n = strlen(s);
// reverse string
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
char temp = s[i];
s[i] = s[n - i - 1];
s[n - i - 1] = temp;
}
// swap '(' and ')'
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') s[i] = ')';
else if (s[i] == ')') s[i] = '(';
}
char result[200];
int k = 0;
// infix to postfix conversion
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = s[i];
if (isalnum(c)) {
result[k++] = c;
}
else if (c == '(') {
push(c);
}
else if (c == ')') {
while (!isEmpty() && peek() != '(') {
result[k++] = pop();
}
if (!isEmpty()) pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (!isEmpty() && peek() != '(' &&
(precedence(peek()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(peek()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result[k++] = pop();
}
push(c);
}
}
while (!isEmpty()) {
result[k++] = pop();
}
result[k] = '\0';
// reverse result for prefix
for (int i = 0; i < k / 2; i++) {
char temp = result[i];
result[i] = result[k - i - 1];
result[k - i - 1] = temp;
}
printf("%s\n", result);
}
int main() {
char s[] = "a*(b+c)/d";
infixToPrefix(s);
return 0;
}
import java.util.Stack;
public class GFG {
// function to return precedence
static int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
static boolean isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// check if operator is right-associative
static boolean isRightAssociative(char c) {
return (c == '^');
}
// function to convert infix to prefix using reverse-trick
static String infixToPrefix(String s) {
// reverse string
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s).reverse();
char[] arr = sb.toString().toCharArray();
// swap ( and )
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == '(') arr[i] = ')';
else if (arr[i] == ')') arr[i] = '(';
}
Stack<Character> st = new Stack<>();
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
// infix to postfix on reversed string
for (char c : arr) {
if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
result.append(c);
}
else if (c == '(') {
st.push(c);
}
else if (c == ')') {
while (!st.isEmpty() && st.peek() != '(') {
result.append(st.pop());
}
if (!st.isEmpty()) st.pop();
}
else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (!st.isEmpty() && st.peek() != '(' &&
(precedence(st.peek()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st.peek()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result.append(st.pop());
}
st.push(c);
}
}
while (!st.isEmpty()) {
result.append(st.pop());
}
// reverse result for prefix
return result.reverse().toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "a*(b+c)/d";
System.out.println(infixToPrefix(s));
}
}
# function to return precedence
def precedence(c):
if c == '^': return 3
elif c in ['*', '/']: return 2
elif c in ['+', '-']: return 1
else: return -1
def isOperator(c):
return c in ['+', '-', '*', '/', '^']
# check if operator is right-associative
def isRightAssociative(c):
return c == '^'
# function to convert infix to prefix
# using reverse-trick
def infixToPrefix(s):
# reverse string
s = s[::-1]
# swap ( and )
s = ''.join(')' if c == '(' else '(' if c == ')' else c for c in s)
st = []
result = []
# infix to postfix on reversed string
for c in s:
if c.isalnum():
result.append(c)
elif c == '(':
st.append(c)
elif c == ')':
while st and st[-1] != '(':
result.append(st.pop())
if st: st.pop()
elif isOperator(c):
while (st and st[-1] != '(' and
(precedence(st[-1]) > precedence(c) or
(precedence(st[-1]) == precedence(c) and isRightAssociative(c)))):
result.append(st.pop())
st.append(c)
while st:
result.append(st.pop())
# reverse result
return ''.join(result[::-1])
if __name__ == "__main__":
s = "a*(b+c)/d"
print(infixToPrefix(s))
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// precedence function
static int precedence(char c) {
if (c == '^') return 3;
else if (c == '*' || c == '/') return 2;
else if (c == '+' || c == '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
static bool isOperator(char c) {
return (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/' || c == '^');
}
// check right-associativity
static bool isRightAssociative(char c) {
return c == '^';
}
// function to convert infix to prefix
// using reverse-trick
static string infixToPrefix(string s) {
// reverse string
char[] arr = s.ToCharArray();
Array.Reverse(arr);
s = new string(arr);
// swap ( and )
char[] chars = s.ToCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.Length; i++) {
if (chars[i] == '(') chars[i] = ')';
else if (chars[i] == ')') chars[i] = '(';
}
s = new string(chars);
Stack<char> st = new Stack<char>();
string result = "";
// infix to postfix (on reversed string)
foreach (char c in s) {
if (Char.IsLetterOrDigit(c)) {
result += c;
} else if (c == '(') {
st.Push(c);
} else if (c == ')') {
while (st.Count > 0 && st.Peek() != '(') {
result += st.Pop();
}
if (st.Count > 0) st.Pop();
} else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (st.Count > 0 && st.Peek() != '(' &&
(precedence(st.Peek()) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st.Peek()) == precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))) {
result += st.Pop();
}
st.Push(c);
}
}
while (st.Count > 0) {
result += st.Pop();
}
// reverse result to get prefix
char[] res = result.ToCharArray();
Array.Reverse(res);
return new string(res);
}
static void Main() {
string s = "a*(b+c)/d";
Console.WriteLine(infixToPrefix(s));
}
}
// precedence function
function precedence(c) {
if (c === '^') return 3;
else if (c === '*' || c === '/') return 2;
else if (c === '+' || c === '-') return 1;
else return -1;
}
function isOperator(c) {
return ['+', '-', '*', '/', '^'].includes(c);
}
// check right-associativity
function isRightAssociative(c) {
return c === '^';
}
// function to convert infix to
// prefix using reverse-trick
function infixToPrefix(s) {
// reverse string
s = s.split('').reverse().join('');
// swap ( and )
s = s.split('')
.map(c => (c === '(' ? ')' : c === ')' ? '(' : c))
.join('');
let st = [];
let result = "";
// infix to postfix (on reversed string)
for (let c of s) {
if (/[a-zA-Z0-9]/.test(c)) {
result += c;
} else if (c === '(') {
st.push(c);
} else if (c === ')') {
while (st.length > 0 && st[st.length - 1] !== '(') {
result += st.pop();
}
if (st.length > 0) st.pop();
} else if (isOperator(c)) {
while (
st.length > 0 &&
st[st.length - 1] !== '(' &&
(precedence(st[st.length - 1]) > precedence(c) ||
(precedence(st[st.length - 1]) === precedence(c) && isRightAssociative(c)))
) {
result += st.pop();
}
st.push(c);
}
}
while (st.length > 0) {
result += st.pop();
}
// reverse result → prefix
return result.split('').reverse().join('');
}
// Driver Code
let s = "a*(b+c)/d";
console.log(infixToPrefix(s));
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile