Introduction To Subnetting
Last Updated :
07 Oct, 2025
Subnetting is the process of dividing a large network into smaller networks called subnets. Each subnet provides its own space for devices to communicate, improving network performance, security, and management.
Example: In a company, different departments (Sales, HR, IT) can have their own subnets, keeping their traffic separate and organized.
 Subnetting
SubnettingWhy Subnetting is Important
Let's consider a company that follows classful addressing, it has a Class C network (192.168.1.0/24) with 256 IP addresses. It has three departments:
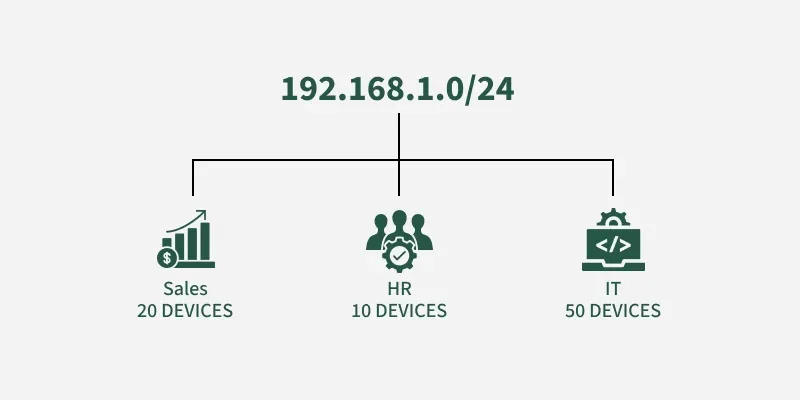 Subnetting
Subnetting Without subnetting, all departments share the same network, and all 256 IP addresses are available to everyone, which leads to:
- IP Waste: Only 80 devices used out of 256 addresses i.e 176 wasted.
- Performance Issues: All traffic floods the same network, slowing communication.
- Security Risks: Devices from different departments can access each other freely.
With Subnetting, we split the network into three subnets, allocating just enough IP addresses for each department:
| Department | Devices | IPs Allocated (after subnetting) |
|---|
| Sales | 20 | 32 (192.168.1.0/27) |
| HR | 10 | 16 (192.168.1.32/28) |
| IT | 50 | 64 (192.168.1.48/26) |
By subnetting, we:
- Efficient IP usage: Only 112 addresses used, leaving space for growth.
- Better performance: Traffic stays within each subnet.
- Improved security: Each department is isolated.
Key Concepts in Subnetting
IP Addressing
An IP address is made up of different parts, each serving a specific purpose in identifying a device on a network. An IPv4 address consists of four parts called "octets," separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.1.1). It has two main sections:
- Network Portion: Identifies the network the device belongs to.
- Host Portion: Uniquely identifies a device within the network.
IPv4 addresses are divided into classes based on the length of the network and host portions:
- Class A: 8-bit network ID, 24-bit host ID.
- Class B: 16-bit network ID, 16-bit host ID.
- Class C: 24-bit network ID, 8-bit host ID.
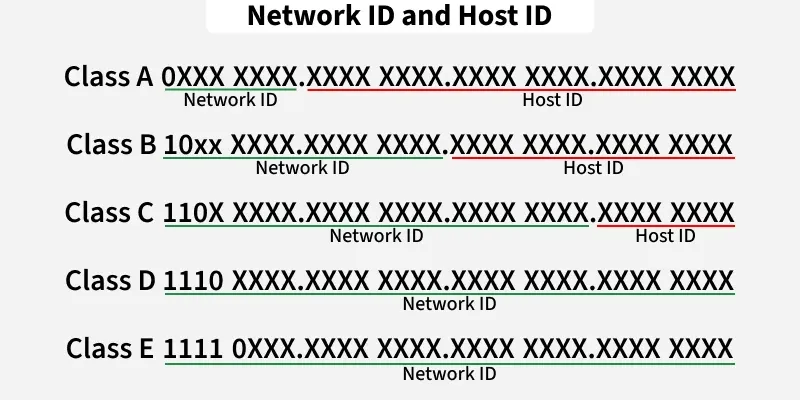 Classful Addressing
Classful AddressingWhat is a Subnet Mask?
A subnet mask is a 32-bit number used in IP addressing to separate the network portion of an IP address from the host portion. It helps computers and devices determine which part of an IP address refers to the network they are present, and which part refers to their specific location or address within that network.
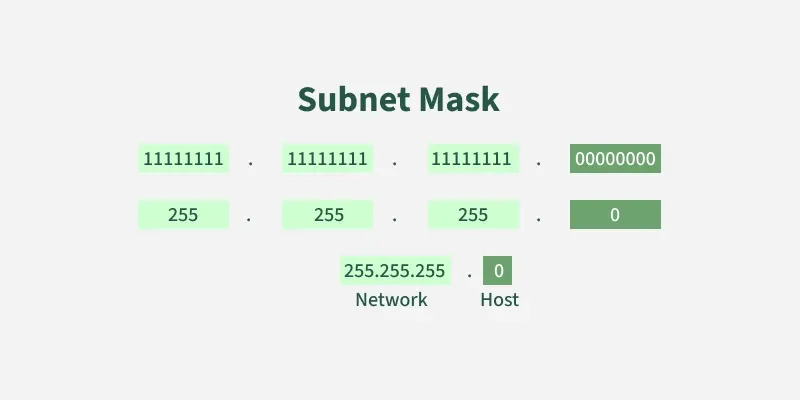 Subnet mask
Subnet maskCIDR Notation: A Simplified Approach to Subnetting
Instead of using a long subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0), CIDR uses a simple format like /24. The number after the slash (/n) represents the number of bits used for the network portion of the IP address.
How Subnetting Works?
The working of subnets starts in such a way that firstly it divides the subnets into smaller subnets. For communicating between subnets, routers are used. Each subnet allows its linked devices to communicate with each other. Subnetting for a network should be done in such a way that it does not affect the network bits.
In class C the first 3 octets are network bits so it remains as it is.
- For Subnet-1: The first bit which is chosen from the host id part is zero and the range will be from (193.1.2.00000000 till you get all 1's in the host ID part i.e, 193.1.2.01111111) except for the first bit which is chosen zero for subnet id part.
Thus, the range of subnet 1 is: 193.1.2.0 to 193.1.2.127
Subnet id of Subnet 1 is: 193.1.2.0
The direct Broadcast id of Subnet-1 is: 193.1.2.127
The total number of hosts possible is: 126 (Out of 128, 2 id's are used for Subnet id & Direct Broadcast id)
The subnet mask of Subnet- 1 is: 255.255.255.128
- For Subnet-2: The first bit chosen from the host id part is one and the range will be from (193.1.2.100000000 till you get all 1's in the host ID part i.e, 193.1.2.11111111).
Thus, the range of subnet-2 is: 193.1.2.128 to 193.1.2.255
Subnet id of Subnet 2 is : 193.1.2.128
The direct Broadcast id of Subnet-2 is: 193.1.2.255
The total number of hosts possible is: 126 (Out of 128, 2 id's are used for Subnet id & Direct Broadcast id)
The subnet mask of Subnet- 2 is: 255.255.255.128
The best way to find out the subnet mask of a subnet is to set the fixed bit of host-id to 1 and the rest to 0.
Finally, after using the subnetting the total number of usable hosts is reduced from 254 to 252.
Note:
- To divide a network into four (2 2 ) parts you need to choose two bits from the host id part for each subnet i.e, (00, 01, 10, 11).
- To divide a network into eight (2 3 ) parts you need to choose three bits from the host id part for each subnet i.e, (000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111) and so on.
- We can say that if the total number of subnets in a network increases the total number of usable hosts decreases.
The network can be divided into two parts: To divide a network into two parts, you need to choose one bit for each Subnet from the host ID part.
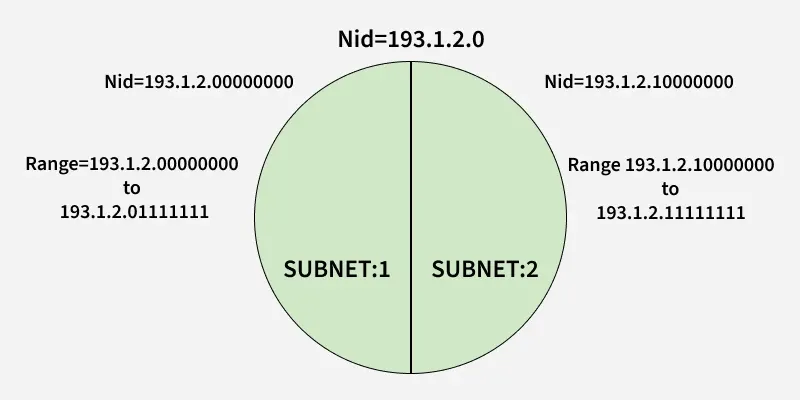 Subnet
SubnetIn the above diagram, there are two Subnets.
Note: It is a class C IP so, there are 24 bits in the network id part and 8 bits in the host id part.
Advantages of Subnetting
- Improved Security: Subnets isolate departments, preventing unauthorized access (e.g., HR data hidden from Sales).
- Traffic Prioritization: Critical subnets (e.g., Sales hosting video conferences) can get higher priority.
- Easier Maintenance: Smaller, segmented networks are simpler to manage.
Disadvantages of Subnetting
- Extra Overhead: Each subnet wastes 2 IP addresses (network ID and broadcast address).
- Higher Cost: Subnetting often requires additional devices like routers and switches, increasing expenses.
- More Complexity: Compared to a single flat network, subnetting adds extra steps in communication and requires careful planning.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice
My Profile