Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Last Updated :
29 Sep, 2025
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a network layer protocol widely used by network devices such as routers, gateways and hosts to send error messages and operational information.. Since the Internet Protocol (IP) itself does not have an inbuilt error-reporting or correction mechanism, ICMP is a supporting protocol within the IP suite that helps in reporting errors and sending diagnostic messages. It is primarily used for:
- Error reporting: When data packets cannot reach their destination due to issues such as unreachable hosts, timeouts or fragmentation errors.
- Operational queries: For example, echo requests and replies used in tools like ping.
Note: Without ICMP, devices would not be able to inform the sender about delivery failures, congestion or misrouting, making network troubleshooting almost impossible.
Uses of ICMP
Error Reporting
- If a message cannot be delivered, ICMP informs the source about the failure.
- Example: If a packet is too large and cannot be forwarded, the receiver drops the packet and sends an ICMP error message to the sender.
Network Diagnostics
- Traceroute: Used to determine the path packets take across routers to reach the destination.
- Ping: Sends echo-request and echo-reply messages to measure round-trip time and test connectivity.
How ICMP Works
- ICMP is connectionless (unlike TCP) and does not require a handshake.
- Messages are encapsulated within IP datagrams, consisting of an IP header followed by an ICMP header and payload.
- Devices send ICMP packets when encountering errors such as unreachable hosts, expired time-to-live (TTL) or routing issues.
ICMP header comes after IPv4 and IPv6 packet header. In the ICMP packet format, the first 32 bits of the packet contain three fields:
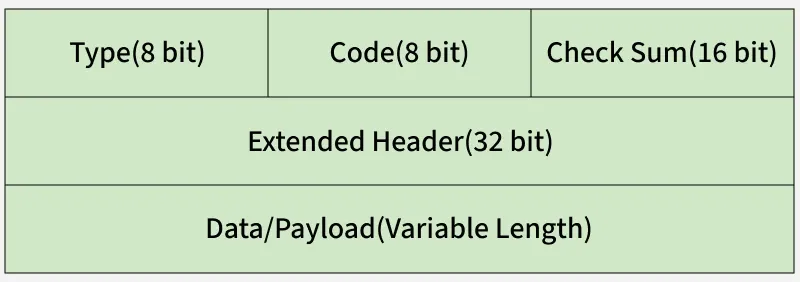 ICMPv4 Packet Format
ICMPv4 Packet Format- Type (8-bit): The initial 8-bit of the packet is for message type, it provides a brief description of the message so that receiving network would know what kind of message it is receiving and how to respond to it. Some common message types are as follows:
Type 0 - Echo reply
Type 3 - Destination unreachable
Type 5 - Redirect Message
Type 8 - Echo Request
Type 11 - Time Exceeded
Type 12 - Parameter problem
- Code (8-bit): Code is the next 8 bits of the ICMP packet format, this field carries some additional information about the error message and type.
- Checksum (16-bit): Last 16 bits are for the checksum field in the ICMP packet header. The checksum is used to check the number of bits of the complete message and enable the ICMP tool to ensure that complete data is delivered.
- The next 32 bits of the ICMP Header are Extended Header which has the work of pointing out the problem in IP Message. Byte locations are identified by the pointer which causes the problem message and receiving device looks here for pointing to the problem.
- The last part of the ICMP packet is Data or Payload of variable length. The bytes included in IPv4 are 576 bytes and in IPv6, 1280 bytes.
ICMP in DDoS Attacks
In Distributed DOS (DDoS) attacks, attackers provide so much extra traffic to the target, so that it cannot provide service to users. There are so many ways through which an attacker executes these attacks, which are described below.
1. Ping of Death Attack
- Whenever an attacker sends a ping, whose size is greater than the maximum allowable size, oversized packets are broken into smaller parts.
- When the sender re-assembles it, the size exceeds the limit which causes a buffer overflowand makes the machine freeze.
- This is simply called a Ping of Death Attack. Newer devices have protection from this attack, but older devices did not have protection from this attack.
2. ICMP Flood Attack
- Whenever the sender sends so many pings that the device on whom the target is done is unable to handle the echo request.
- This type of attack is called an ICMP Flood Attack. This attack is also called a ping flood attack.
- It stops the target computer's resources and causes a denial of service for the target computer.
3. Smurf Attack
- Smurf Attack is a type of attack in which the attacker sends an ICMP packet with a spoofed source IP address.
- These type of attacks generally works on older devices like the ping of death attack.
Types of ICMP Messages
| Type | Code | Description |
|---|
| 0 - Echo Reply | 0 | Echo reply |
| 3 - Destination Unreachable | 0 | Destination network unreachable |
| 1 | Destination host unreachable |
| 2 | Destination protocol unreachable |
| 3 | Destination port unreachable |
| 4 | Fragmentation is needed and the DF flag set |
| 5 | Source route failed |
| 5 - Redirect Message | 0 | Redirect the datagram for the network |
| 1 | Redirect datagram for the host |
| 2 | Redirect the datagram for the Type of Service and Network |
| 3 | Redirect datagram for the Service and Host |
| 8 - Echo Request | 0 | Echo request |
| 9 - Router Advertisement | 0 | Use to discover the addresses of operational routers |
| 10 - Router Solicitation | 0 |
| 11 - Time Exceeded | 0 | Time to live exceeded in transit |
| 1 | Fragment reassembly time exceeded. |
| 12 - Parameter Problem | 0 | The pointer indicates an error. |
| 1 | Missing required option |
| 2 | Bad length |
| 13 - Timestamp | 0 | Used for time synchronization |
| 14 - Timestamp Reply | 0 | Reply to Timestamp message |
1. Source Quench Message
- A source quench message is a request to decrease the traffic rate for messages sent to the host destination) .
- Or we can say when receiving host detects that the rate of sending packets (traffic rate) to it is too fast it sends the source quench message to the source to slow the pace down so that no packet can be lost.
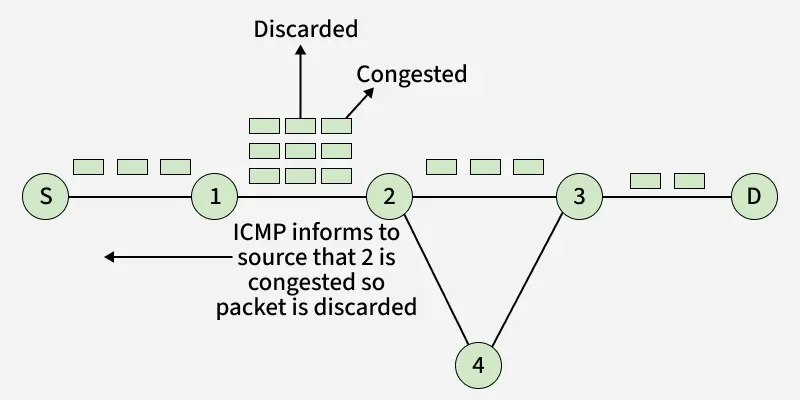 Source Quench Message
Source Quench Message- ICMP will take the source IP from the discarded packet and inform the source by sending a source quench message. The source will reduce the speed of transmission so that router will be free from congestion.
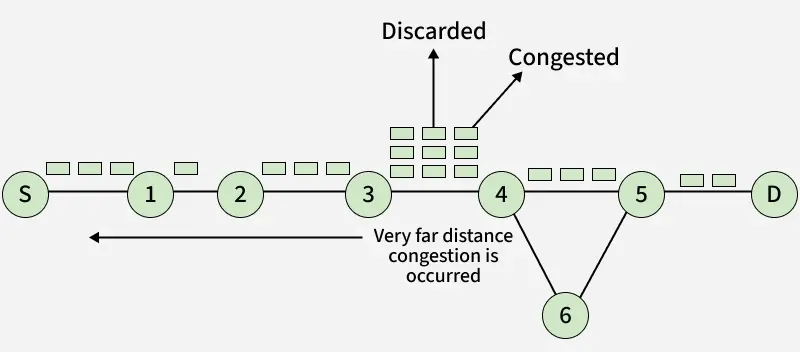 Source Quench Message with Reduced Speed
Source Quench Message with Reduced SpeedNote: When the congestion router is far away from the source the ICMP will send a hop-by-hop source quench message so that every router will reduce the speed of transmission.
2. Parameter Problem
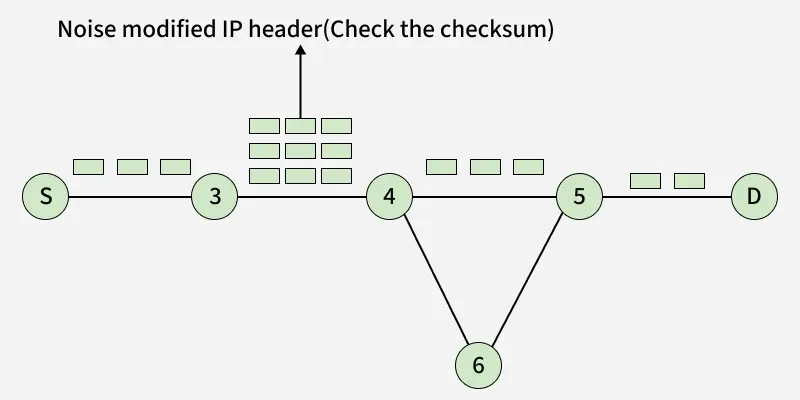 Parameter Problem
Parameter Problem- Whenever packets come to the router then the calculated header checksum should be equal to the received header checksum then only the packet is accepted by the router.
- If there is a mismatch packet will be dropped by the router.
- ICMP will take the source IP from the discarded packet and inform the source by sending a parameter problem message.
3. Time Exceeded Message
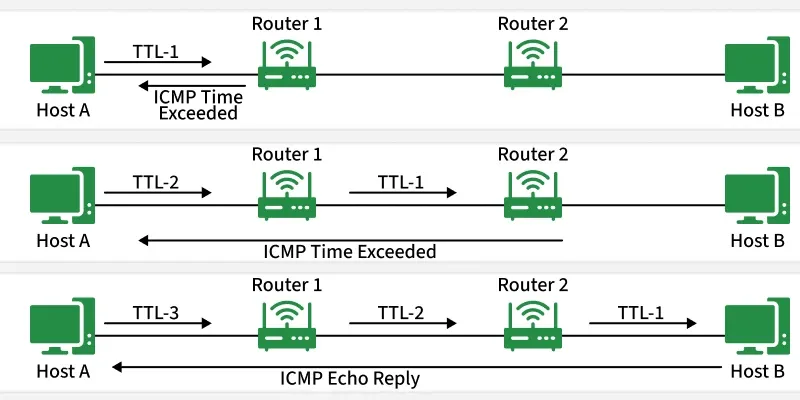 Time Exceeded Message
Time Exceeded Message- A notification with the subject line "Time Exceeded" is typically generated by routers or gateways.
- You need to know what an IP header is in a packet in order to comprehend this ICMP message in its entirety.
- The IP protocol structure is covered in great detail in the section on IP Protocol, which is freely available to our readers.
4. Destination Un-reachable
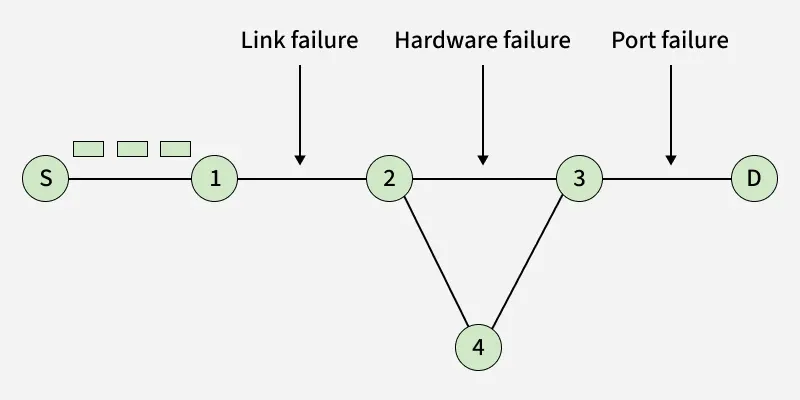 Destination Unreachable Message
Destination Unreachable Message- The destination is unreachable and is generated by the host or its inbound gateway to inform the client that the destination is unreachable for some reason.
- There is no necessary condition that only the router gives the ICMP error message time the destination host sends an ICMP error message when any type of failure (link failure, hardware failure, port failure, etc) happens in the network.
5. Redirection Message
- Redirect requests data packets are sent on an alternate route. The message informs a host to update its routing information (to send packets on an alternate route).
- Example: If the host tries to send data through a router R1 and R1 sends data on a router R2 and there is a direct way from the host to R2.
- Then R1 will send a redirect message to inform the host that there is the best way to the destination directly through R2 available. The host then sends data packets for the destination directly to R2.
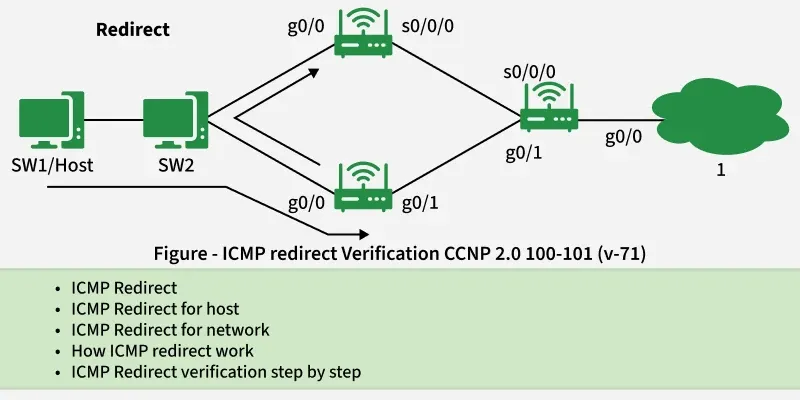 Redirection Message
Redirection Message- The router R2 will send the original datagram to the intended destination.
- But if the datagram contains routing information then this message will not be sent even if a better route is available as redirects should only be sent by gateways and should not be sent by Internet hosts.
- Whenever a packet is forwarded in the wrong direction later it is re-directed in a current direction then ICMP will send a re-directed message.
For more, you can refer to Types of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Messages.
Advantages of ICMP
- Enables error reporting and diagnostics for IP communication.
- Tools like Ping and Traceroute rely on ICMP to check connectivity and network paths.
- Helps administrators quickly identify routing, congestion or connectivity issues.
- Supports network monitoring and performance testing.
Disadvantages of ICMP
- Some dropped packets may not generate ICMP errors due to IP design limitations.
- Vulnerable to misuse in DDoS attacks such as ICMP floods and smurf attacks.
- Can be blocked by firewalls, limiting its diagnostic usefulness.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice