Generations of Programming Languages
Last Updated :
22 Nov, 2025
Programming languages have evolved significantly over time, moving from fundamental machine-specific code to complex languages that are simpler to write and understand. There are five generations of Programming languages. They are:
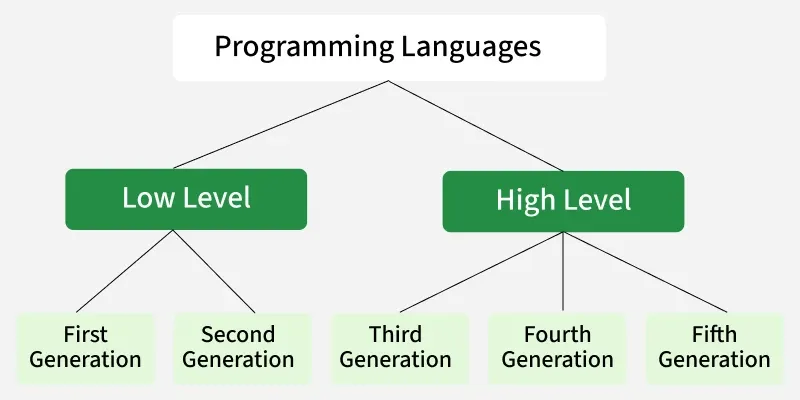 Programming Languages
Programming Languages1. First-Generation Language :
The first-generation languages are also called machine languages/ 1G language. This language is machine-dependent. The machine language statements are written in binary code (0/1 form) because the computer can understand only binary language.
Advantages :
1. Fast & efficient as statements are directly written in binary language.
2. No translator is required.
Disadvantages :
1. Difficult to learn binary codes.
2. Difficult to understand - both programs & where the error occurred.
2. Second Generation Language :
The second-generation languages are also called assembler languages/ 2G languages. Assembly language contains human-readable notations that can be further converted to machine language using an assembler.
Assembler - converts assembly level instructions to machine-level instructions.
Programmers can write the code using symbolic instruction codes that are meaningful abbreviations of mnemonics. It is also known as low-level language.
Advantages :
1. It is easier to understand if compared to machine language.
2. Modifications are easy.
3. Correction & location of errors are easy.
Disadvantages :
1. Assembler is required.
2. This language is architecture /machine-dependent, with a different instruction set for different machines.
3. Third-Generation Language :
The third generation, or 3GL, is a procedural high-level programming language that uses English-like words to write instructions. Programs written in 3GLs must be translated into machine language using a compiler or interpreter. Common examples include C, PASCAL, FORTRAN, and COBOL.
Advantages :
1. Use of English-like words makes it a human-understandable language.
2. Lesser number of lines of code as compared to the above 2 languages.
3. Same code can be copied to another machine & executed on that machine by using compiler-specific to that machine.
Disadvantages :
1. Compiler/ interpreter is needed.
2. Different compilers are needed for different machines.
4. Fourth Generation Language :
The fourth-generation language is also called a non - procedural language/ 4GL. It enables users to access the database. Examples: SQL, Foxpro, Focus, etc.
These languages are also human-friendly to understand.
Advantages :
1. Easy to understand & learn.
2. Less time is required for application creation.
3. It is less prone to errors.
Disadvantages :
1. Memory consumption is high.
2. Has poor control over Hardware.
3. Less flexible.
5. Fifth Generation Language :
Fifth-generation languages (5GL) are based on artificial intelligence. Instead of solving problems algorithmically, they let applications learn and solve tasks using defined constraints. They rely on parallel processing and superconductors to support real AI capabilities.
Examples: PROLOG, LISP, etc.
Advantages :
1. Machines can make decisions.
2. Programmer effort reduces to solve a problem.
3. Easier than 3GL or 4GL to learn and use.
Disadvantages :
1. Complex and long code.
2. More resources are required & they are expensive too.
Explore
How To Become
Roadmap
Interview Preparation
Project Ideas
Certification
My Profile