AuthKit
Easy to use authentication platform designed to provide a flexible, secure, and fast integration.
Introduction
Integrating AuthKit into your app is quick and easy. In this guide, we’ll walk you through adding a hosted authentication flow to your application using AuthKit.
In addition to this guide, there are a variety of example apps available to help with your integration.
Before getting started
To get the most out of this guide, you’ll need:
- A WorkOS account
- Your WorkOS API Key and Client ID
Additionally you’ll need to activate AuthKit in your WorkOS Dashboard if you haven’t already. In the Overview section, click the Set up User Management button and follow the instructions.
Let’s add the necessary dependencies and configuration in your WorkOS Dashboard.
For a Next.js integration, use the authkit-nextjs library. Start by installing it in your Next.js project via npm.
npm install @workos-inc/authkit-nextjs
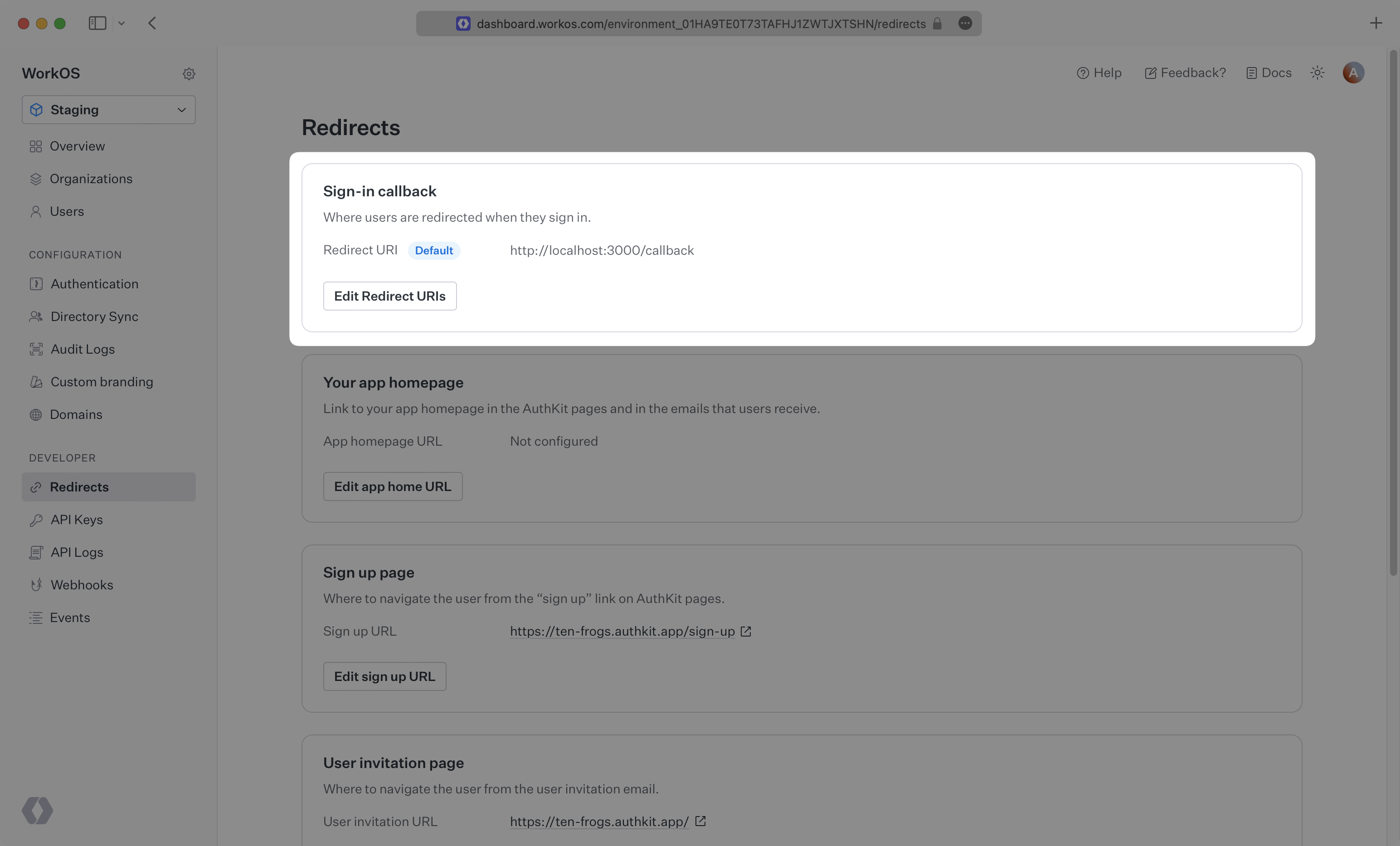
A redirect URI is a callback endpoint that WorkOS will redirect to after a user has authenticated. This endpoint will exchange the authorization code returned by WorkOS for an authenticated User object. We’ll create this endpoint in the next step.
You can set a redirect URI in the Redirects section of the WorkOS Dashboard. While wildcards in your URIs can be used in the staging environment, they and query parameters cannot be used in production.
When users sign out of their application, they will be redirected to your app’s Logout redirect location which is configured in the same dashboard area.
Login requests should originate from your application. In some instances, requests may not begin at your app. For example, some users might bookmark the hosted login page or they might be led directly to the hosted login page when clicking on a password reset link in an email.
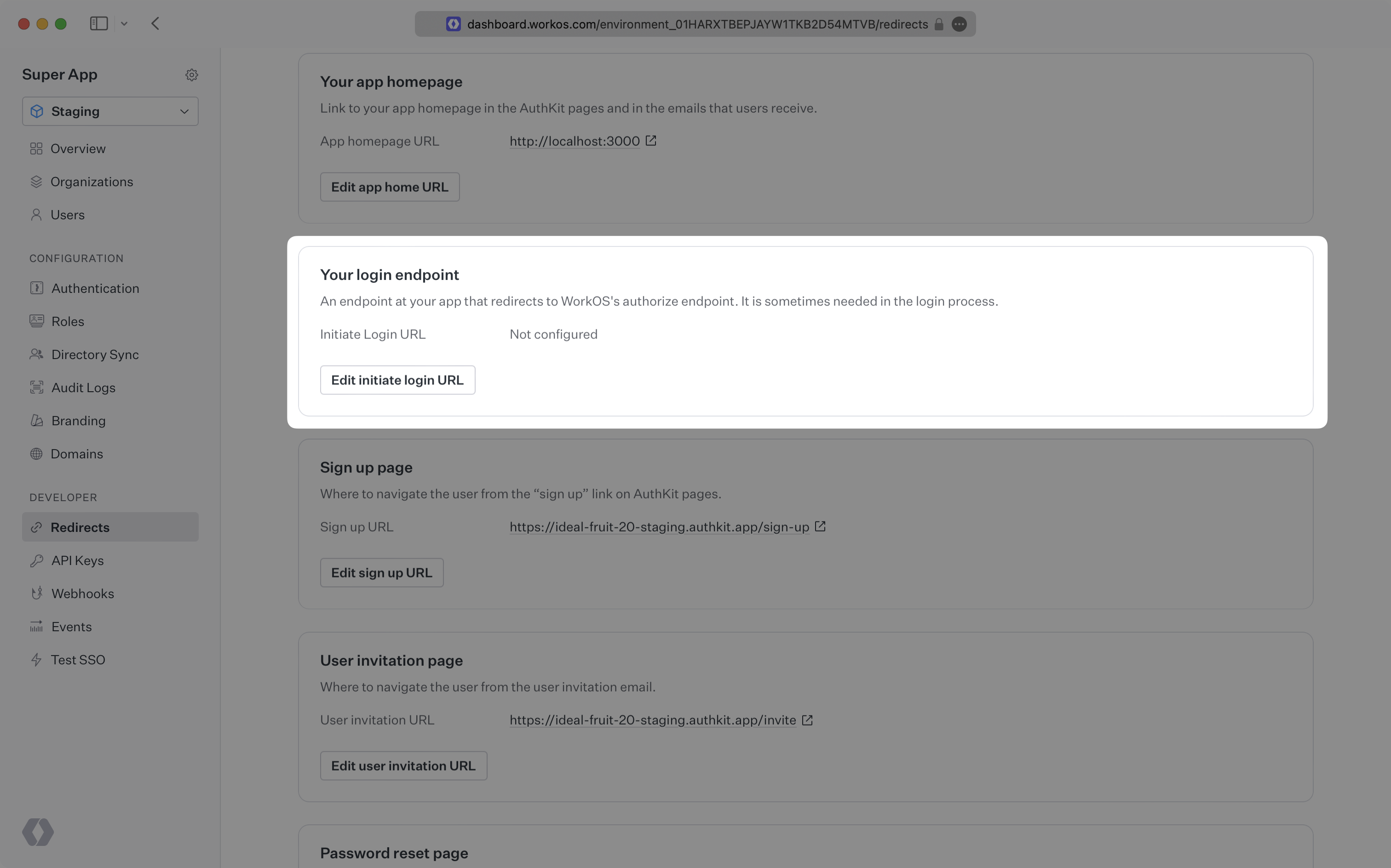
In these cases, AuthKit will detect when a login request did not originate at your application and redirect to your application’s login endpoint. This is an endpoint that you define at your application that redirects users to sign in using AuthKit. We’ll create this endpoint in the next step.
You can configure the initiate login URL from the Redirects section of the WorkOS dashboard.
To make calls to WorkOS, provide the API key and the client ID. Store these values as managed secrets and pass them to the SDKs either as environment variables or directly in your app’s configuration depending on your preferences.
WORKOS_API_KEY='sk_example_123456789' WORKOS_CLIENT_ID='client_123456789' WORKOS_COOKIE_PASSWORD="<your password>" # generate a secure password here # configured in the WorkOS dashboard NEXT_PUBLIC_WORKOS_REDIRECT_URI="http://localhost:3000/callback"
The NEXT_PUBLIC_WORKOS_REDIRECT_URI uses the NEXT_PUBLIC prefix so the variable is accessible in edge functions and middleware configurations. This is useful for configuring operations like Vercel preview deployments.
The SDK requires you to set a strong password to encrypt cookies. This password must be at least 32 characters long. You can generate a secure password by using the 1Password generator or the openssl library via the command line:
openssl rand -base64 32
The code examples use your staging API keys when signed in
The AuthKitProvider component adds protections for auth edge cases and is required to wrap your app layout.
import { AuthKitProvider } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs/components'; export default function RootLayout({ children }) { return ( <html lang="en"> <body> <AuthKitProvider>{children}</AuthKitProvider> </body> </html> ); }
Next.js middleware is required to determine which routes require authentication.
Implementing the middleware
When implementing, you can opt to use either the complete authkitMiddleware solution or the composable authkit method. You’d use the former in cases where your middleware is only used for authentication. The latter is used for more complex apps where you want to have your middleware perform tasks in addition to auth.
The middleware can be implemented in the middleware.ts file. This is a full middleware solution that handles all the auth logic including session management and redirects for you.
With the complete middleware solution, you can choose between page based auth and middleware auth.
Page based auth
Protected routes are determined via the use of the withAuth method, specifically whether the ensureSignedIn option is used. Usage of withAuth is covered further down in the Access authentication data section.
import { authkitMiddleware } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; export default authkitMiddleware(); // Match against pages that require authentication // Leave this out if you want authentication on every page in your application export const config = { matcher: ['/'] };
Middleware auth
In this mode the middleware is used to protect all routes by default, redirecting users to AuthKit if no session is available. Exceptions can be configured via an allow list.
import { authkitMiddleware } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; // In middleware auth mode, each page is protected by default. // Exceptions are configured via the `unauthenticatedPaths` option. export default authkitMiddleware({ middlewareAuth: { enabled: true, unauthenticatedPaths: ['/'], }, }); // Match against pages that require authentication // Leave this out if you want authentication on every page in your application export const config = { matcher: ['/', '/account/:page*'] };
In the above example, the home page / can be viewed by unauthenticated users. The /account page and its children can only be viewed by authenticated users.
The middleware can be implemented in the middleware.ts file. This is a composable middleware solution that handles the session management part for you but leaves the redirect and route protection logic to you.
import { authkit } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; export default async function middleware(request) { // Perform logic before or after AuthKit // Auth object contains the session, response headers and an auhorization // URL in the case that the session isn't valid. This method will automatically // handle setting the cookie and refreshing the session const { session, headers, authorizationUrl } = await authkit(request, { debug: true, }); // Control of what to do when there's no session on a protected route // is left to the developer if (request.url.includes('/account') && !session.user) { console.log('No session on protected path'); return NextResponse.redirect(authorizationUrl); } // Headers from the authkit response need to be included in every non-redirect // response to ensure that `withAuth` works as expected return NextResponse.next({ headers: headers, }); } // Match against pages that require authentication // Leave this out if you want authentication on every page in your application export const config = { matcher: ['/', '/account'] };
When a user has authenticated via AuthKit, they will be redirected to your app’s callback route. Make sure this route matches the WORKOS_REDIRECT_URI environment variable and the configured redirect URI in your WorkOS dashboard.
import { handleAuth } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; // Redirect the user to `/` after successful sign in // The redirect can be customized: `handleAuth({ returnPathname: '/foo' })` export const GET = handleAuth();
We’ll need an initiate login endpoint to direct users to sign in using AuthKit before redirecting them back to your application. We’ll do this by generating an AuthKit authorization URL server side and redirecting the user to it.
import { getSignInUrl } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'; export const GET = async () => { const signInUrl = await getSignInUrl(); return redirect(signInUrl); };
AuthKit can be used in both server and client components.
The withAuth method is used to retrieve the current logged in user and their details.
import Link from 'next/link'; import { getSignUpUrl, withAuth } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; export default async function HomePage() { // Retrieves the user from the session or returns `null` if no user is signed in const { user } = await withAuth(); // Get the URL to redirect the user to AuthKit to sign up const signUpUrl = await getSignUpUrl(); if (!user) { return ( <> <a href="/login">Sign in</a> <Link href={signUpUrl}>Sign up</Link> </> ); } return ( <> <p>Welcome back{user.firstName && `, ${user.firstName}`}</p> </> ); }
The useAuth hook is used to retrieve the current logged in user and their details.
'use client'; import { useAuth } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs/components'; export default function HomePage() { // Retrieves the user from the session or returns `null` if no user is signed in const { user, loading } = useAuth(); if (loading) { return <div>Loading...</div>; } return ( <> <p>Welcome back{user.firstName && `, ${user.firstName}`}</p> </> ); }
For routes where a signed in user is mandatory, you can use the ensureSignedIn option.
import { withAuth } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; export default async function ProtectedPage() { // If the user isn't signed in, they will be automatically redirected to AuthKit const { user } = await withAuth({ ensureSignedIn: true }); return ( <> <p>Welcome back{user.firstName && `, ${user.firstName}`}</p> </> ); }
'use client'; import { useAuth } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs/components'; export default function HomePage() { // If the user isn't signed in, they will be automatically redirected to AuthKit const { user, loading } = useAuth({ ensureSignedIn: true }); if (loading) { return <div>Loading...</div>; } return ( <> <p>Welcome back{user.firstName && `, ${user.firstName}`}</p> </> ); }
Finally, ensure the user can end their session by redirecting them to the logout URL. After successfully signing out, the user will be redirected to your app’s Logout redirect location, which is configured in the WorkOS dashboard.
import Link from 'next/link'; import { getSignUpUrl, withAuth, signOut, } from '@workos-inc/authkit-nextjs'; export default async function HomePage() { // Retrieves the user from the session or returns `null` if no user is signed in const { user } = await withAuth(); // Get the URL to redirect the user to AuthKit to sign up const signUpUrl = await getSignUpUrl(); if (!user) { return ( <> <a href="/login">Sign in</a> <Link href={signUpUrl}>Sign up</Link> </> ); } return ( <form action={async () => { 'use server'; await signOut(); }} > <p>Welcome back{user.firstName && `, ${user.firstName}`}</p> <button type="submit">Sign out</button> </form> ); }
If you haven’t configured a Logout redirect in the WorkOS dashboard, users will see an error when logging out.
Navigate to the authentication endpoint we created and sign up for an account. You can then sign in with the newly created credentials and see the user listed in the Users section of the WorkOS Dashboard.