Mastering Vibe Coding: Essential Skills for the Future of Tech
Vibe coding is transforming software development by letting developers use AI to generate code through conversation, fundamentally changing the way software is built. Coined by Andrej Karpathy in February 2025, vibe coding allows developers to describe their requirements in natural language, which AI models then translate into working code.
What is Vibe Coding
Vibe coding is a new, AI-powered approach to software development where developers write code by describing what they want in natural language, and an AI agent (like GitHub Copilot, Claude, or Cursor) generates the code for them.
In Simple Terms:
It’s like saying: “Build a login screen with Google OAuth and passwordless email auth”
And the AI writes the code, sets up the UI, and maybe even deploys it — all through a conversational process.
The Rise of Vibe Coding and Agentic AI
- Vibe Coding = building software by conversing with AI agents (like Claude 4, Copilot, Cursor).
- Agentic AI can reason, act, and interact with systems to complete tasks autonomously.
- VSCode Agent Mode and GitHub Copilot (with Claude Sonnet 4) are leading this movement.
- Gartner named Agentic AI the top tech trend of 2025.
Referencs: Suggestions for Successful Agentic Development
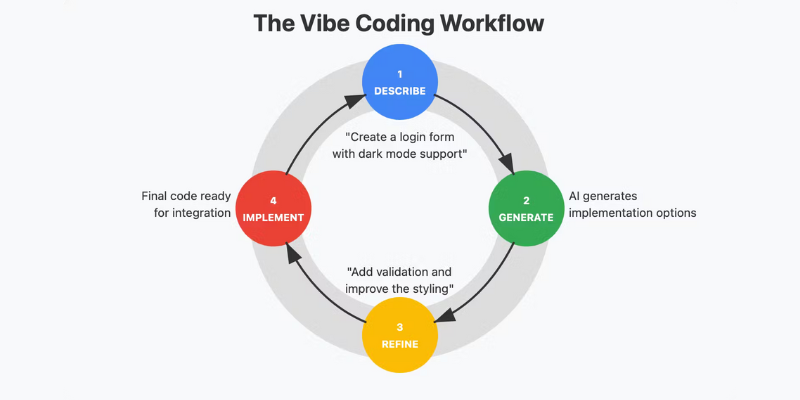
The Mechanics of Vibe Coding
Vibe coding simplifies the coding process with a conversational approach. Developers follow these steps:
- Describe their requirements in plain language, akin to explaining concepts to a colleague.
- Review AI-generated options, often multiple implementations.
- Provide feedback on the AI’s output, identifying what works and what doesn’t.
- Refine the output through iterative conversation until the code meets specifications.
This technique turns coding into a dialogue with AI, enhancing productivity significantly. Tools like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Replit are pivotal in facilitating this new workflow.
Key Features of Vibe Coding
| Aspect | Description |
| Conversational | Developers talk to AI in natural language — like giving instructions to a teammate. |
| Agentic AI | The AI doesn’t just autocomplete — it reasons, iterates, and can even run/test/debug code. |
| Iterative | You guide the AI by refining the output until it meets your needs. |
| Speed-focused | Helps build MVPs, UI flows, or backend logic much faster than traditional hand-coding. |
| Tools like | Cursor, Copilot, Replit Ghostwriter, Claude Code, Windsurf, DevIn, and Sourcegraph Cody. |
Difference Between Traditional Coding and Vibe Coding
While traditional coding and vibe coding both aim to build functional software, the way developers interact with the tools and logic is fundamentally different. Below is a breakdown of how these two paradigms compare:
| Aspect | Traditional Coding | Vibe Coding |
| Interaction Model | Developers manually write code line-by-line in a text editor or IDE | Developers describe functionality in plain language; AI generates code through a conversation |
| Tooling | Requires knowledge of specific programming languages, frameworks, and syntax | Uses AI coding assistants like GitHub Copilot, Claude, Cursor, and Replit |
| Speed | Slower—especially in early development or prototyping phases | Rapid MVP and feature delivery by skipping boilerplate and scaffolding |
| Learning Curve | Steeper; beginners must learn to code from scratch | Lower barrier to entry; ideal for those who can describe logic clearly but lack deep coding experience |
| Code Ownership | Full control over every line, with high precision | AI takes first pass; developers act more like reviewers, editors, and system designers |
| Error Handling | Debugging done manually with logs, breakpoints, etc. | Some tools support auto-debugging or error correction via conversational refinement |
| Best Use Cases | Mission-critical systems, low-level programming, custom algorithms | UI/UX development, CRUD apps, integrations, internal tools, rapid experiments |
| Collaboration Model | Developer-centric; collaboration often requires shared codebases | More fluid; teams can align faster around feature specs while AI does the heavy lifting |
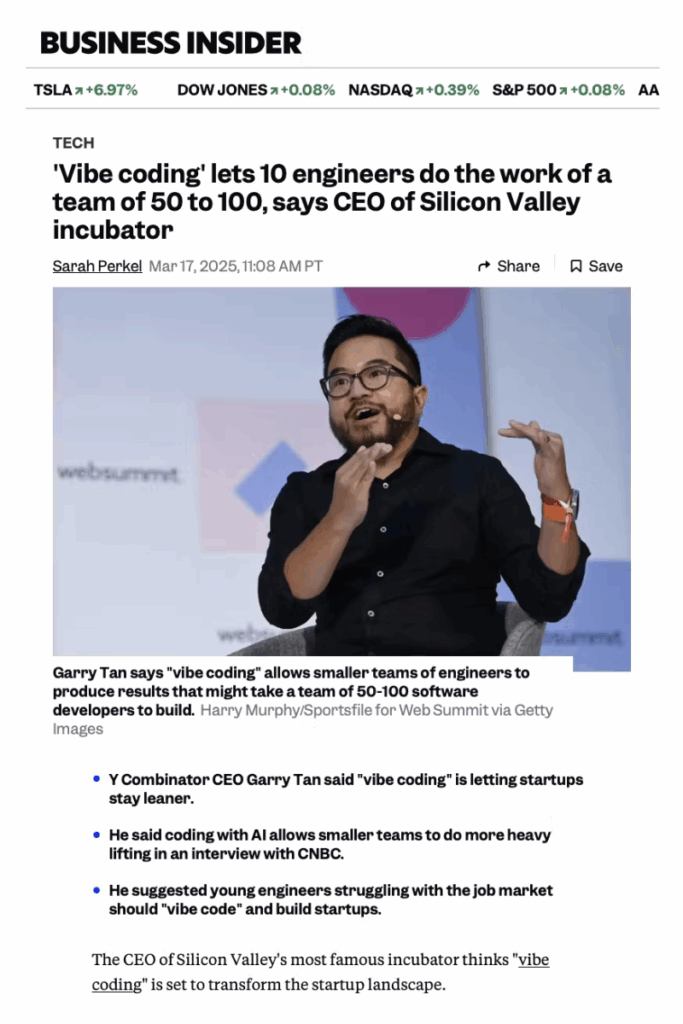
Why Companies Are Adopting Vibe Coding
Data from Y Combinator indicates that a quarter of their Winter 2025 cohort has codebases that are 95% AI-generated. This shift allows startups to operate with fewer engineers—10 engineers can now accomplish the work that once required 50-100. Garry Tan, Y Combinator’s CEO, highlighted this transformation, noting substantial efficiency gains. Companies leveraging vibe coding report completing in weeks what traditionally took months.
Where Vibe Coding Works Best
- Rapid prototyping
- UI/UX development
- Repetitive backend tasks
- Solo projects or early-stage startups
- Code scaffolding and refactoring
Essential Skills for Vibe Coders
Success in this new coding paradigm requires a unique skill set:
- Clear Communication: Articulating technical requirements effectively.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying when AI-generated code requires adjustments.
- Systems Thinking: Understanding how various components interact.
- UX Intuition: Prioritizing user experience in final products.
Karpathy emphasizes that while technical knowledge remains valuable, it is more crucial to recognize good code than to write every line independently.
When Vibe Coding Excels and Its Limitations
Vibe coding is particularly effective for:
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly developing minimum viable products (MVPs).
- User Interfaces: Designing responsive and modern front-end applications.
- Standard Features: Implementing common functionalities like authentication or payment processing.
- Solo Projects: Allowing individual developers to achieve what typically requires teams.
However, challenges arise in areas such as:
- Complex Algorithms: Where mathematical precision is critical.
- Mission-Critical Systems: Like healthcare or financial applications where bugs can have severe repercussions.
- Security-Sensitive Components: Where AI could inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities.
- Legacy System Integration: Where undocumented code behaviors pose challenges for AI.
A cloud architect’s experience highlights the risks: an AI-generated infrastructure code for Azure missed crucial security configurations, resulting in significant issues post-deployment.
Career Implications in the Vibe Coding Era
Developers must adapt their strategies based on experience level:
Junior Developers:
- Utilize tools like GitHub Copilot to enhance learning.
- Focus on understanding AI-generated code rather than just using it.
- Participate in AI developer communities on platforms like Discord and LinkedIn.
Mid-Level Developers:
- Integrate AI into existing workflows while maintaining traditional skills.
- Develop expertise in evaluating and refining AI outputs.
- Use AI to automate tedious tasks, allowing time for creative endeavors.
Senior Developers and Tech Leads:
- Create strategies for incorporating vibe coding into team processes.
- Establish review protocols for AI-generated code.
- Focus on system design skills that AI struggles with, ensuring effective team training in prompt engineering.
A balanced approach is crucial, as one developer noted, “Our team still writes traditional code when it makes sense, but we can now build 5x faster by knowing when and how to leverage AI.”
The Future of Software Development
The emergence of vibe coding signals a shift towards a more conversational form of programming. While this trend can democratize coding, it also raises questions about the future of software engineering roles. The ability to articulate requirements and manage AI outputs will become increasingly critical.
Vibe coding does not eliminate the need for skilled developers; instead, it reshapes their roles. As companies embrace these changes, SSOJet’s API-first platform offers secure SSO and user management solutions tailored for enterprise clients, featuring directory sync, SAML, OIDC, and magic link authentication. Explore our services to enhance your development processes effectively.
For more information, visit SSOJet at https://ssojet.com.
FAQs
1. What is the main goal of vibe coding?
Vibe coding aims to simplify and accelerate software development by allowing developers to describe what they want in natural language, while AI agents generate the corresponding code. This conversational approach helps teams build faster, iterate more smoothly, and focus on higher-level system design.
2. Which tools are best for getting started with vibe coding?
Popular tools for vibe coding include GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Replit Ghostwriter, Claude Code, Windsurf, and DevIn. These tools provide AI-powered code suggestions, UI generation, and even deployment capabilities through natural-language interactions.
3. Is vibe coding replacing traditional software development?
No, vibe coding is not replacing traditional development—it’s augmenting it. While AI can generate standard or repetitive code, human developers are still essential for system architecture, complex logic, and security-critical applications. The best results come from a hybrid workflow.
4. How can junior developers benefit from vibe coding?
Vibe coding can be an excellent learning tool for junior developers. It helps them quickly prototype ideas, understand how different components work, and receive real-time feedback from AI-generated code—all while building foundational coding and communication skills.

