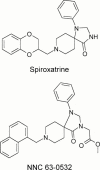
(8-Naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-spiro[4. 5]dec-3-yl)-acetic acid methyl ester (NNC 63-0532) is a novel potent nociceptin receptor agonist
- PMID: 11053209
- PMCID: PMC1572417
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703661
(8-Naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-spiro[4. 5]dec-3-yl)-acetic acid methyl ester (NNC 63-0532) is a novel potent nociceptin receptor agonist
Abstract
Spiroxatrine was identified as a moderately potent (K:(i)=118 nM) but non-selective agonist at the human nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor, ORL1. This compound was subject to chemical modification and one of the resulting compounds, (8-naphthalen-1-ylmethyl-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triaza-s piro[4. 5]dec-3-yl)-acetic acid methyl ester (NNC 63-0532) was shown to have high affinity for ORL1 (K:(i)=7.3 nM). NNC 63-0532 showed only moderate affinity for the following receptors (K:(i) values in parentheses): mu-opioid (140 nM), kappa-opioid (405 nM), dopamine D(2S) (209 nM), dopamine D(3) (133 nM) and dopamine D(4.4) (107 nM) out of 75 different receptors, ion-channels and transporters. In functional assays, NNC 63-0532 was shown to be an agonist at ORL1 (EC(50)=305 nM), a much weaker agonist at the mu-opioid receptor (EC(50)>10 microM) and an antagonist or weak partial agonist at dopamine D(2S) (IC(50)=2830 nM). Thus, NNC 63-0532 is a novel non-peptide agonist with approximately 12 fold selectivity for ORL1 and may be useful for exploring the physiological roles of this receptor owing to its brain-penetrating properties.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Distribution of nociceptin and Ro64-6198 activated [35S]-GTPgammaS binding in the rat brain.Neuropeptides. 2006 Apr;40(2):95-105. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2005.11.002. Epub 2006 Jan 3. Neuropeptides. 2006. PMID: 16403422
-
Opioid activity profiles indicate similarities between the nociceptin/orphanin FQ and opioid receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb 18;389(2-3):107-14. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00904-8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10688973
-
Nonpeptide/peptide chimeric ligands for the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor: design, synthesis and in vitro pharmacological activity.J Pept Res. 2004 Jun;63(6):477-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.2004.00157.x. J Pept Res. 2004. PMID: 15175020
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helix-constrained nociceptin peptides are potent agonists and antagonists of ORL-1 and nociception.Vitam Horm. 2015;97:1-55. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2014.10.001. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Vitam Horm. 2015. PMID: 25677767 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide and nonpeptide ligands for the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor ORL1: research tools and potential therapeutic agents.Life Sci. 2003 Jun 27;73(6):663-78. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00387-4. Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12801588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biased Opioid Ligands.Molecules. 2020 Sep 16;25(18):4257. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184257. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32948048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of opiates, neuroleptics, and synthetic analogs at ORL1 and opioid receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Sep 28;428(1):29-36. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01282-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11779034 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel, Selective, and Nonbasic Agonists for the Kappa-Opioid Receptor Determined by Salvinorin A-Based Virtual Screening.J Med Chem. 2024 Aug 22;67(16):13788-13801. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00590. Epub 2024 Aug 1. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39088801 Free PMC article.
-
Structure- and conformation-activity studies of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor dimeric ligands.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 6;7:45817. doi: 10.1038/srep45817. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28383520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADAPA I.D., TOLL L. Relationship between binding affinity and functional activity of nociceptin/orphanin FQ. Neuropeptides. 1997;31:403–408. - PubMed
-
- ALBRECHT E., SAMOVILOVA N.N., OSWALD S., BAEGER I., BERGER H. Nociceptin (orphanin FQ): high-affinity and high capacity binding site coupled to low potency stimulation of guanylyl-5′-o-(γ-thio)-triphosphate binding in rat brain membranes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;286:896–902. - PubMed
-
- ARDATI A., HENNINGSEN R.A., HIGELIN J., REINSCHEID R.K., CIVELLI O., MONSMA F.J. Interaction of [3H]orphanin FQ and 125I-Tyr14-orphanin FQ with the orphanin FQ receptor: kinetics and modulation by cations and guanine nucleotides. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997;51:816–824. - PubMed
-
- BUTOUR J.L., MOISAND C., MAZARGUIL H., MOLLEREAU C., MEUNIER J.C. Recognition and activation of the opioid receptor-like ORL 1 receptor by nociceptin, nociceptin analogs and opioids. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;321:97–103. - PubMed
-
- DARLAND T., HEINRICHER M.M., GRANDY D.K. Orphanin FQ/nociceptin – a role in pain and analgesia, but so much more. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:215–221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

