Abstract
Introduction
Aging has been shown to be associated with decreases in brain and muscle tissues, accompanied by dysfunction in cognition and functionality, respectively. Resistance training (RT) has been widely recommended to mitigate muscle loss but its effects on brain tissue are still unclear.
Purpose
This study verified the effects of 12 weeks of RT on gray matter density in elderly.
Methods
Seven participants (four men and three women; 61.3 ± 2.8 years; 68.7 ± 16.5 kg; 161 ± 12 cm) had the brain anatomy and thigh cross sectional area obtained through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before and after RT. Gray matter density was then separated and compared between pre and post exercise intervention.
Results
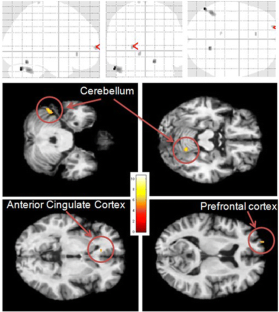
Data showed that RT promoted increases in gray matter density in the posterior and anterior lobe of cerebellum, superior frontal gyrus in the frontal lobe and anterior cingulate cortex in the limbic lobe (p < 0.001). Additionally, RT also increased thigh cross-sectional area and muscle strength (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Our study indicates that resistance training may be an alternative intervention to improve neuronal density in brain regions related to motor control and cognition in the elderly.
References
Tisserand DJ, van Boxtel MP, Pruessner JC, Hofman P, Evans AC, Jolles J (2004) A voxel-based morphometric study to determine individual differences in gray matter density associated with age and cognitive change over time. Cereb Cortex 14(9):966–973
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14(1 Pt 1):21–36
Fjell AM, Walhovd KB (2010) Structural brain changes in aging: courses, causes and cognitive consequences. Rev Neurosci 21(3):187–221
Frontera WR, Hughes VA, Fielding RA, Fiatarone MA, Evans WJ, Roubenoff R (2000) Aging of skeletal muscle: a 12-year longitudinal study. J Appl Physiol 88(4):1321–1326
Hunter GR, McCarthy JP, Bamman MM (2004) Effects of resistance training on older adults. Sports Med 34(5):329–348
Moreland JD, Richardson JA, Goldsmith CH, Clase CM (2004) Muscle weakness and falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 52(7):1121–1129
Leavitt VM, Cirnigliaro C, Cohen A, Farag A, Brooks M, Wecht JM, Wylie GR, Chiaravalloti ND, DeLuca J, Sumowski JF (2013) Aerobic exercise increases hippocampal volume and improves memory in multiple sclerosis: preliminary findings. Neurocase 20(6):695–697
Tseng BY, Uh J, Rossetti HC, Cullum CM, Diaz-Arrastia RF, Levine BD, Lu H, Zhang R (2013) Masters athletes exhibit larger regional brain volume and better cognitive performance than sedentary older adults. J Magn Reson Imaging 38(5):1169–1176
Colcombe SJ, Erickson KI, Scalf PE, Kim JS, Prakash R, McAuley E, Elavsky S, Marquez DX, Hu L, Kramer AF (2006) Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61(11):1166–1170
ACSM (1998) American college of sports medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30(6):992–1008
ACSM (2009) American college of sports medicine position stand. Exercise and physical activity for older adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(7):1510–1530
Acsm (2011) American college of sports medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(7):1334–1359
Acsm (2009) American college of sports medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(3):687–708
Liu-Ambrose T, Donaldson MG (2009) Exercise and cognition in older adults: is there a role for resistance training programmes? Br J Sports Med 43(1):25–27
Erickson KI, Leckie RL, Weinstein AM (2014) Physical activity, fitness, and gray matter volume. Neurobiol Aging 35(Suppl 2):S20–S28
Stephan S, de Castro Pereira CA, Coletta EM, Ferreira RG, Otta JS, Nery LE (2007) Oxygen desaturation during a 4-min step test: predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 24(1):70–76
Burdette JH, Laurienti PJ, Espeland MA, Morgan A, Telesford Q, Vechlekar CD, Hayasaka S, Jennings JM, Katula JA, Kraft RA, Rejeski WJ (2010) Using network science to evaluate exercise-associated brain changes in older adults. Front Aging Neurosci 2:23
Black JE, Isaacs KR, Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Greenough WT (1990) Learning causes synaptogenesis, whereas motor activity causes angiogenesis, in cerebellar cortex of adult rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(14):5568–5572
Wright IC, McGuire PK, Poline JB, Travere JM, Murray RM, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS, Friston KJ (1995) A voxel-based method for the statistical analysis of gray and white matter density applied to schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2(4):244–252
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2001) Why voxel-based morphometry should be used. NeuroImage 14(6):1238–1243
Whitwell JL, Josephs KA (2007) Voxel-based morphometry and its application to movement disorders. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13(Suppl 3):S406–S416
Li J, Pan P, Huang R, Shang H (2012) A meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies of white matter volume alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(2):757–763
Jacini WF, Cannonieri GC, Fernandes PT, Bonilha L, Cendes F, Li LM (2009) Can exercise shape your brain? Cortical differences associated with judo practice. J Sci Med Sport 12(6):688–690
Florindo A, Latorre M (2003) Validação e reprodutibilidade do questionário de Baecke de avaliação da atividade física habitual em homens adultos. Rev Bras Med Esporte 9(3):7
Bertolucci PH, Brucki SM, Campacci SR, Juliano Y (1994) The mini-mental state examination in a general population: impact of educational status. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 52(1):1–7
Brown LE, Weir JP (2001) Procedures recommendation I: Accurate assessment of muscular strength and power. J Exerc Physiol Online 4:1–21
Bernard JA, Seidler RD (2014) Moving forward: age effects on the cerebellum underlie cognitive and motor declines. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 42:193–207
Groiss SJ, Ugawa Y (2013) Cerebellum. Handb Clin Neurol 116:643–653
Carson RG (2006) Changes in muscle coordination with training. J Appl Physiol 101(5):1506–1513
Folland JP, Williams AG (2007) The adaptations to strength training : morphological and neurological contributions to increased strength. Sports Med 37(2):145–168
Gabriel DA, Kamen G, Frost G (2006) Neural adaptations to resistive exercise: mechanisms and recommendations for training practices. Sports Med 36(2):133–149
Shackman AJ, Salomons TV, Slagter HA, Fox AS, Winter JJ, Davidson RJ (2011) The integration of negative affect, pain and cognitive control in the cingulate cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(3):154–167
Goldberg II, Harel M, Malach R (2006) When the brain loses its self: prefrontal inactivation during sensorimotor processing. Neuron 50(2):329–339
Tsai CL, Wang CH, Pan CY, Chen FC (2015) The effects of long-term resistance exercise on the relationship between neurocognitive performance and GH, IGF-1, and homocysteine levels in the elderly. Front Behav Neurosci 9:23
Mehta RK (2016) Stunted PFC activity during neuromuscular control under stress with obesity. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(2):319–326
Frontera WR, Meredith CN, O’Reilly KP, Knuttgen HG, Evans WJ (1988) Strength conditioning in older men: skeletal muscle hypertrophy and improved function. J Appl Physiol 64(3):1038–1044
Frontera WR, Reid KF, Phillips EM, Krivickas LS, Hughes VA, Roubenoff R, Fielding RA (2008) Muscle fiber size and function in elderly humans: a longitudinal study. J Appl Physiol 105(2):637–642
Stewart VH, Saunders DH, Greig CA (2014) Responsiveness of muscle size and strength to physical training in very elderly people: a systematic review. Scand J Med Sci Sports 24(1):e1–e10
Ozcan A, Donat H, Gelecek N, Ozdirenc M, Karadibak D (2005) The relationship between risk factors for falling and the quality of life in older adults. BMC Public Health 5:90
Voss MW, Vivar C, Kramer AF, van Praag H (2013) Bridging animal and human models of exercise-induced brain plasticity. Trends Cogn Sci 17(10):525–544
Kobilo T, Liu QR, Gandhi K, Mughal M, Shaham Y, van Praag H (2011) Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment. Learn Mem 18(9):605–609
Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Voss MW, Chaddock L, Hu L, Morris KS, White SM, Wojcicki TR, McAuley E, Kramer AF (2009) Aerobic fitness is associated with hippocampal volume in elderly humans. Hippocampus 19(10):1030–1039
Weinstein AM, Voss MW, Prakash RS, Chaddock L, Szabo A, White SM, Wojcicki TR, Mailey E, McAuley E, Kramer AF, Erickson KI (2012) The association between aerobic fitness and executive function is mediated by prefrontal cortex volume. Brain Behav Immun 26(5):811–819
Sehm B, Taubert M, Conde V, Weise D, Classen J, Dukart J, Draganski B, Villringer A, Ragert P (2014) Structural brain plasticity in Parkinson’s disease induced by balance training. Neurobiol Aging 35(1):232–239
Wallerstein LF, Tricoli V, Barroso R, Rodacki AL, Russo L, Aihara AY, da Rocha Correa Fernandes A, de Mello MT, Ugrinowitsch C (2012) Effects of strength and power training on neuromuscular variables in older adults. J Aging Phys Act 20(2):171–185
Persch LN, Ugrinowitsch C, Pereira G, Rodacki AL (2009) Strength training improves fall-related gait kinematics in the elderly: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 24:819–825. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2009.07.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was funded by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development- CNPq/Brazil: 476107/2011-3. EBF received a scholarship from FAPESP # 2011/01466-8; AHO received a scholarship from FAPESP # 13/10187-0. CU was supported by CNPq (304205/2011-7, 500388/2012-1) and FAPESP (2012/22817-6).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontes, E.B., Libardi, C.A., Castellano, G. et al. Effects of resistance training in gray matter density of elderly. Sport Sci Health 13, 233–238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-016-0298-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-016-0298-5

