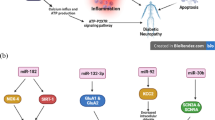
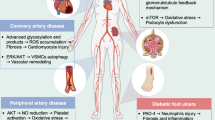
Abstract
In today’s culture, obesity and overweight are serious issues that have an impact on how quickly diabetes develops and how it causes complications. For the development of more effective therapies, it is crucial to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the chronic problems of diabetes. The most prominent effects of diabetes are microvascular abnormalities such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, especially diabetes foot ulcers, as well as macrovascular abnormalities such as heart disease and atherosclerosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which are highly conserved endogenous short non-coding RNA molecules, have been implicated in several physiological functions recently, including the earliest stages of the disease. By binding to particular messenger RNAs (mRNAs), which cause mRNA degradation, translation inhibition, or even gene activation, it primarily regulates posttranscriptional gene expression. These molecules exhibit considerable potential as diagnostic biomarkers for disease and are interesting treatment targets. This review will provide an overview of the latest findings on the key functions that miRNAs role in diabetes and its complications, with an emphasis on the various stages of diabetic wound healing.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- DFU:
-
Diabetes foot ulcer
- MMP:
-
Metalloproteinase
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- DN:
-
Diabetes neuropathy
- PDGF:
-
Platelet derived growth factor
- EC :
-
Extracellular
- 5-HT:
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
- RBC:
-
Red blood cells
- HMGB-1:
-
High mobility group box-1
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- NFKB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells
- IRAK-1:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1
- TRAF6:
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor-6
- HIC-5:
-
Hydrogen peroxideinducible clone 5
- HIC-5 :
-
Hydrogen peroxideinducible clone 5
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase-C
- T2D :
-
Type 2 diabetess
- DM:
-
Diabetes Mellitus
- miRNA:
-
MacroRNA
- mRNA :
-
Messenger RNAs
- AGE:
-
Advanced glycation end products
- USD:
-
United States dollars
- US:
-
United States
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- FGF2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor-2
- DPN:
-
Diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- DN:
-
Diabetes neuropathy
- PVD :
-
Peripheral vascular disease
- PAD:
-
Peripheral artery disease
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- M1:
-
Pro-inflammatory phenotype
- M2:
-
Anti-inflammatory phenotype
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- RNAi :
-
RNA inference
- NETs:
-
Neutrophil extracellular trap
- TIMPs:
-
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases
- GTPase:
-
GTP-binding proteins
- SHIP1:
-
SH-2 containing inositol 5’ polyphosphate 1
- FIZZ1:
-
Inflammatory zone protein
- BCL-6:
-
B-cell lymphoma 6
- STAT4:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4
- IFN- γ:
-
Interferon-gamma
- NK Cells:
-
Natural killer cells
- PDCD-4:
-
Programmed Cell Death 4
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens-1
- DAXX:
-
Death-domain associated protein
- GLUT-1:
-
Glucose transporter 1
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- TSP-1:
-
Thrombospondin 1
- TSP-2:
-
Thrombospondin-2
- MTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- IGF1R:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- SIRT-1:
-
Sirtuin (silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog) 1
- SMAD-4:
-
SMAD family member 4
- E2F3:
-
E2F Transcription Factor 3
- COL3A1:
-
Collagen, type III, alpha 1
- COL4A1:
-
Collagen, type IV, alpha 1
- COL4A2:
-
Collagen, type IV, alpha 2
- COL5A1:
-
Collagen, type V, alpha 1
- COLIA1:
-
Collagen, type I, alpha 1
- ZEB2:
-
Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 2
- ZEB1:
-
Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1
- HBEGF:
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- HBOT:
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- NPWT:
-
Negative pressure wound therapy
- ESWT:
-
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- IL-10:
-
Interlukin-10
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumour necrosis factor
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- siRNA:
-
Short interfering RNA or Silencing RNA
- snoRNA :
-
Small nucleolar RNA
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
References
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW et al (2018) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281
Tuttolomondo A, Maida C, Pinto A (2015) Diabetic foot syndrome as a possible cardiovascular marker in diabetic patients. J Diabetes Res 2015:268390
Nellaiappan K, Preeti K, Khatri DK, Singh SB (2022) Diabetic complications: an update on pathobiology and therapeutic strategies. Current diabetes reviews. 18(1):31-44
Bhoomika, Sherkhane Gundu, Chayanika Anika, Sood Dharmendra Kumar, Khatri Shashi Bala, Singh (2021) Mitochondrial remodelling—a vicious cycle in diabetic complications Molecular Biology Reports 48(5):4721–4731 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06408-8
Donnelly R, Emslie-Smith AM, Gardner ID, Morris AD (2000) ABC of arterial and venous disease: vascular complications of diabetes. BMJ (Clinical Research ed) 320(7241):1062–1066
Sethuram L, Thomas J, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2022) A review on contemporary nanomaterial-based therapeutics for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) with special reference to the Indian scenario. Nanoscale Adv 4(11):2367–2398
Mattick JS, Makunin IV (2006) Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 15:R17–R29
Kurkipuro J, Mierau I, Wirth T, Samaranayake H, Smith W, Kärkkäinen HR et al (2022) Four in one-combination therapy using live Lactococcus lactis expressing three therapeutic proteins for the treatment of chronic non-healing wounds. PLoS ONE 17(2):e0264775
Nandy M (2022) Nandy. Relationship between RandD and financial performance in Indian pharmaceutical industry. Springer, Berlin
Bonnet JB, Nicolet G, Papinaud L, Avignon A, Duflos C, Sultan A (2022) Effects of social deprivation and healthcare access on major amputation following a diabetic foot Ulcer in a French administrative area: analysis using the French claim data. Diabet Med: J Br Diabet Assoc 39(6):e14820
de Miguel-Yanes JM, Jimenez-Garcia R, de Miguel-Diez J, Hernández-Barrera V, Carabantes-Alarcon D, Zamorano-Leon JJ et al (2022) Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the incidence and outcomes of COVID-19 needing hospital admission according to sex: retrospective cohort study using hospital discharge data in Spain, year 2022. J Clin Med. 11(9):2654
Ko KI, Sculean A, Graves DT (2021) Diabetic wound healing in soft and hard oral tissues. Trans Res: The J Lab Clin Med 236:72–86
Solarte David VA, Güiza-Argüello VR, Arango-Rodríguez ML, Sossa CL, Becerra-Bayona SM (2022) Decellularized tissues for wound healing: towards closing the gap between scaffold design and effective extracellular matrix remodeling. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:821852
Nahar N, Mohamed S, Mustapha NM, Fong LSJJD, Disorders M (2022) Protective effects of Labisia pumila against neuropathy in a diabetic rat model. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21(1):1–11
Singh K, Kumar J (2022) Current status of apple scab disease and management strategies in Uttaranchal Himalayas. Apple Academic Press, New Jersey, pp 1–29
Dhanalakshmi B, Shijith K, Sharma PJMJDDPV (2022) A prospective interventional study to assess the advantage of premedication with sublingual nitroglycerin in evaluation of peripheral vascular disease with computed tomography peripheral angiography. Med J Dr. DY Patil Univ 15(3):359
Alven S, Peter S, Mbese Z, Aderibigbe BAJP (2022) Polymer-based wound dressing materials loaded with bioactive agents: potential materials for the treatment of diabetic wounds. Polymers 14(4):724
Patel BK, Patel KH, Huang RY, Lee CN, Moochhala SMJIJMS (2022) The gut-skin microbiota axis and its role in diabetic wound healing—a rev based curr literature. Int J Mol Sci 23(4):2375
Bandyk DF (2018) The diabetic foot: pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment. Semin Vasc Surg 31(2–4):43–48
Li M, Huang S, Zhang Y, Song Z, Fu H, Lin Z et al (2022) Regulation of the unfolded protein response transducer IRE1α by SERPINH1 aggravates periodontitis with diabetes mellitus via prolonged ER stress. Cell Signal 91:110241
Mudigonda J, Chenicheri S, Ramachandran R (2022) Tissue engineering: Current Status and Challenges. Academic Press, pp 101–122
Wagner K, Unger L, Salman MM, Kitchen P, Bill RM, Yool AJ (2022) Signaling mechanisms and pharmacological modulators governing diverse aquaporin functions in human health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1388
Bannon P, Wood S, Restivo T, Campbell L, Hardman MJ, Mace KAJD et al (2013) Diabetes induces stable intrinsic changes to myeloid cells that contribute to chronic inflammation during wound healing in mice. Dis Models Mech 6(6):1434–1447
Zykova SN, Jenssen TG, Berdal M, Olsen R, Myklebust R, Seljelid RJD (2000) Altered cytokine and nitric oxide secretion in vitro by macrophages from diabetic type II-like db/db mice. Diabetes 49(9):1451–1458
Loot M, Kenter S, Au F, van Galen WJEJCB, Middelkoop E, Bos JD, Mekkes JR (2002) JR fibroblasts derived from chronic diabetic ulcers differ in their response to stimulation with EGF, IGF-I, bFGF and PDGF-AB compared to controls. Eur J Cell Biol 81:153
Velnar T, Bailey T, Smrkolj V (2009) The wound healing process: an overview of the cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Int Med Res 37(5):1528–1542
Rathinam VA, Fitzgerald KA (2016) Inflammasome complexes: emerging mechanisms and effector functions. Cell 165(4):792–800
Cheng F, Shen Y, Mohanasundaram P, Lindström M, Ivaska J, Ny T et al (2016) Vimentin coordinates fibroblast proliferation and keratinocyte differentiation in wound healing via TGF-β-Slug signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(30):E4320–E4327
DiPietro LA (2016) Angiogenesis and wound repair: when enough is enough. J Leukoc Biol 100(5):979–984
Mutschler W (2012) Physiology and pathophysiology of wound healing of wound defects. Unfallchirurg 115(9):767–773
Soliman AM, Das S, Abd Ghafar N, Teoh SL (2018) Role of MicroRNA in proliferation phase of Wound Healing. Front Genet 9:38
Karmaker M, Sanyal SK, Sultana M, Hossain MA (2016) Association of bacteria in diabetic and non-diabetic foot Infection – an investigation in patients from Bangladesh. J Infect Public Health 9(3):267–277
Tecilazich F, Dinh TL, Veves A (2013) Emerging drugs for the treatment of diabetic ulcers. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 18(2):207–217
Knighton DR, Halliday B, Hunt TK (1986) Oxygen as an antibiotic. A comparison of the effects of inspired oxygen concentration and antibiotic administration on in vivo bacterial clearance. Arch surg 121(2):191–195
Löndahl M, Katzman P, Nilsson A, Hammarlund C (2010) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy facilitates healing of chronic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 33(5):998–1003
Stojadinovic A, Elster EA, Anam K, Tadaki D, Amare M, Zins S et al (2008) Angiogenic response to extracorporeal shock wave treatment in murine skin isografts. Angiogenesis 11(4):369–380
Saggini R, Figus A, Troccola A, Cocco V, Saggini A, Scuderi N (2008) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for management of chronic ulcers in the lower extremities. Ultrasound Med Biol 34(8):1261–1271
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B et al (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408(6808):86–89
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ et al (2005) Comb microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37(5):495–500
Maqbool R, Ul Hussain M (2014) MicroRNAs and human diseases: diagnostic and therapeutic potential. Cell Tissue Res 358(1):1–15
Ying SY, Chang DC, Lin SL (2008) The microRNA (miRNA): overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol Biotechnol 38(3):257–268
Verdel A, Moazed D (2005) RNAi-directed assembly of heterochromatin in fission yeast. FEBS Lett 579(26):5872–5878
Yekta S, Shih IH, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNA-directed cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science 304(5670):594–596
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233
Qin B, Peng Q, Dong H, Lei L, Wu S (2023) Non-coding RNAs in diabetic foot ulcer- a focus on infected wounds. Diab/Metab Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3740
Tian M, Dong J, Yuan B, Jia H (2021) Identification of potential circRNAs and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in the development of diabetic foot ulcers by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Int Wound J 18(3):323–331
Li B, Luan S, Chen J, Zhou Y, Wang T, Li Z et al (2020) The MSC-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 promotes wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers by upregulating PTEN via microRNA-152-3p. Mol Therapy Nucleic Acids 19:814–826
Mirza RE, Fang MM, Weinheimer-Haus EM, Ennis WJ, Koh TJ (2014) Sustained inflammasome activity in macrophages impairs wound healing in type 2 diabetic humans and mice. Diabetes 63(3):1103–1114
Eming SA, Wynn TA, Martin P (2017) Inflammation and metabolism in tissue repair and regeneration. Science 356(6342):1026–1030
Tanaka K, Kim SE, Yano H, Matsumoto G, Ohuchida R, Ishikura Y et al (2017) MiR-142 is required for Staphylococcus aureus clearance at skin wound sites via small GTPase-Mediated regulation of the neutrophil actin cytoskeleton. J Invest Dermatol 137(4):931–940
Xu J, Wu W, Zhang L, Dorset-Martin W, Morris MW, Mitchell ME et al (2012) The role of microRNA-146a in the pathogenesis of the diabetic wound-healing impairment: correction with mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Diabetes 61(11):2906–2912
van Solingen C, Araldi E, Chamorro-Jorganes A, Fernández-Hernando C, Suárez Y (2014) Improved repair of dermal wounds in mice lacking microRNA-155. J Cell Mol Med 18(6):1104–1112
Shaked I, Meerson A, Wolf Y, Avni R, Greenberg D, Gilboa-Geffen A et al (2009) MicroRNA-132 potentiates cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting acetylcholinesterase. Immunity 31(6):965–973
Li D, Wang A, Liu X, Meisgen F, Grünler J, Botusan IR et al (2015) MicroRNA-132 enhances transition from inflammation to proliferation during wound healing. J Clin Investig 125(8):3008–3026
Recchiuti A, Krishnamoorthy S, Fredman G, Chiang N, Serhan CN (2011) MicroRNAs in resolution of acute inflammation: identification of novel resolvin D1-miRNA circuits. FASEB J: Off Publ Federation Am Soc Exp Biol 25(2):544–560
Liechty C, Hu J, Zhang L, Liechty KW, Xu J (2020) Role of microRNA-21 and its underlying mechanisms in inflammatory responses in diabetic wounds. Int J Mol Sci 21(9):3328
Herter EK, Xu Landén N (2017) Non-coding RNAs: new players in skin wound healing. Adv Wound Care 6(3):93–107
Dangwal S, Stratmann B, Bang C, Lorenzen JM, Kumarswamy R, Fiedler J et al (2015) Impairment of wound healing in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus influences circulating MicroRNA patterns via inflammatory cytokines. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35(6):1480–1488
Ghatak S, Chan YC, Khanna S, Banerjee J, Weist J, Roy S et al (2015) Barrier function of the repaired skin is disrupted following arrest of dicer in keratinocytes. Mol Therapy: J Am Soc Gene Therapy 23(7):1201–1210
Anand S, Majeti BK, Acevedo LM, Murphy EA, Mukthavaram R, Scheppke L et al (2010) MicroRNA-132-mediated loss of p120RasGAP activates the endothelium to facilitate pathological angiogenesis. Nat Med 16(8):909–914
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Nakajima Y, Omura S, Maruyama M (2012) MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound healing: promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int Wound J 9(4):355–361
Liu X, Abraham JM, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Zhang G et al (2018) Synthetic circular RNA functions as a miR-21 sponge to suppress gastric carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol Therapy Nucleic Acids 13:312–321
Icli B, Wara AK, Moslehi J, Sun X, Plovie E, Cahill M et al (2013) MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling. Circul Res 113(11):1231–1241
Liu B, Wu X, Liu B, Wang C, Liu Y, Zhou Q et al (2012) MiR-26a enhances Metastasis potential of lung cancer cells via AKT pathway by targeting PTEN. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(11):1692–1704
Wang JM, Tao J, Chen DD, Cai JJ, Irani K, Wang Q et al (2014) MicroRNA miR-27b rescues bone marrow-derived angiogenic cell function and accelerates wound healing in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(1):99–109
Jin Y, Tymen SD, Chen D, Fang ZJ, Zhao Y, Dragas D et al (2013) MicroRNA-99 family targets AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in dermal wound healing. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64434
Viticchiè G, Lena AM, Cianfarani F, Odorisio T, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Melino G et al (2012) MicroRNA-203 contributes to skin re-epithelialization. Cell Death Dis 3(11):e435
An J, Chen X, Chen W, Liang R, Reinach PS, Yan D et al (2015) MicroRNA expression profile and the role of miR-204 in corneal wound healing. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(6):3673–3683
Wang T, Zhao N, Long S, Ge L, Wang A, Sun H et al (2016) Downregulation of miR-205 in migrating epithelial tongue facilitates skin wound re-epithelialization by derepressing ITGA5. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862(8):1443–1452
Huang X, Zuo J (2014) Emerging roles of miR-210 and other non-coding RNAs in the hypoxic response. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 46(3):220–232
Okizaki S, Ito Y, Hosono K, Oba K, Ohkubo H, Amano H et al (2015) Suppressed recruitment of alternatively activated macrophages reduces TGF-β1 and impairs wound healing in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 70:317–325
Fahs F, Bi X, Yu FS, Zhou L, Mi QS (2015) New insights into microRNAs in skin wound healing. IUBMB Life 67(12):889–896
Ciechomska M, O’Reilly S, Suwara M, Bogunia-Kubik K, van Laar JM (2014) MiR-29a reduces TIMP-1 production by dermal fibroblasts via targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1 binding protein 1, implications for systemic sclerosis. PLoS ONE 9(12):e115596
Guo J, Lin Q, Shao Y, Rong L, Zhang D (2017) miR-29b promotes skin wound healing and reduces excessive scar formation by inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95(4):437–442
Bi S, Chai L, Yuan X, Cao C, Li S (2017) MicroRNA-98 inhibits the cell proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts via targeting Col1A1. Biol Res 50(1):22
Singh K, Sinha M, Pal D, Tabasum S, Gnyawali SC, Khona D et al (2019) Cutaneous epithelial to mesenchymal transition activator ZEB1 regulates wound angiogenesis and closure in a glycemic status-dependent manner. Diabetes 68(11):2175–2190
Diepenbruck M, Tiede S, Saxena M, Ivanek R, Kalathur RKR, Lüönd F et al (2017) Mir-1199-5p and Zeb1 function in a double-negative feedback loop potentially coordinating EMT and tumour metastasis. Nat Commun 8(1):1168
Zhao P, Wang S, Zhou Y, Zheng H, Zhao G (2017) MicroRNA-185 regulates spinal cord injuries induced by thoracolumbar spine compression fractures by targeting transforming growth factor-β1. Exp Ther Med 13(3):1127–1132
Ye J, Kang Y, Sun X, Ni P, Wu M, Lu SJT (2017) MicroRNA-155 inhibition promoted wound healing in diabetic rats. J Investig Dermatol 16(2):74–84
Li X, Li D, Wang A, Chu T, Lohcharoenkal W, Zheng X et al (2017) MicroRNA-132 with therapeutic potential in chronic wounds. J Investig Dermatol 137(12):2630–2638
Meisgen F, Xu Landén N, Bouez C, Zuccolo M, Gueniche A, Ståhle M et al (2014) Activation of toll-like receptors alters the microRNA expression profile of keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol 23(4):281–283
Pichu S, Vimalraj S, Viswanathan V (2021) Impact of microRNA-210 on wound healing among the patients with diabetic foot ulcer. PLoS ONE 16(7):e0254921
Wei Y, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Neth P, Weber C, Schober AJA (2013) MicroRNA-126,-145, and-155: a therapeutic triad in atherosclerosis? Thromb Vasc Biol 33(3):449–454
Wang B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Burns W, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Watson A et al (2010) E-cadherin expression is regulated by miR-192/215 by a mechanism that is Independent of the profibrotic effects of transforming growth factor-beta. Diabetes 59(7):1794–1802
Pritchard CC, Cheng HH, Tewari M (2012) MicroRNA profiling: approaches and considerations. Nat Rev Genet 13(5):358–369
Guay C, Regazzi R (2013) Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for diabetes mellitus. Nat Reviews Endocrinol 9(9):513–521
Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Rovira O, Guerra E, Esteve E et al (2014) Profiling of circulating microRNAs reveals common microRNAs linked to type 2 diabetes that change with insulin sensitization. Diabetes Care 37(5):1375–1383
Yang X, Wang J, Guo SL, Fan KJ, Li J, Wang YL et al (2011) miR-21 promotes keratinocyte migration and re-epithelialization during wound healing. Int J Biol Sci 7(5):685–690
Zampetaki A, Kiechl S, Drozdov I, Willeit P, Mayr U, Prokopi M et al (2010) Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circul Res 107(6):810–817
Nesca V, Guay C, Jacovetti C, Menoud V, Peyot ML, Laybutt DR et al (2013) Identification of particular groups of microRNAs that positively or negatively impact on beta cell function in obese models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 56(10):2203–2212
Al-Wahbi AM (2010) Impact of a diabetic foot care education program on lower limb amputation rate. Vasc Health Risk Manag 6:923–934
Martí-Carvajal AJ, Gluud C, Nicola S, Simancas-Racines D, Reveiz L, Oliva P et al (2015) Growth factors for treating diabetic foot ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015(10):Cd008548
Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M et al (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs.’ Nature 438(7068):685–689
Moura J, da Silva L, Cruz MT, Carvalho E (2013) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of bone morphogenetic proteins and activins in the skin: potential benefits for wound healing. Arch Dermatol Res 305(7):557–569
Sakai A, Saitow F, Miyake N, Miyake K, Shimada T, Suzuki H (2013) miR-7a alleviates the maintenance of neuropathic pain through regulation of neuronal excitability. Brain 136(Pt 9):2738–2750
Tellechea A, Leal E, Veves A, Carvalho EJTOC, Journal V (2010) Inflammatory and angiogenic abnormalities in diabetic wound healing: role of neuropeptides and therapeutic perspectives. Open Circ Vasc J. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874382601003010043
Kovacs B, Lumayag S, Cowan C, Xu S (2011) MicroRNAs in early diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(7):4402–4409
Alipour MR, Khamaneh AM, Yousefzadeh N, Mohammad-nejad D, Soufi FGJM (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-146a was not accompanied by downregulation of pro-inflammatory markers in diabetic kidney. Mol biol Rep 40:6477–6483
Kasiewicz LN, Whitehead KA (2019) Lipid nanoparticles silence Tumor necrosis factor α to improve wound healing in diabetic mice. Bioeng Translational Med 4(1):75–82
Acknowledgements
The Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, as well as the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER), Hyderabad, India, are all acknowledged by the authors for providing the necessary facilities, infrastructure, and financial support.
Funding
Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, Govt. of India, Department of Pharmaceutics, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER) Hyderabad, India, and also acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology (DST), Govt of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declares no Conflict of interest.
Human and animal participants
There are no studies by any of the writers in this article that used human or animal subjects.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors read and reviewed the manuscript and gave their consent for communication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anuradha, U., Mehra, N.K. & Khatri, D.K. Understanding molecular mechanisms and miRNA-based targets in diabetes foot ulcers. Mol Biol Rep 51, 82 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09074-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09074-0