Abstract
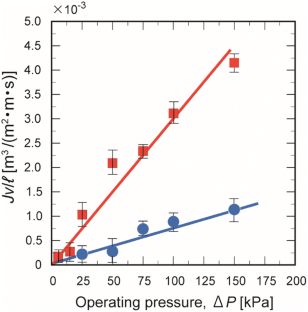
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) membranes have strong potential for application as molecular-scale separators. For this study, stable CMC membranes were fabricated with aluminum chloride (AlCl3) and iron(III) chloride (FeCl3) serving as cross-linkers. The resulting CMC-Al and CMC-Fe membranes were optically transparent and water-insoluble with sufficient mechanical strength for practical applications. The water permeation flux through the membranes was directly proportional to the operating pressure. With just a 10-fold increase in the molecular weight from 60 Da (urea) to 604 Da (bordeaux S), the effective diffusion coefficient (Deff) of the CMC-Al membrane increased 56-fold, and that of the CMC-Fe membrane increased 3500-fold. This significant correlation between Deff on molecular size indicated that the sizes of the mass transfer channels through the membrane were strictly monodisperse, in the range of molecular sizes that were tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A c :
-
Initial cross-sectional area of membrane [m2]
- A m :
-
Effective area of membrane [m2]
- C fi :
-
Initial concentration of the feed solution [mol/L]
- C s :
-
Concentration of the stripping solution [mol/L]
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient estimated from an empirical equation in bulk aqueous phase [m2/s]
- D eff :
-
Effective diffusion coefficient of membrane [m2/s]
- d :
-
Diameter of the glass petri dish [m]
- F max :
-
Maximum load at rupture [N]
- H V :
-
Volumetric water content of membrane, as defined by Eq. (1) [-]
- J V :
-
Volumetric water flux [\({\text{m}}_{\text{water}}^{3}\)/(\({\text{m}}_{\text{area}}^{2}\) s)]
- K OL :
-
Overall mass transfer coefficient [m/s]
- K −1 OL :
-
Overall mass transfer resistance [(m/s)−1]
- k −1 L1 :
-
Membrane mass transfer resistance on feed side [(m/s)−1]
- k −1 L2 :
-
Membrane mass transfer resistance on stripping side [(m/s)−1]
- k m :
-
Membrane mass transfer coefficient [m/s]
- k −1 m :
-
Membrane mass transfer resistance [(m/s)−1]
- L :
-
Length of membrane at rupture [m]
- L i :
-
Initial length of membrane [m]
- L p :
-
Water permeability coefficient [\({\text{m}}_{\text{water}}^{3}\)/(\({\text{m}}_{\text{area}}^{2}\) Pa s)]
- l m :
-
Initial thickness of swollen membrane [m]
- M P :
-
Mass of permeated water [kg]
- MW:
-
Molecular weight [Da]
- ΔP :
-
Operating pressure [Pa]
- t :
-
Operating time [s]
- V :
-
Volume of aqueous phase in each transfer cell [m3]
- V p :
-
Volumetric amount of permeated water [m3]
- w d :
-
Mass of the dried membrane [kg]
- w s :
-
Mass of the swollen membrane [kg]
- δ :
-
Tensile strength [Pa]
- λ :
-
Maximum strain [%]
- ΔΠ :
-
Osmotic pressure [Pa]
- ρ s :
-
Apparent density of the swollen membrane [kg/m3]
- ρ w :
-
Density of water [kg/m3]
- σ :
-
Reflection coefficient of solute [-]
- τ :
-
Tortuosity of the membrane [-]
References
Arthanareeswaran G, Thanikaivelan P, Srinivasn K, Mohan D, Rajendran M (2004) Eur Polym J 40:2153–2159
Baker RW (ed) (2012) 3rd membrane technology and applications. Wiley, Chichester
Yang Z, Ma XH, Tang CY (2018) Desalination 434:37–59
Pan K, Zhang X, Ren R, Cao B (2010) J Membr Sci 356:133–137
Petrychkovych R, Setnickova K, Uchytil P (2013) Sep Purif Technol 107:85–90
Nomura M, Sakanishi T, Utsumi YNK, Nakamura R (2013) Energy Procedia 37:1004–1011
Lue SJ, Chen CH, Shih CM, Tsai MC, Kuo CY, Lai JY (2011) J Membr Sci 379:330–340
Gierszewska M, Ostrowska-Czubenko J, Chrzanowska E (2018) Eur Polym J 101:282–290
Wandera D, Wickramasinghe SR, Husson SM (2011) J Membr Sci 373:178–188
Kadhom M, Deng B (2018) Appl Mater Today 11:219–230
Liu M, Yu S, Tao J, Gao C (2008) J Membr Sci 325:947–956
Liu B, Law AWK, Zhou K (2018) J Membr Sci 550:554–562
Wu C, Wu Y, Luo J, Xu T, Fu Y (2010) J Membr Sci 356:96–104
Xiong X, Duan J, Zou W, He X, Zheng W (2010) J Membr Sci 363:96–102
Ibrahim MM, Koschella A, Kadry G, Heinze T (2013) Carbohydr Polym 95:414–420
Sukma FM, Çulfaz-Emecen PZC (2018) J Membr Sci 545:329–336
Hofman JAMH, Beerendonk EF, Folmer HC, Kruithof JC (1997) Desalination 113:209–214
Murphy AP, Moody CD, Riley R, Lin SW, Murugaverl B, Rusin P (2001) J Membr Sci 193:111–121
Sayed SE, Mahmoud KH, Fatah AA, Hassen A (2011) Phys B 406:4068–4076
Hatanaka D, Yamamoto K, Kadokawa J (2014) Int J Biol Macromol 69:35–38
Chen YM, Sun L, Yang SA, Shi L, Zheng WJ, Wei Z, Hu C (2017) Eur Polym J 94:501–510
Liu Q, Zhang Y, Laskowski JS (2000) Int J Miner Process 60:229–245
Corin KC, Harris PJ (2010) Miner Eng 23:915–920
Pugh RJ (1989) Int J Miner Process 25:101–130
Rodgers KE, Robertson JT, Espinoza T, Oppelt W, Cortese S, diZerega GS, Berg RA (2003) Spine J 3:277–284
Huei GOS, Muniyandy S, Sathasivam T, Veeramachineni AK, Janarthanan P (2016) Chem Pap 70:243–252
Nie H, Liu M, Zhan F, Guo M (2004) Carbohydr Polym 58:185–189
Chitprasert P, Sudsai P, Rodklongtan A (2012) Carbohydr Polym 90:78–86
Sathasivam T, Muniyandy S, Chuah LH, Janarthanan P (2018) J Food Eng 231:10–21
Iannuccelli V, Fomi F, Vandelli MA, Bernabei MT, Forni F (1993) J Control Release 23:13–20
Hosny EA, Al-Helw AA (1998) Pharm Acta Helv 72:255–261
Wu P, Imai M (2013) Desalin Water Treat 51:5237–5247
Kashima K, Imai M (2017) Food Bioprod Process 102:213–221
Takahashi T, Imai M, Suzuki I (2008) Biochem Eng J 42:20–27
Sarkar C, Chowdhuri AR, Kumar A, Laha D, Garai S, Chakraborty J, Sahu SK (2018) Carbohydr Polym 181:710–718
Zhang W, Yu Z, Qian Q, Zhang Z, Wang X (2010) J Membr Sci 348:213–223
Boricha AG, Murthy ZVP (2010) Chem Eng J 157:393–400
Kedem O, Katchalsky A (1963) Trans Faraday Soc 59:1918–1930
Mehiguene K, Garba Y, Taha S, Gondrexon N, Dorange G (1999) Sep Purif Technol 15:181–187
Wu P, Imai M (2011) Desalin Water Treat 34:239–245
So MT, Eirich FR, Strathmann H, Baker RW (1973) J Polymer Sci Polym Lett Ed 11:201–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakayama, Ri., Yano, T., Namiki, N. et al. Highly Size-Selective Water-Insoluble Cross-Linked Carboxymethyl Cellulose Membranes. J Polym Environ 27, 2439–2444 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01532-w
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01532-w