A detailed guide to contributing to the Conveyor CI Driver runtime.
Introduction
A brief introduction on the Conveyor CI Driver runtime.
The Conveyor CI Driver runtime is a collection of SDKs(Software Development Kits) used by developers to build Conveyor CI Drivers. These SDKs are libraries that contain Utility functions that expose different Conveyor CI functionality. In this Guide we shall explore how one can contribute to the Conveyor CI Driver Runtime. This Guide is written to be language agnostic, meaning it can guide you to build or contribute to a driver runtime of your language of choice.
How the Driver Runtime Works
Lets explore what the Runtime is
What is the Driver Runtime
You can think of the Driver runtime as the wrapper of Driver applications and is the environment in which Drivers execute. You can define it as the software layer that provides necessary services, infrastructure, and behavior for executing the driver. Think of how language runtime work like the JVM, Go Runtime, V8, CPython etc. If you where to write a program in those languages, run in an environment that contains your code and the language runtime.
So even when building a Conveyor CI Driver, the final program is a combination of the Driver runtime and your custom Driver code.
What Features does it Provide
As mentioned earlier, the driver runtime provides necessary services and utilities for building CI Drivers. Some of these features are not just exclusive to the runtime but rather and extension of the base features provided by the Conveyor CI Ecosystem. These features include:
- A mealtime Event System: The driver runtime is designed to ensure drivers receive and publish events within the Conveyor System to ensure quick and instant execution of tasks.
- Log Management: The Driver runtime provided a Driver Logger, that provides drivers with functionality to export and save necessary logs in real-time. These can then be fetched or streamed in real-time or for future use.
- Horizontal Scaling: The Driver runtime provides out of the box Horizontal Scaling to Drivers, meaning once you build a driver. It comes with the ability to horizontally scale into a distributed system efficiently without you writing any custom code. This feature can be really important in Cloud Native environments.
- Conveyor CI API Server Interaction: No driver runtime package is complete without utility functions to interact with the Conveyor API Server to for example create and manipulate Resources.
- Observability out of the Box: The Driver runtime is designed to provide a comprehensive observability platform that follows all the three pillars that include Metrics, Tracing and Logging.
And many more...
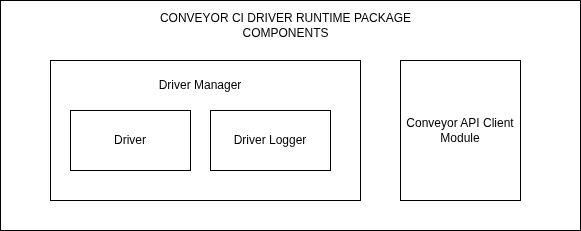
Driver runtime Components
The Driver runtime contains mainly two components. The Driver Manager and the Client Library.
Driver Manager
The Driver manager, the component that encapsulates the Driver and provides utilities that are used by the Driver. By design, it is usually a Class or a Class-like data type that has a run() method that is called to start the program. Its is responsible for the following functionality.
- Listening for events from Conveyor CI sent via NATS Jetstream: This is accomplished using JetStream Streams and Consumers. The Driver manager contains a Consumer that listens for events from the
messagesstream and filters out subjects depending on the resources that the Driver defines to listen to. - Provides the Driver Logger to the Driver. The driver logger is a component that collects logs from the driver and send them to Grafana Loki for Storage. After storing them it also streams them via a NATS connection on the subject with the following semantics
driver:{DRIVER_NAME}:logs:{RUN_ID}with the place holdersDRIVER_NAMEandRUN_IDreferring to the name of the driver and the current run id respectively. - Runs the
Reconcilefunction of the Drivers upon each event from JetStream and passes in the appropriate parameters.
Driver Logger
The Driver logger component is in charge of collecting logs from the Driver, sending them to Loki Grafana for storage and also streaming them via the NATs connection. It accomplished this by following the rules stated above in the Driver manager section
Driver
The Driver is the main component that developers interact with. It contains the Reconcile function that contains the custom code that includes the drivers intended functionality. When initializing it, the constructor must require the developer to specify the Resources that the driver wants to control, the driver name and also the Reconcile function. The Reconcile function, is a function that takes in these parameters. payload, event, driverName, logger.
Client Library
The client Library is a component of the driver runtime that contains functions that interact with the Conveyor CI API Server. these are normal HTTP Requests to the API Server. It also has the ability to fetch Conveyor CI API Server metadata like the API Host and Port.
Note: The Class Diagrams above represent the general expected Structure of those components however due to differences is language syntax and semantics in programming languages. The structure can be tweaked to provide the Developers a good user experience.
Component Diagram
Contributing Guide
Now that you have a solid understanding of the high level structure of the Driver runtime. Lets move on to the practical guide of the Workflow of Contributing to or building a driver runtime SDK package. Shall first go through the Development Environment setup then also go through the general contribution workflow followed when contributing to the source code of official Conveyor CI Driver runtime SDKs.
Environment Setup
To setup your environment to run conveyor, all you need is to have Docker installed on you computer. You can head over to the Docker Installation Page to install it on your system.
Once you have it, you will need to download two configuration files that are used to run Conveyor API Server and System dependencies. Head over to the Conveyor CI Releases Page and on the assests of the latest release, download compose.yml and loki.yml and store them in the same directory. Or you can simply run these commands.
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/open-ug/conveyor/releases/latest | grep browser_download_url | grep compose.yml | cut -d '"' -f 4 | xargs curl -L -o compose.yml
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/open-ug/conveyor/releases/latest | grep browser_download_url | grep loki.yml | cut -d '"' -f 4 | xargs curl -L -o loki.yml
Once you have both those files in the same directory, you can then start the Conveyor CI Containers by running.
docker compose up
# OR
docker compose up -d
Take note of the ports and host that these containers run no, or you can just open the
compose.ymlfile and see what ports are being exposed so when you are developing the packages, you are aware what ports and host to connect to. Also note that in-case its a requirement to set different Ports or you want to configure your own ports. always follow the convention of setting environment variableCONVEYOR_SERVER_HOSTandCONVEYOR_SERVER_PORT
Once you have everything running your are good to go onto development.
Workflow
We welcome contributions of all kinds, Whether you're fixing a typo, reporting a bug, improving documentation, or adding a new feature, your help is appreciated. However when contributing to the Driver runtime, you need to follow a specific contribution workflow.
There are multiple kinds of contributions we follow and they include
Reporting Bugs
If you find a bug, you can help fix it by submiting and issue to the appropriate repository. within your issue Include:
- A clear and descriptive title
- Steps to reproduce the issue
- What you expected to happen
- What actually happened
If the repository has an issue tempate. you should follow it.
Before submitting, check if the issue already exists in the repository issue list.
Suggesting Enhancements
We also welcome feature suggestions and ideas for improvement. When submitting a feature request:
- Explain why the feature is useful
- Provide example scenarios where it would help
- Suggest a possible implementation, if you have one
Try to keep requests focused and concise.
Submitting Code Changes
Once you have identified and issue or an enhancement you would like to work on. you can folloe this workflow to submit your code changes.
- Fork the repository
- Clone your fork:
git clone https://github.com/your-username/project-name.git
cd project-name
- Create a new branch:
git checkout -b feature/your-feature-name
# OR
git checkout -b fix/your-fixture-name
- Make your changes
- Write or update tests, if applicable
-
Commit your changes with clear messages:
git commit -m "feat: add new feature X" # OR git commit -m "fix: solved issue Y" -
Push your changes:
git push origin feature/your-feature-name Open a Pull Request on the GitHub repository and describe what you’ve done
Pull requests should be:
- Focused on a single change
- Thoroughly tested
- Aligned with project’s code style and guidelines
Improving Tests or Documentation
Improving test coverage and documentation is highly valuable. You can:
- Add test cases for untested components
- Update outdated documentation
- Fix typos or formatting issues
No contribution is too small!
Resources
A few resources that you might find useful when trying to understand the Conveyor System
NATS AND JETSTREAM RESOURCES
CONVEYOR GO PACKAGE AND DRIVER RUNTIME
OTHER RESOURCES







Top comments (0)