Project Introduction:
In this project, I automated the installation of Git on a remote Managed Host using an Ansible Playbook executed from a Control Host. The objective was to demonstrate real-world configuration management by securely provisioning software across systems using Ansible’s agentless architecture.
After setting up passwordless sudo access for the ansible user on the managed host, I created a playbook (install_git.yml) that uses the aptmodule to install Git, ensuring the system cache is updated and the package is present.
This project highlights core automation principles including:
- Playbook creation
- Privilege escalation with
become: yes - Secure SSH-based remote execution
- Inventory group targeting with Ansible
The successful execution of this playbook marks a key milestone in simplifying repeatable tasks in server administration — a foundational DevOps skill.
Let's begin...
Requirement:
Ensure you have enabled passwordless sudo on the managed-host.
Run the command on the managed-host as the ansible user;
su - ansible
sudo visudo
Add the command below at the end of the file.
ansible ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Save (CTRL+S) and exit (CTRL+X).
Creating the First Ansible Playbook
On the control-host, as the ansible user, create the playbook file:
Run the command: vi install_git.yml. An editor will open. Paste the following instructions into it. Remember to set paste (ESC KEY, then colon(:). type set paste and enter) then right click to paste. You do set paste so your instructions are well aligned when you paste. Exit editor (esc:wq enter).
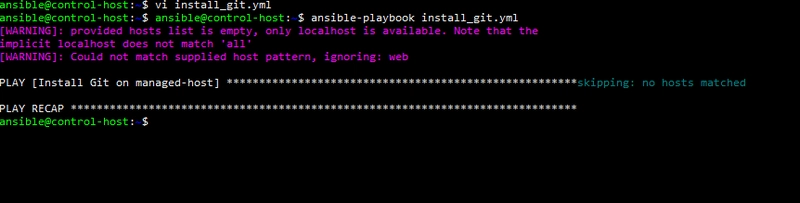
Run the command below to execute the Playbook:
ansible-playbook install_git.yml
Verify Git Installation on Work-station
Once the playbook runs successfully, In the** control-host*, **SSH* into the managed-host and check Git version:
ssh ansible@<managed-host ip>
git --version
You should see something like:
git version 2.43.0
Achievements: Installing Git Using Ansible Playbook
Granted passwordless sudo access to the ansible user on the Managed Host via
visudo.Created an Ansible playbook (
install_git.yml) to automate Git installation.Defined the target host group (web) in the playbook matching the inventory file.
Used
become: yesin the playbook to allow privilege escalation (sudo access).Included an** apt module** task to:
- Update the package cache
- Ensure Git is installed and up-to-date.
- Executed the playbook using the ansible-playbook command from the Control Host.
Successfully connected to the Managed Host over
SSHusing the ansible user.Verified the Git installation by running
git --versionon the Managed Host.






Top comments (0)