Abstract
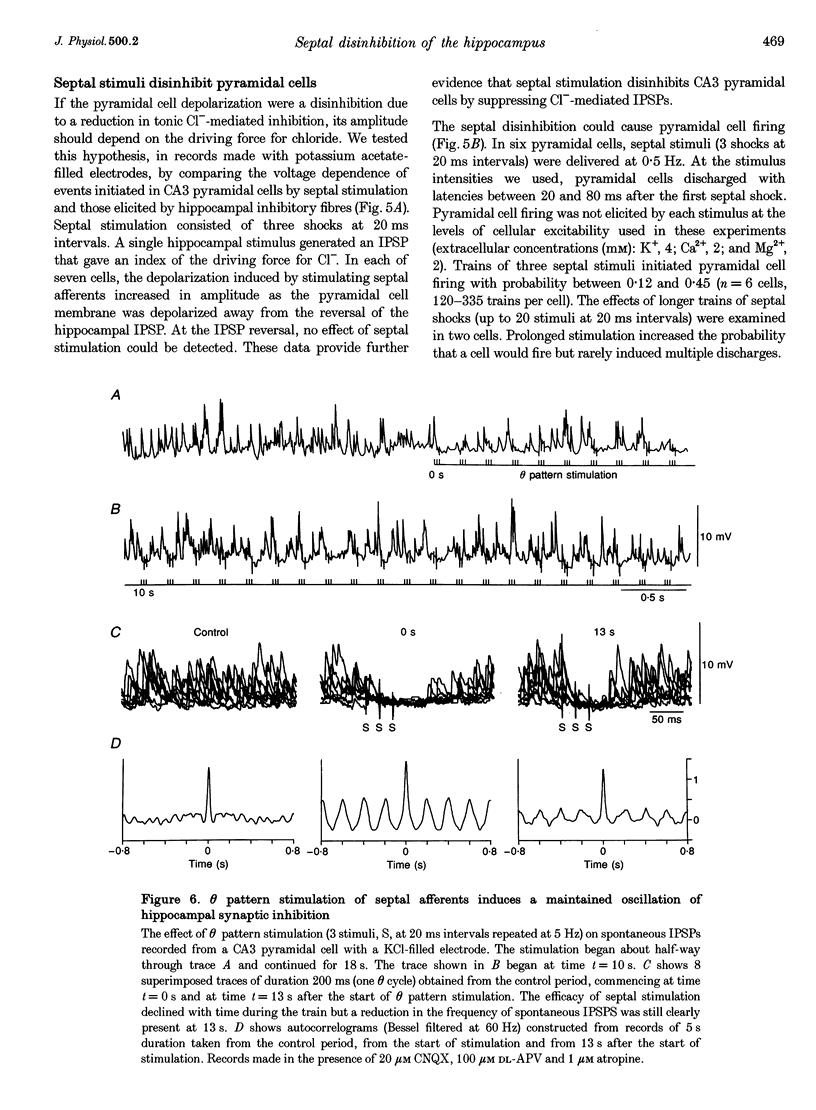
1. Slices were prepared from rat forebrain to include both the septum and the hippocampus in order to examine the effects of septal stimulation on hippocampal inhibitory circuits. 2. Repetitive stimulation of septo-hippocampal fibres caused a maintained decrease in the frequency of spontaneous IPSPs recorded from CA3 pyramidal cells in the presence of antagonists of excitatory amino acid receptors and of muscarine receptors. 3. In records made from pyramidal cells with CsCl-filled electrodes, IPSPs were examined at potentials both more positive and more negative than their reversal potential. Single septal stimuli hyperpolarized pyramidal cells when IPSPs were depolarizing events and depolarized them when IPSPs were hyperpolarizing. The GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin abolished the effects of septal stimulation. 4. Activation of septal afferents initiated an IPSP in hippocampal inhibitory cells but not in pyramidal cells. Septal IPSPs had similar kinetics to those initiated by local hippocampal stimulation and could suppress inhibitory cell discharge. 5. In pyramidal cells recorded with potassium acetate-filled electrodes, septal stimuli initiated a depolarization that increased with the driving force for Cl- and that could cause firing. 6. Rhythmic stimulation of septo-hippocampal fibres at 5 Hz initiated, in the hippocampus, a maintained out-of-phase oscillation of pyramidal cell discharge and inhibitory cell firing, as detected by the occurrence of spontaneous IPSPs. 7. These results suggest that GABAergic septo-hippocampal afferents selectively inhibit hippocampal inhibitory cells and so disinhibit pyramidal cells. This disinhibition could contribute to the transmission of the theta rhythm from the septum to the hippocampus.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso A., Khateb A., Fort P., Jones B. E., Mühlethaler M. Differential oscillatory properties of cholinergic and noncholinergic nucleus basalis neurons in guinea pig brain slice. Eur J Neurosci. 1996 Jan;8(1):169–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Krnjević K., Reinhardt W., Ropert N. Intracellular observations on the disinhibitory action of acetylcholine in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2475–2484. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilkey D. K., Goddard G. V. Medial septal facilitation of hippocampal granule cell activity is mediated by inhibition of inhibitory interneurones. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):823–828. doi: 10.1038/368823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caeser M., Brown D. A., Gähwiler B. H., Knöpfel T. Characterization of a calcium-dependent current generating a slow afterdepolarization of CA3 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Jun 1;5(6):560–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. R., Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Paulsen O., Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):75–78. doi: 10.1038/378075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. E., Ranck J. B., Jr Localization and anatomical identification of theta and complex spike cells in dorsal hippocampal formation of rats. Exp Neurol. 1975 Oct;49(1 Pt 1):299–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. D., MacVicar B. A. Low-threshold transient calcium current in rat hippocampal lacunosum-moleculare interneurons: kinetics and modulation by neurotransmitters. J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2812–2820. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Antal M. GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):170–173. doi: 10.1038/336170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F. GABAergic septohippocampal neurons contain parvalbumin. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 30;478(2):375–381. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M., Léránth C. Cholinergic innervation of the rat hippocampus as revealed by choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry: a combined light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 8;239(2):237–246. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., ARDUINI A. A. Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;17(6):533–557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getting P. A., Dekin M. S. Mechanisms of pattern generation underlying swimming in Tritonia. IV. Gating of central pattern generator. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Feb;53(2):466–480. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.2.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. A., McNaughton N., James D. T., Kelly P. H. Effect of minor tranquillisers on hippocampal theta rhythm mimicked by depletion of forebrain noradrenaline. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):424–425. doi: 10.1038/258424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Miles R., Hájos N., Freund T. F. Precision and variability in postsynaptic target selection of inhibitory cells in the hippocampal CA3 region. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Dec 1;5(12):1729–1751. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta P. T., Lisman J. E. Heightened synaptic plasticity of hippocampal CA1 neurons during a cholinergically induced rhythmic state. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):723–725. doi: 10.1038/364723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Jankowska E., Lindström S., Roberts W. Neuronal pathway of the recurrent facilitation of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):495–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab R. L., Leranth C. Synaptology and origin of somatostatin fibers in the rat lateral septal area: convergent somatostatinergic and hippocampal inputs of somatospiny neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 22;565(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91743-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk I. J., McNaughton N. Supramammillary cell firing and hippocampal rhythmical slow activity. Neuroreport. 1991 Nov;2(11):723–725. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199111000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Ropert N. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characteristics of facilitation of hippocampal population spikes by stimulation of the medial septum. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2165–2183. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Chan-Palay V., Wu J. Y. Septal neurons containing glutamic acid decarboxylase immunoreactivity project to the hippocampal region in the rat brain. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1984;169(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00300585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. S., Yim C. Y. Intracellular records of theta rhythm in hippocampal CA1 cells of the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 5;367(1-2):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91611-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C., Silver A. Confirmation from choline acetylase analyses of a massive cholinergic innervation to the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):215–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Tse F. W. Local neuronal circuitry underlying cholinergic rhythmical slow activity in CA3 area of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:197–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Tóth K., Gulyás A. I., Hájos N., Freund T. F. Differences between somatic and dendritic inhibition in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1996 Apr;16(4):815–823. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETSCHE H., STUMPF C., GOGOLAK G. [The significance of the rabbit's septum as a relay station between the midbrain and the hippocampus. I. The control of hippocampus arousal activity by the septum cells]. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1962 Apr;14:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(62)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncer J. C., Shinozaki H., Miles R. Dual modulation of synaptic inhibition by distinct metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1995 May 15;485(Pt 1):121–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Fox S. E. Do septal neurons pace the hippocampal theta rhythm? Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90040-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Fox S. E. Two populations of rhythmically bursting neurons in rat medial septum are revealed by atropine. J Neurophysiol. 1989 May;61(5):982–993. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tóth K., Borhegyi Z., Freund T. F. Postsynaptic targets of GABAergic hippocampal neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of broca complex. J Neurosci. 1993 Sep;13(9):3712–3724. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-09-03712.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winson J. Loss of hippocampal theta rhythm results in spatial memory deficit in the rat. Science. 1978 Jul 14;201(4351):160–163. doi: 10.1126/science.663646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylinen A., Soltész I., Bragin A., Penttonen M., Sik A., Buzsáki G. Intracellular correlates of hippocampal theta rhythm in identified pyramidal cells, granule cells, and basket cells. Hippocampus. 1995;5(1):78–90. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450050110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



