Configure the BGP Maximum-Prefix Feature
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes configuration and troubleshooting information on the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Maximum-Prefix feature.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of this topic:
Components Used
The information in this document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions, but the outputs were taken from these software versions:
- Cisco IOS® Software Releases 12.2(27)
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Background Information
This document provides configuration and troubleshooting information on the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Maximum-Prefix feature.
The BGP Maximum-Prefix feature allows you to control how many prefixes can be received from a neighbor.
By default, this feature allows a router to bring down a peer when the number of received prefixes from that peer exceeds the configured Maximum-Prefix limit.
This feature is commonly used for external BGP peers, but can be applied to internal BGP peers also.
The Maximum-Prefix feature is useful when, at a change of outbound policy at the remote peering site, a router starts to receive more routes than the router memory can take.
If this same router is peering with BGP and also performs critical routing functions within a network, this overhead could turn out bad.
A BGP problem could disrupt internal network connectivity. With the neighbor maximum-prefix command, it is possible to protect a router against this situation.
When you plan to use this feature, consider these key points:
-
Know how many routes the remote BGP peering router normally sends.
-
Set a threshold a little higher than the number of BGP prefixes expected to be received during normal operations.
-
Know the action to take in case the remote BGP peer sends more prefixes than those expected. Available actions could either be to bring down the session and to keep the BGP neighbor relationship down until you use the clear ip bgp x.x.x.x command or, alternatively, to only log a warning message.

Note: An enhancement to this feature is introduced in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(22)S and 12.2(15)T. The enhancement allows the user to automatically reestablish a peering session that has been brought down because the configured Maximum-Prefix limit is exceeded. No intervention from the network operator is required when this feature is enabled. For further information, refer to BGP Restart Session After Maximum-Prefix Limit.
Configure
In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document.
The command syntax used in order to configure the BGP Maximum-Prefix feature is:
neighbor {ip-address | peer-group-name} maximum-prefix <maximum> [threshold] [restart restart-interval] [warning-only]
Where:
-
maximum—Represents the maximum number of prefixes allowed from the neighbor.
-
threshold—An optional integer value that specifies at what percentage maximum-value is configured. The router starts to generate a warning message. The range is from 1 to 100 percent, and the default is 75 percent.
For example, if the maximum-value configured is 20 and the threshold 60, the router generates warning messages when the number of BGP learned routes from the neighbor exceeds 60 percent of 20 (12) routes.
restart-interval—An optional Time interval (in minutes) that a peering session is reestablished. The range is from 1 to 65535 minutes.
warning-only—(optional) Allows the router to generate a log message when the Maximum-Prefix limit is exceeded, instead of terminating the peering session.
In order to better illustrate the usage, consider this example:
neighbor 10.1.1.1 maximum-prefix 3000 !--- Drops the peering to 10.1.1.1 when !--- more than 3000 prefixes are received. neighbor 10.1.1.1 maximum-prefix 3000 warning-only !--- Logs a warning message when the peer sends !--- more than 3000 prefixes. neighbor 10.1.1.1 maximum-prefix 3000 50 !--- Logs a warning message at 1500 and drops the !--- peering when over 3000 prefixes are sent. neighbor 10.1.1.1 maximum-prefix 3000 50 warning-only !--- Initially warns at 1500 and re-warns !--- (different message) at 3000 prefixes received. !--- However, the BGP Peer is not disconnected.
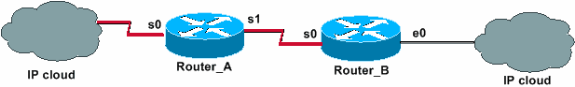
Network Diagram
This document uses this network setup:
Configurations
This document uses these configurations:
-
Maximum-Prefix Configured for Warning-Only Message When Threshold Exceeds Threshold Set
-
Maximum-Prefix Configured to Bring Down Neighbor Relationship When Threshold Exceeds Threshold Set
Maximum-Prefix Configured for Warning-Only Message When Threshold Exceeds Threshold Set
In the Maximum-Prefix warning-only configuration, Router_B is configured to log only a warning message when the number of prefixes received from Router_A exceeds the threshold set.
Configuration of both routers is as shown in this table. Notice the presence of the warning-only keyword configured with the neighbor command.
| Router_A | Router_B |
|---|---|
hostname Router_A ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Serial1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ! router bgp 200 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.1.2 local-as 100 neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 300 neighbor 10.0.0.2 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.0.0.2 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.0.0.2 version 4 no auto-summary ! ip route 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 Serial1 |
hostname Router_B ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ! router bgp 300 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.0.0.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 200 neighbor 10.0.0.1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.0.0.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.0.0.1 version 4 neighbor 10.0.0.1 maximum-prefix 10 80 warning-only !--- Enables warning message logging when the number !--- of BGP routes learned from neighbor !--- 10.0.0.1 exceeds eight. no auto-summary ! ip route 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 Serial0 |
The show and debug command outputs in the Verify and Troubleshoot section of this document report what really happens on Router_B whenever the number of prefixes received from Router_A exceeds the threshold set.
Maximum-Prefix Configured to Bring Down Neighbor Relationship When Threshold Exceeds Threshold Set
In the Maximum-Prefix configured to bring down the neighbor relationship configuration, Router_B is configured to generate warning messages when the number of prefixes received from Router_A exceeds the threshold set. Router_B is also configured to bring down the BGP neighbor when the maximum prefix limit is exceeded. Configuration of both routers is as shown in the table. Notice the absence of the warning-only keyword set with the neighbor command.
| Router_A | Router_B |
|---|---|
hostname Router_A ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Serial1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ! router bgp 200 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.1.2 local-as 100 neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 300 neighbor 10.0.0.2 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.0.0.2 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.0.0.2 version 4 no auto-summary ! ip route 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 Serial1 |
hostname Router_B ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Serial0 ip unnumbered Loopback0 ! router bgp 300 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.0.0.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 200 neighbor 10.0.0.1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.0.0.1 update-source Loopback0 neighbor 10.0.0.1 version 4 neighbor 10.0.0.1 maximum-prefix 10 80 !--- This forces the neighbor session to tear down !--- when the BGP learned routes from !--- the neighbor exceeds 10. no auto-summary ! ip route 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 Serial0 |
The show and debug command outputs in the Verify and Troubleshoot section report what really happens on Router_B whenever the number of prefixes it receives from Router_A exceeds the threshold set.
Verify and Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to confirm your configuration is working properly.
The command syntax and defaults of the feature used in this document are available at the BGP Command page.

Note: Refer to Understand Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands.
-
show ip bgp neighbor —Displays the BGP neighbor status.
-
show ip bgp summary —Displays the status of all BGP connections.
-
debug ip bgp updates in —Displays information related to BGP updates.
Maximum-Prefix Warning-Only
Pay attention to these numbers:
-
Maximum prefixes agreed: 10
-
Warning threshold: 80 percent (eight)
As long as the number of received prefixes does not get higher than the threshold set, eight, no messages are logged.
As soon as the number of BGP routes learned from neighbor 10.0.0.1 exceeds the threshold limit of eight, Router_B logs this message.
This situation is simulated when nine prefixes are sent:
%BGP-4-MAXPFX: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0) reaches 9, max 10
If the situation gets worse, and exceeds the Maximum-Prefix number set of 10, then the router logs this message. This situation is simulated when 12 prefixes are sent:
%BGP-3-MAXPFXEXCEED: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0): 11 exceed limit 10
When you activate debug ip bgp updates in , you are able to get a closer look at what happens. However, do not use this command in a live environment with several thousands of prefixes.
The situation depicted is that Router_B already has an established peering. Six prefixes have been advertised to Router B by Router_A. Now three additional prefixes are advertised by the peer Router_A.
Router_B# debug ip bgp updates in *Mar 12 07:31:18.944: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.0.0.1, origin i, metric 0, path 200 *Mar 12 07:31:18.948: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.1.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:31:18.952: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.2.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:31:18.960: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.3.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:32:20.224: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.4.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:32:20.228: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.5.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:32:20.232: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.6.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 07:34:19.768: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.7.0/24 *Mar 12 07:34:19.772: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.8.0/24 *Mar 12 07:34:19.780: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.9.0/24 *Mar 12 07:34:19.780: %BGP-4-MAXPFX: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0 ) reaches 9, max 10 *Mar 12 07:34:19.792: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.7.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 07:34:19.796: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.8.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 07:34:19.804: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.9.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table
Router_B#show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.1
BGP neighbor is 10.0.0.1, remote AS 200, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.0.0.1
BGP state = Established, up for 00:13:22
Last read 00:00:21, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
Route refresh: advertised and received(old & new)
Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
IPv4 MPLS Label capability:
Received 930 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue
Sent 919 messages, 1 notifications, 0 in queue
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 30 seconds
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 30, neighbor version 30
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Route refresh request: received 0, sent 0
9 accepted prefixes consume 432 bytes
Prefix advertised 0, suppressed 0, withdrawn 0, maximum limit 10 (warning-only)
Threshold for warning message 80%
Connections established 2; dropped 1
Last reset 00:29:13, due to BGP Notification sent, update malformed
Message received that caused BGP to send a Notification:
FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF
003C0200 00001940 01010040 02040201
00C84003 040A0000 01800404 00000000
180A000A 180A000B 180A000C
External BGP neighbor can be up to 2 hops away.
Connection state is ESTAB, I/O status: 1, unread input bytes: 0
Local host: 10.0.0.2, Local port: 15668
Foreign host: 10.0.0.1, Foreign port: 179
Enqueued packets for retransmit: 0, input: 0 mis-ordered: 0 (0 bytes)
Event Timers (current time is 0x3A46EB54):
Timer Starts Wakeups Next
Retrans 18 0 0x0
TimeWait 0 0 0x0
AckHold 22 9 0x0
SendWnd 0 0 0x0
KeepAlive 0 0 0x0
GiveUp 0 0 0x0
PmtuAger 0 0 0x0
DeadWait 0 0 0x0
iss: 2047376434 snduna: 2047376784 sndnxt: 2047376784 sndwnd: 16035
irs: 821061364 rcvnxt: 821062116 rcvwnd: 16188 delrcvwnd: 196
SRTT: 279 ms, RTTO: 500 ms, RTV: 221 ms, KRTT: 0 ms
minRTT: 24 ms, maxRTT: 384 ms, ACK hold: 200 ms
Flags: higher precedence, nagle
Datagrams (max data segment is 536 bytes):
Rcvd: 33 (out of order: 0), with data: 22, total data bytes: 751
Sent: 29 (retransmit: 0, fastretransmit: 0), with data: 17, total data bytes: 349
Router_B#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 10.0.0.2, local AS number 300 BGP table version is 30, main routing table version 30 9 network entries and 9 paths using 1341 bytes of memory 1 BGP path attribute entries using 60 bytes of memory 1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP activity 36/101 prefixes, 36/27 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.0.0.1 4 200 932 921 30 0 0 00:15:08 9
Suppose that the situation gets worse and that Router_A sends three additional prefixes, which increases the total number up to 12.
Router_B# debug ip bgp updates in *Mar 12 07:39:21.192: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.0.0.1, origin i, metric 0, path 200 *Mar 12 07:39:21.196: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.10.0/24 *Mar 12 07:39:21.200: %BGP-4-MAXPFX: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0) reaches 10, max 10 *Mar 12 07:39:21.208: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.11.0/24 *Mar 12 07:39:21.212: %BGP-3-MAXPFXEXCEED: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0): 11 exceed limit 10 *Mar 12 07:39:21.216: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.12.0/24 *Mar 12 07:39:21.228: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.10.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 07:39:21.236: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.11.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 07:39:21.240: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.12.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table
Router_B# show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.1
BGP neighbor is 10.0.0.1, remote AS 200, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.0.0.1
BGP state = Established, up for 00:19:56
Last read 00:00:56, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
Route refresh: advertised and received(old & new)
Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
IPv4 MPLS Label capability:
Received 937 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue
Sent 925 messages, 1 notifications, 0 in queue
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 30 seconds
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 33, neighbor version 33
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Route refresh request: received 0, sent 0
12 accepted prefixes consume 576 bytes
Prefix advertised 0, suppressed 0, withdrawn 0, maximum limit 10 (warning-only)
Threshold for warning message 80%
Connections established 2; dropped 1
Last reset 00:35:47, due to BGP Notification sent, update malformed
Message received that caused BGP to send a Notification:
FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF
003C0200 00001940 01010040 02040201
00C84003 040A0000 01800404 00000000
180A000A 180A000B 180A000C
External BGP neighbor can be up to 2 hops away.
Connection state is ESTAB, I/O status: 1, unread input bytes: 0
Local host: 10.0.0.2, Local port: 15668
Foreign host: 10.0.0.1, Foreign port: 179
Enqueued packets for retransmit: 0, input: 0 mis-ordered: 0 (0 bytes)
Event Timers (current time is 0x3A4CEA98):
Timer Starts Wakeups Next
Retrans 24 0 0x0
TimeWait 0 0 0x0
AckHold 29 16 0x0
SendWnd 0 0 0x0
KeepAlive 0 0 0x0
GiveUp 0 0 0x0
PmtuAger 0 0 0x0
DeadWait 0 0 0x0
iss: 2047376434 snduna: 2047376898 sndnxt: 2047376898 sndwnd: 15921
irs: 821061364 rcvnxt: 821062290 rcvwnd: 16014 delrcvwnd: 370
SRTT: 290 ms, RTTO: 376 ms, RTV: 86 ms, KRTT: 0 ms
minRTT: 24 ms, maxRTT: 384 ms, ACK hold: 200 ms
Flags: higher precedence, nagle
Datagrams (max data segment is 536 bytes):
Rcvd: 40 (out of order: 0), with data: 29, total data bytes: 925
Sent: 42 (retransmit: 0, fastretransmit: 0), with data: 23, total data bytes: 463
Router_B#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 10.0.0.2, local AS number 300 BGP table version is 33, main routing table version 33 12 network entries and 12 paths using 1788 bytes of memory 1 BGP path attribute entries using 60 bytes of memory 1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP activity 39/101 prefixes, 39/27 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.0.0.1 4 200 939 927 33 0 0 00:21:28 12
As you can see from the example shown, the BGP neighbor relationship is maintained even if the neighboring router sends more prefixes than the policy allows.
The result is that only a warning message gets logged by Router_B. No other actions are taken by Router_B.
Maximum-Prefix Configured to Bring Down the Session When Threshold Exceeds Threshold Set
Initial conditions required for this case are to have the BGP neighbor up and running and with six prefixes sent by Router_A to Router_B.
As seen in the example, when Router_A advertises more prefixes (for example, 9), the output of the commands reflects exactly what was already seen for the case where Router_B is configured to just log a warning message.
If you push up the number of prefixes sent and make Router_A advertise 12, Router_B closes the neighbor relationship with Router_A.
Router_B#debug ip bgp updates in *Mar 12 08:03:27.864: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.0.0.1, origin i, metric 0, path 200 *Mar 12 08:03:27.868: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.1.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.876: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.2.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.880: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.3.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.884: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.4.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.892: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.5.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.896: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.6.0/24...duplicate ignored *Mar 12 08:03:27.900: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.7.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:27.908: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.8.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:27.912: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.9.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:27.916: %BGP-4-MAXPFX: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0) reaches 9, max 10 *Mar 12 08:03:27.924: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.10.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:27.932: BGP(0): 10.0.0.1 rcvd 10.0.11.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:27.932: %BGP-3-MAXPFXEXCEED: No. of prefix received from 10.0.0.1 (afi 0): 11 exceed limit 10 *Mar 12 08:03:27.940: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 10.0.0.1 Down BGP Notification sent *Mar 12 08:03:27.940: %BGP-3-NOTIFICATION: sent to neighbor 10.0.0.1 3/1 (update malformed) 0 bytes FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF 0060 0200 0000 1940 0101 0040 0204 0201 00C8 4003 040A 0000 0180 0404 0000 0000 180A 0001 180A 0002 180A 0003 180A 0004 180A 0005 180A 0006 180A 0007 180A 0008 180A 0009 180A 000A 180A 000B 180A 000C *Mar 12 08:03:28.024: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.7.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 08:03:28.032: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.8.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 08:03:28.036: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.9.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 08:03:28.044: BGP(0): Revise route installing 1 of 1 route for 10.0.10.0/24 -> 10.0.0.1 to main IP table *Mar 12 08:03:28.148: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.1.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.152: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.2.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.156: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.3.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.156: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.4.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.160: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.5.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.164: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.6.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.168: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.7.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.168: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.8.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.172: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.9.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.176: BGP(0): no valid path for 10.0.10.0/24 *Mar 12 08:03:28.184: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.1.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.188: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.2.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.192: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.3.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.196: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.4.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.200: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.5.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.204: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.6.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.208: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.7.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.212: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.8.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.212: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.9.0/24 no best path *Mar 12 08:03:28.216: BGP(0): nettable_walker 10.0.10.0/24 no best path
Router_B# show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 10.0.0.2, local AS number 300 BGP table version is 87, main routing table version 87 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.0.0.1 4 200 965 948 0 0 0 00:02:24 Idle (PfxCt)
Router_B# show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.1
BGP neighbor is 10.0.0.1, remote AS 200, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 0.0.0.0
BGP state = Idle
Last read 00:02:43, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Received 965 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue
Sent 948 messages, 2 notifications, 0 in queue
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 30 seconds
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 87, neighbor version 0
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Route refresh request: received 0, sent 0, maximum limit 10
Threshold for warning message 80%
Connections established 2; dropped 2
Last reset 00:02:43, due to BGP Notification sent, update malformed
Message received that caused BGP to send a Notification:
FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF
00600200 00001940 01010040 02040201
00C84003 040A0000 01800404 00000000
180A0001 180A0002 180A0003 180A0004
180A0005 180A0006 180A0007 180A0008
180A0009 180A000A 180A000B 180A000C
Peer had exceeded the max. no. of prefixes configured.
Reduce the no. of prefix and clear ip bgp 10.0.0.1 to restore peering
External BGP neighbor can be up to 2 hops away.
No active TCP connection

Note: Use this command in order to restore the peer ability:
Router_B#clear ip bgp 10.0.0.1
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
09-Jul-2002
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback